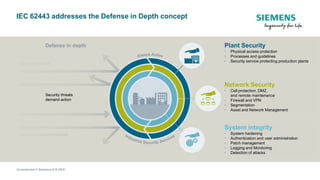
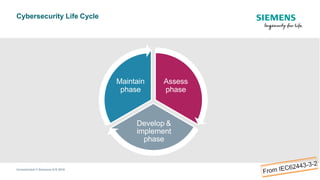
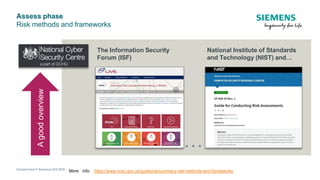
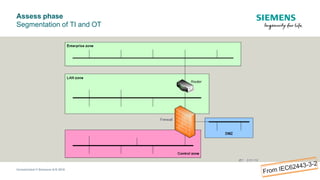
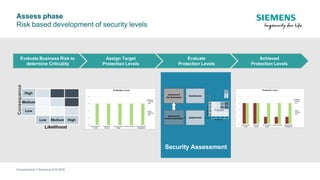
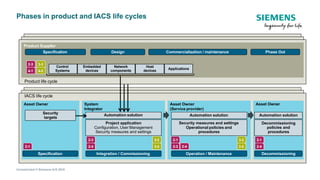
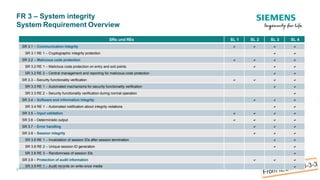
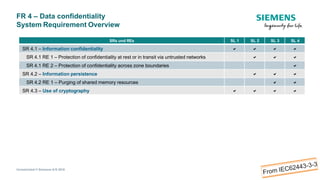
The document discusses IEC 62443, an international standard for industrial automation and control system (IACS) cybersecurity. It provides an overview of key aspects of the standard, including its structure, risk assessment process, protection levels, security requirements, and life cycle approach. The standard is intended to help organizations establish cybersecurity programs for IACS that are risk-based and cover the entire life cycle from planning to decommissioning.