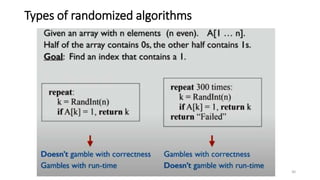
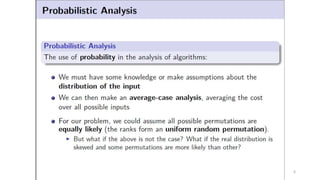
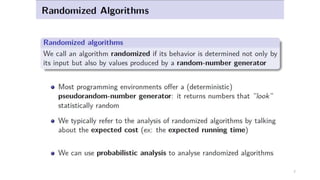
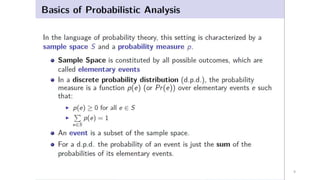
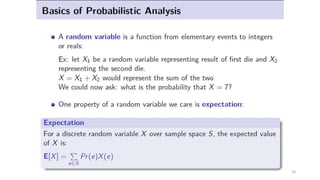
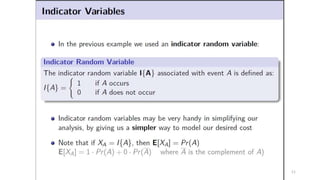
This document discusses various advanced algorithms and probabilistic analysis techniques. It begins with an overview of probabilistic analysis, which involves making assumptions about the distribution of inputs and analyzing average case running time. It then discusses randomized algorithms, which force all inputs to be equally likely by randomizing the input. As an example, it discusses how randomizing the order of candidates in a hiring problem guarantees the expected number of hires will be n + O(1). It introduces the concept of indicator random variables to convert between probabilities and expectations. It also discusses different types of randomized algorithms like Las Vegas algorithms and Monte Carlo algorithms, providing quicksort as an example of a Las Vegas algorithm.










![What is Expected Value? (IRV)
RCPIT 17
• Expected value E[] of a random variable
• Value you "expect" a random variable to have
• Average (mean) value of the variable over many trials
• Does not have to equal the value of any particular trial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaunit2-230522044615-e8d37e27/85/AA_Unit_2-pptx-17-320.jpg)