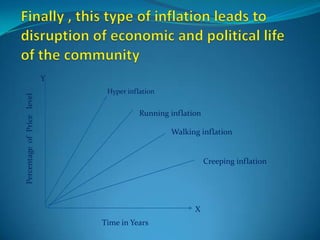
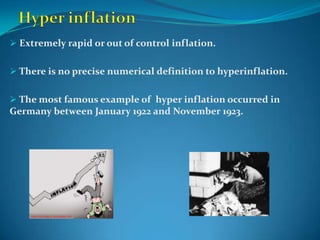
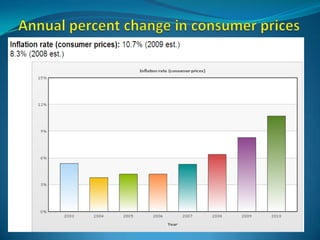
Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy over time. It can be caused by demand-pull factors, like too much money chasing too few goods, or cost-push factors like increases in production costs. Inflation is measured by changes in a consumer price index and can vary in its rate from creeping to hyperinflation. Governments use monetary and fiscal policies like controlling the money supply and public spending to combat inflation.