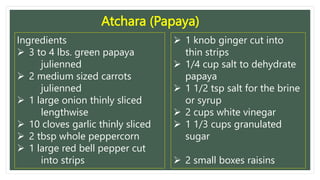
This document provides instructions for preserving papaya (atsara) through pickling. It begins with a list of ingredients including papaya, carrots, onions, garlic, peppers, ginger and seasonings. The instructions explain how to julienne and dehydrate the papaya overnight with salt before rinsing. The papaya is then combined with other vegetables and spices in a jar before pouring in a vinegar-sugar brine. The sealed jar is refrigerated for a week to allow the flavors to develop before serving the preserved papaya cold.