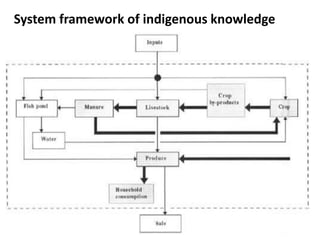
The document discusses various indigenous knowledge practices used in agriculture in Bangladesh. It describes techniques for rice cultivation like using salt water for weed control and pruning rice plants for wind resistance. Other practices discussed include using tree leaves and rice straw for mulching, scarecrows to protect crops, and threshing and drying grains. Biological controls using birds and fruit covering are also summarized. The document also discusses uses of materials like bamboo, neem leaves, and mustard oil for preserving and transporting various agricultural products.