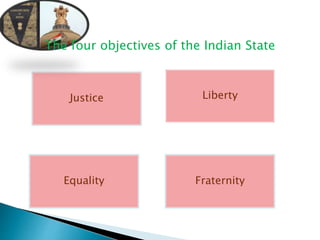
The document summarizes key aspects of the Indian constitution relating to education. It outlines the preamble of the constitution which establishes India as a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic. It then lists the fundamental rights and duties of citizens. In terms of education, the constitution provides for free and compulsory education up to age 14, religious instruction, language safeguards, equality of opportunity, and education of minorities and weaker sections. It also aims to promote secular education, instruction in native languages, and higher education/research. Overall, the constitution seeks to develop democratic values, national integration, social/moral values, and physical/social development through education.