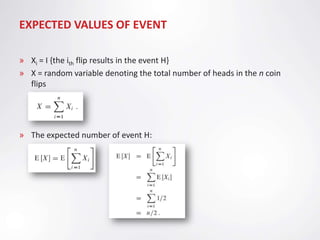
The document discusses indicator random variables and how they can be used to analyze a hiring problem algorithm. An indicator random variable is defined as a random variable associated with a specific event that takes the value 1 if the event occurs and 0 if it does not. The expected value of an indicator random variable is equal to the probability of the associated event. The hiring problem involves interviewing candidates each day and hiring the best one seen so far. Indicator random variables can be used to represent whether each candidate is hired, allowing the expected number of hires to be calculated.







![LEMMA 1
Given a sample space S and an event A in the sample space S, let XA =I{A}.
Then E [XA ] = Pr{A}
Proof:
E [XA ] = E[I{A}]
= 1. Pr{A} + 0. Pr{A’}
= Pr{A}
where A’ is S – A, the complement of A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-121218043846-phpapp01/85/Indicator-Random-Variables-8-320.jpg)
![ANALYSIS OF THE HIRING PROBLEM USING
INDICATOR RANDOM VARIABLES
» Assume the candidates arrive in random order
» X = random variable whose value equals the number of times we hire
a new office assistant
» We may use expected value of random variable equation:
» However, a simplified calculation is using indicator random variables.
» Instead of computing E[X] by defining one variable associated with the
number of times we hire a new office assistant, define n variables
related to whether or not each particular candidate is hired. In
particular, let Xi be the indicator random variable associated with the
event in which the ith candidate is hired
and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-121218043846-phpapp01/85/Indicator-Random-Variables-10-320.jpg)
![ANALYSIS OF THE HIRING PROBLEM USING INDICATOR
RANDOM VARIABLES
» Based on lemma E [XA ] = Pr{A}, we have:
» Since the candidate i arrives in random order, any one of these first i
candidates is likely to be best-qualified candidate so far. Thus, the
probability of candidate i is 1/i better qualified than candidates 1 till i-
1, which yields:
» Now we can compute E[X]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-121218043846-phpapp01/85/Indicator-Random-Variables-11-320.jpg)

