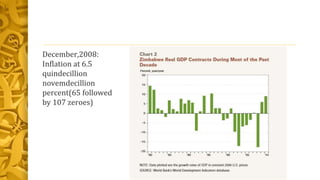
This document discusses inflation, including types of inflation, causes of inflation, and measures to control inflation. It defines inflation as a sustained increase in general price levels over time. The main types are creeping, walking, running, and hyperinflation. Causes include demand-pull and cost-push factors. Measures to control inflation involve monetary policies like changing reserve requirements or interest rates, fiscal policies like adjusting government spending/taxation, and other supply-side policies. Extreme examples of hyperinflation in countries like Hungary, Zimbabwe, Yugoslavia, Germany, and Greece are provided where monthly inflation rates exceeded thousands of percent and prices doubled within days.