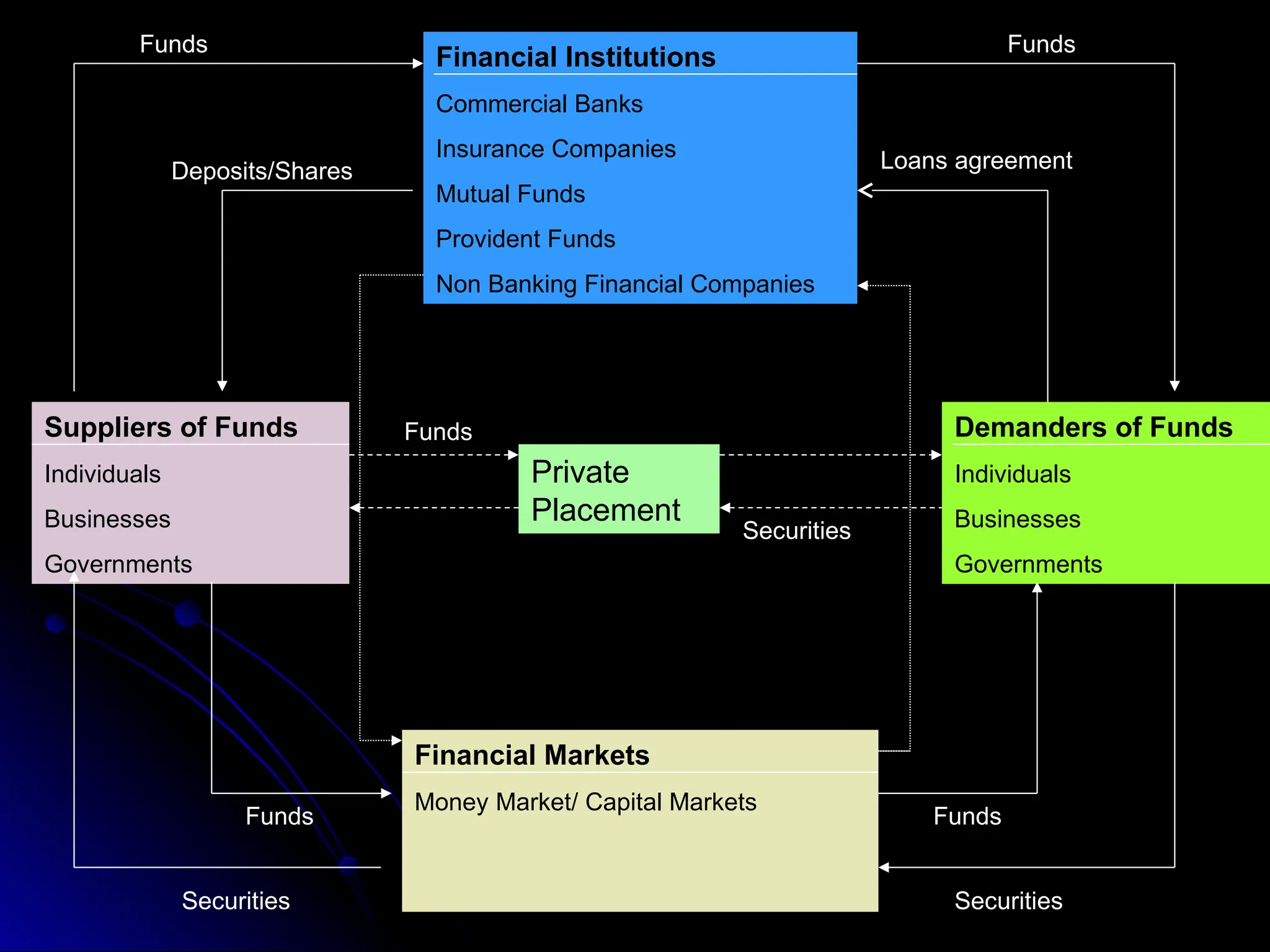
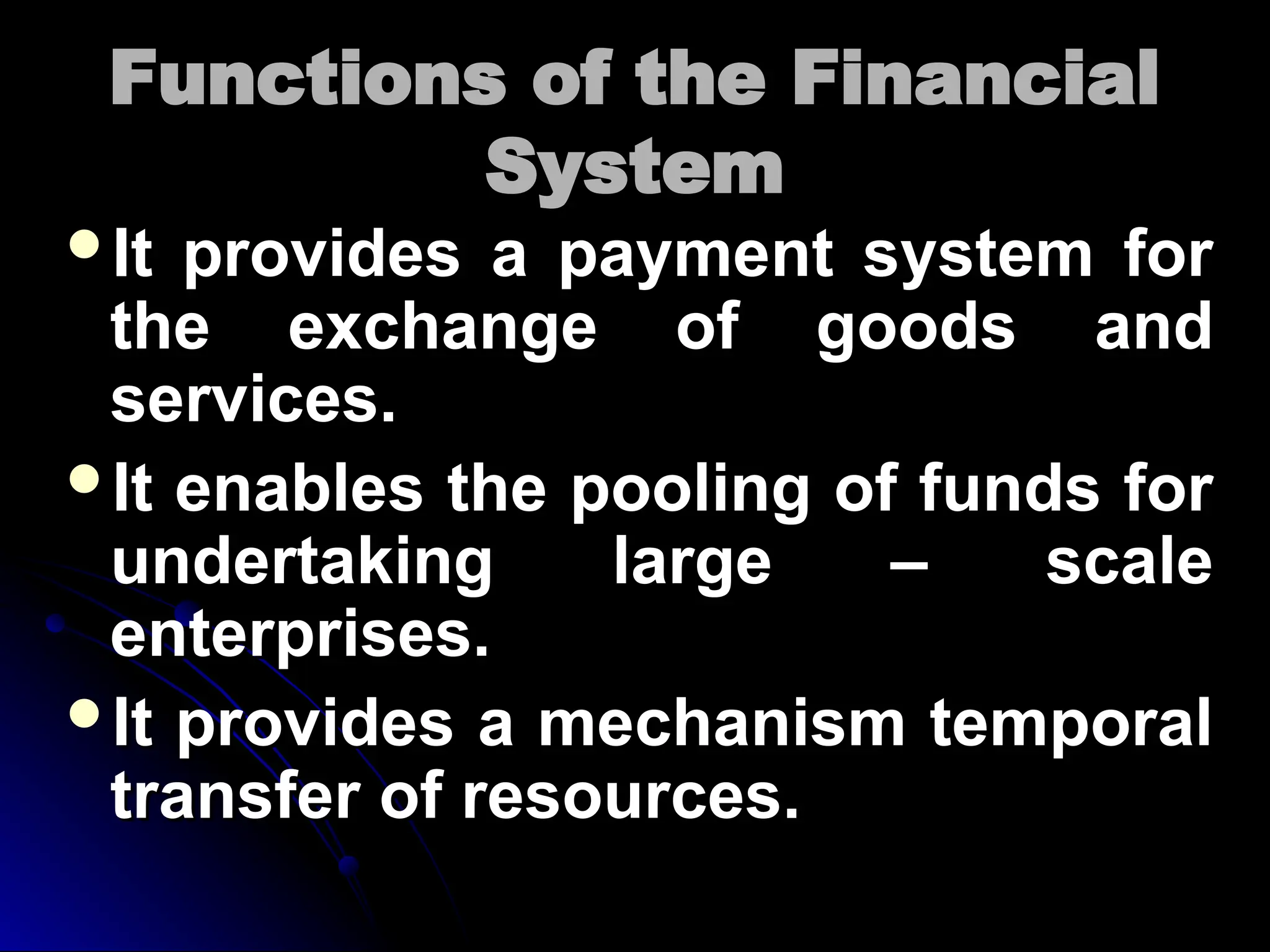
The document discusses the significance of a well-organized financial system for a country's economic development, highlighting its role in mobilizing savings and providing necessary financial inputs for producing goods and services. It outlines various components of the financial system, including markets, institutions, and instruments essential for facilitating resource allocation and managing risks. Moreover, it examines the evolution and reforms of the Indian financial system, addressing challenges and changes within financial markets and institutions.