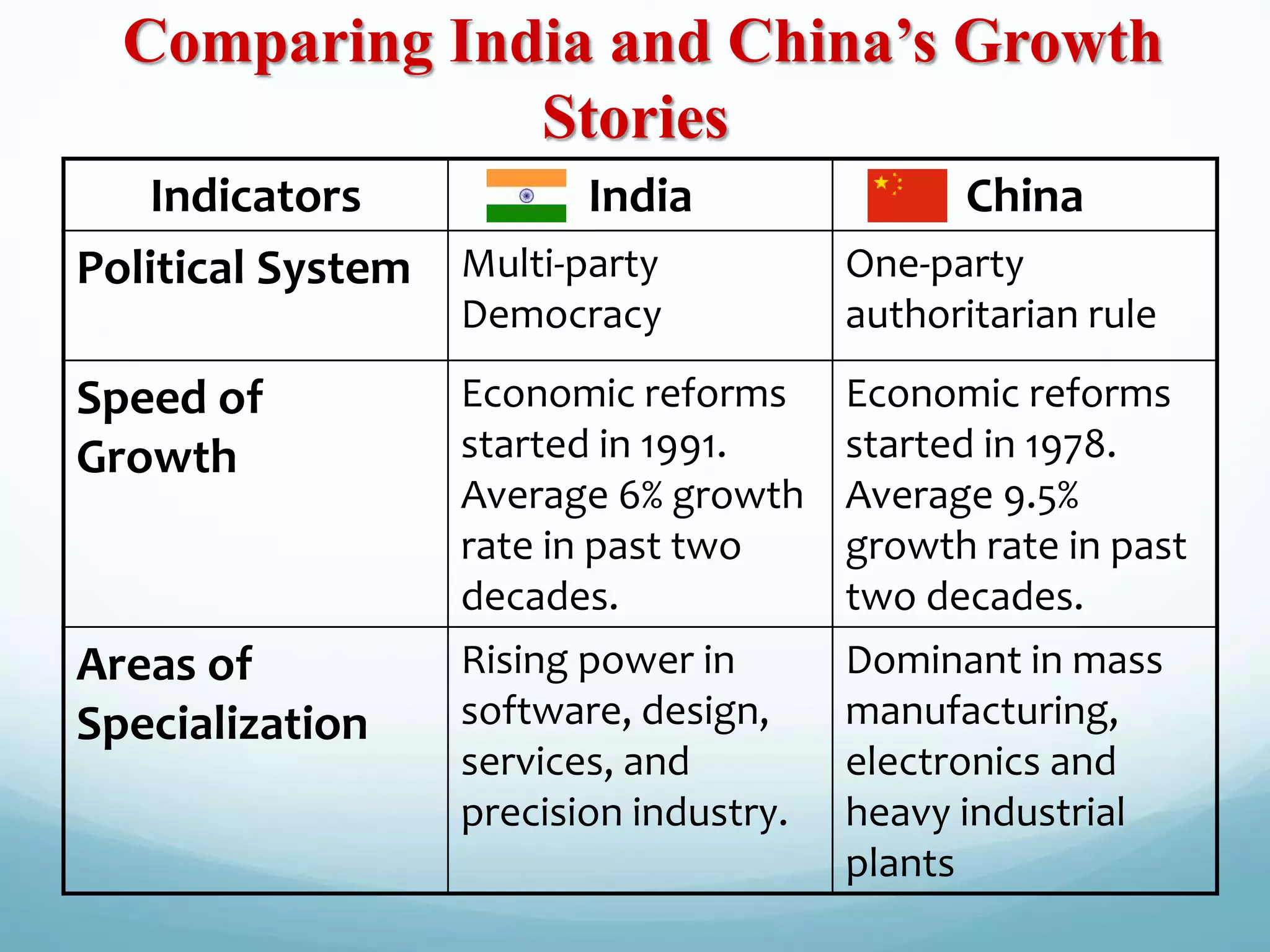
This document compares the economies of India and China over the past 50 years since they were both among the poorest countries. It outlines key differences in their political systems, growth rates, areas of specialization, and economic indicators. China adopted economic reforms earlier in 1978 and has grown faster at 9.5% annually compared to India's 6% growth. While China dominates manufacturing, India is rising in services. Both countries continue facing challenges to transitioning their economies and maintaining growth.