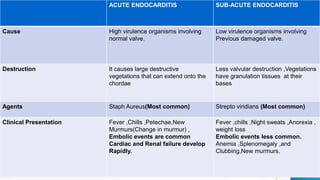
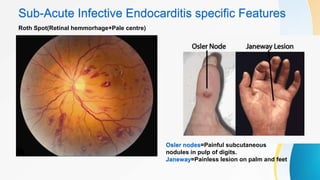
Infective endocarditis refers to a microbial infection of the heart's endothelium, usually affecting the valves. It has an incidence rate of 5 to 15 cases per 100,000 people per year, with over 50% of cases occurring in individuals over age 60. The infection can be either acute or subacute, with acute cases caused by more virulent organisms on normal valves, resulting in large destructive vegetations and embolic events. Subacute cases are caused by less virulent organisms on previously damaged valves, resulting in less valve destruction and the presence of granulation tissue on vegetations. Blood cultures and echocardiography, particularly transesophageal echocardiography, are important for diagnosis. Treatment involves antibiotics,