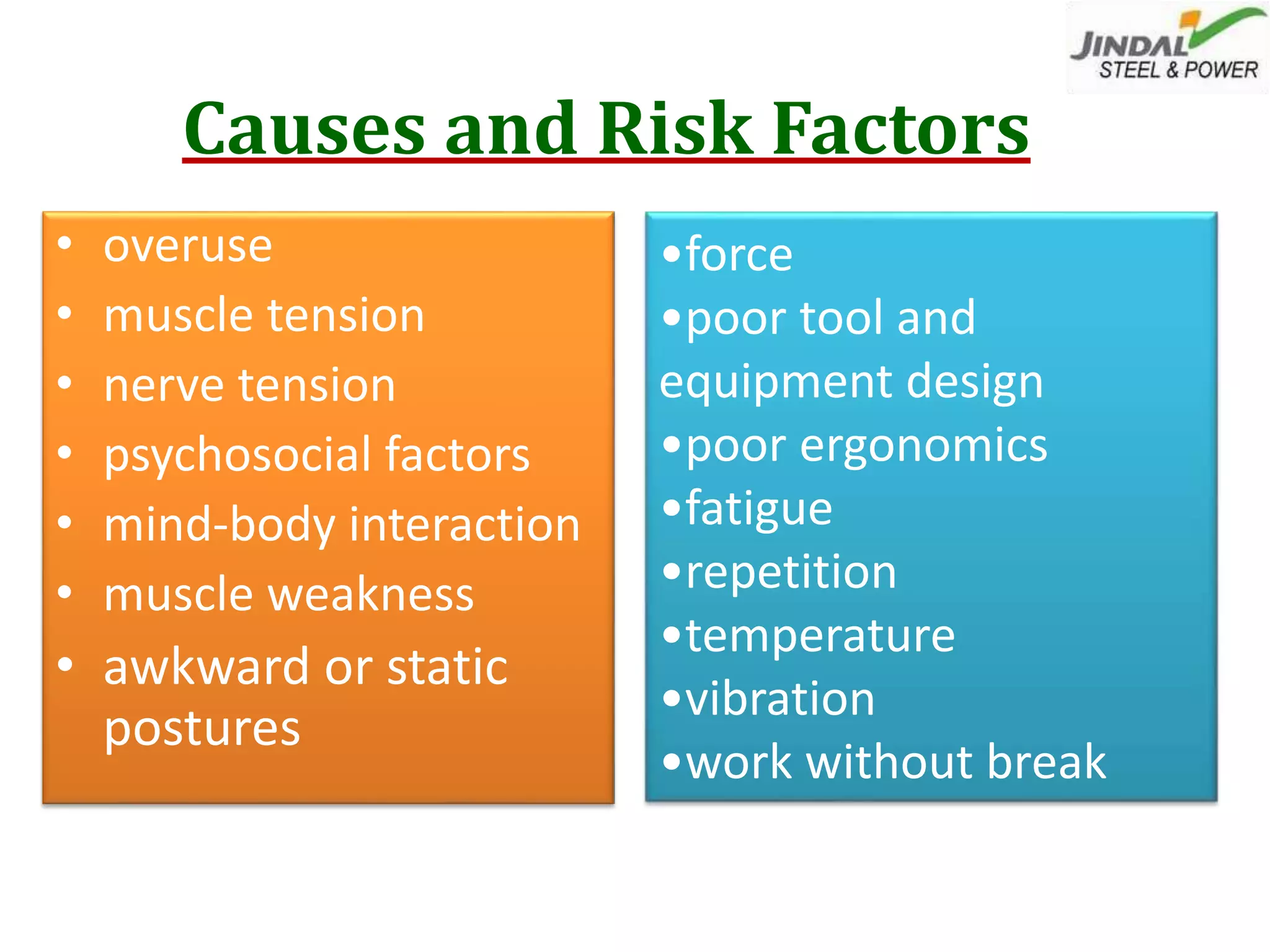
Repetitive Stress Injuries (RSI) are painful conditions caused by repetitive, forceful, or awkward movements, affecting muscles, tendons, and nerves, which can lead to long-term disabilities and decreased productivity. Common examples include carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, and trigger finger, often exacerbated by poor ergonomics and inadequate recovery time. Prevention and management strategies involve ergonomics, occupational therapy, proper work habits, and workstation design to minimize risk factors.