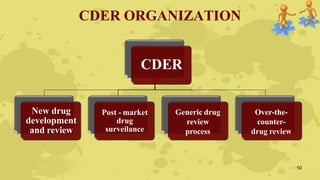
The document discusses industry and FDA liaisons. It describes the FDA's mission to protect public health by regulating food, drugs, and other products. The FDA has 9,000 employees who monitor over $1 trillion worth of products annually. The FDA ensures product safety through inspections, legal sanctions for noncompliance, and scientific review. Industry can communicate with the FDA through various divisions and meetings to facilitate product development and approval processes.