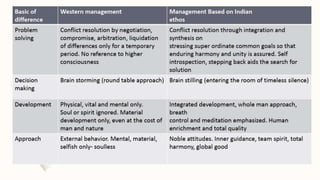
The document discusses Indian management practices and ethos. It defines Indian ethos as principles of self-management and governance revealed in Hindu scriptures. Key features of Indian ethos discussed are the divinity of human beings, balance, importance of character over knowledge, and seeing all work as worship. Indian ethos in management helps managers address problems creatively. The document also outlines challenges faced by Indian managers and discusses the meaning, need, importance and advantages of conducting management audits.