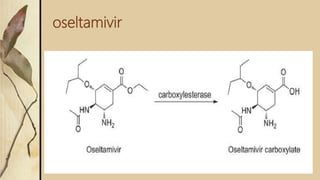
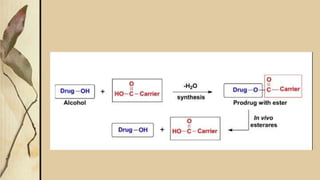
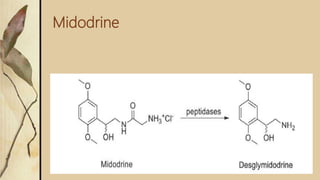
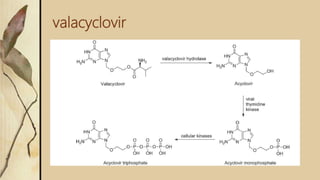
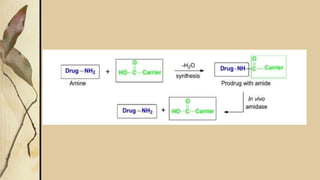
This presentation discusses prodrugs and how they can improve membrane permeability and drug absorption. A prodrug is a medication that is metabolized into an active drug after administration. Prodrugs are used to improve patient acceptability, alter absorption and distribution, alter metabolism and elimination, and allow drugs that do not cross biological barriers like the blood brain barrier to do so. The presentation provides examples of prodrugs like oseltamivir and valacyclovir and explains how they work to improve permeability through passive diffusion or carrier-mediated transport by increasing lipophilicity or allowing recognition by transporters.