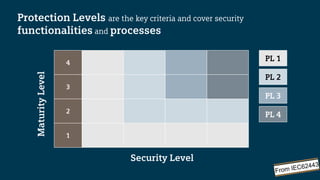
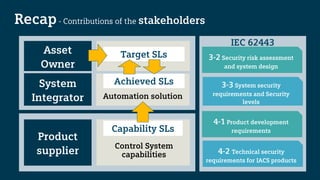
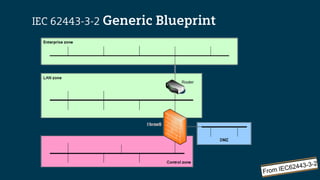
The document outlines the IEC 62443 cybersecurity standards applicable to industrial control systems (ICS), emphasizing a risk management approach that aligns with various regulations and frameworks. It details the multi-layered defense strategies required for securing systems, including risk assessments, security levels, and lifecycle management, aimed at minimizing potential threats to operations and assets. Furthermore, it highlights the significance of a consistent methodology for communication and compliance among stakeholders involved in designing, managing, and securing ICS.