Embed presentation
Downloaded 250 times





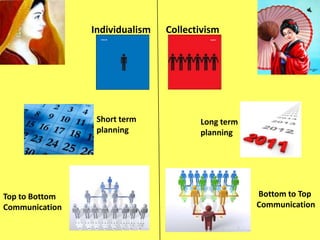
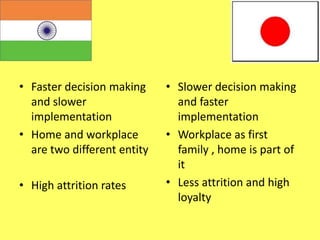



This document compares management practices between India and Japan. It outlines the origins of management in each country, as well as key pillars that guide each approach. The Japanese model emphasizes lifetime employment, seniority-based wages and promotions, and enterprise-based unions. The Indian model focuses on dharma (principles), artha (practical challenges), kama (motivation), and moksha (self-actualization). Additional comparisons note differences in formal vs informal organization structures, individualism vs collectivism, decision-making speeds, and views on risk-taking between the two countries' management approaches.









