- Three-phase induction motors are commonly used in industry due to their simple and rugged design, low cost, easy maintenance, and ability to operate at a constant speed from no load to full load. However, they require a variable frequency drive for optimal variable speed control.
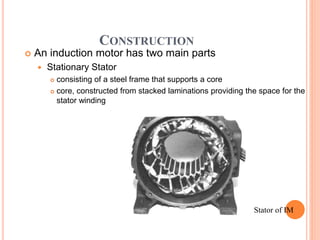
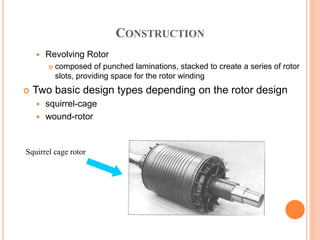
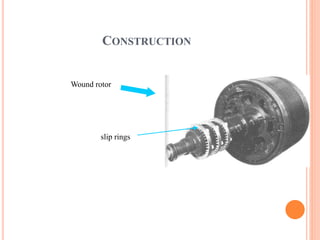
- An induction motor has two main parts - a stationary stator and a revolving rotor. The stator contains windings and the rotor comes in either a squirrel cage or wound rotor design.
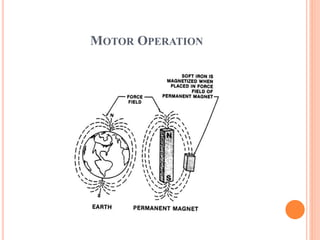
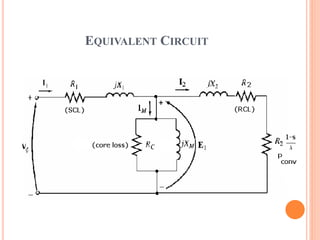
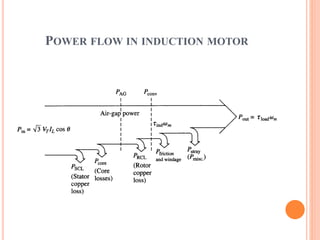
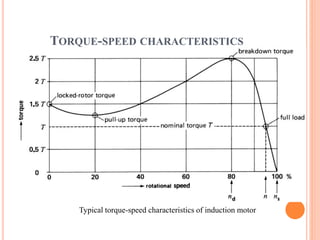
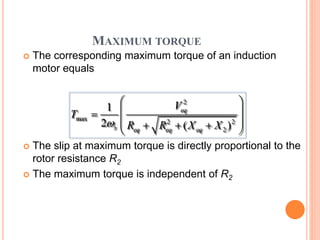
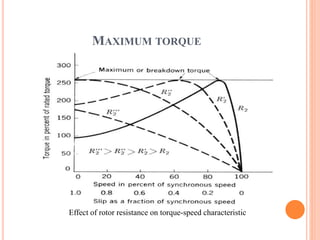
- The motor operates based on electromagnetic induction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields. An equivalent circuit model and diagrams of power flow help explain the motor's operation and torque-speed characteristics. The maximum torque is determined by a formula involving slip