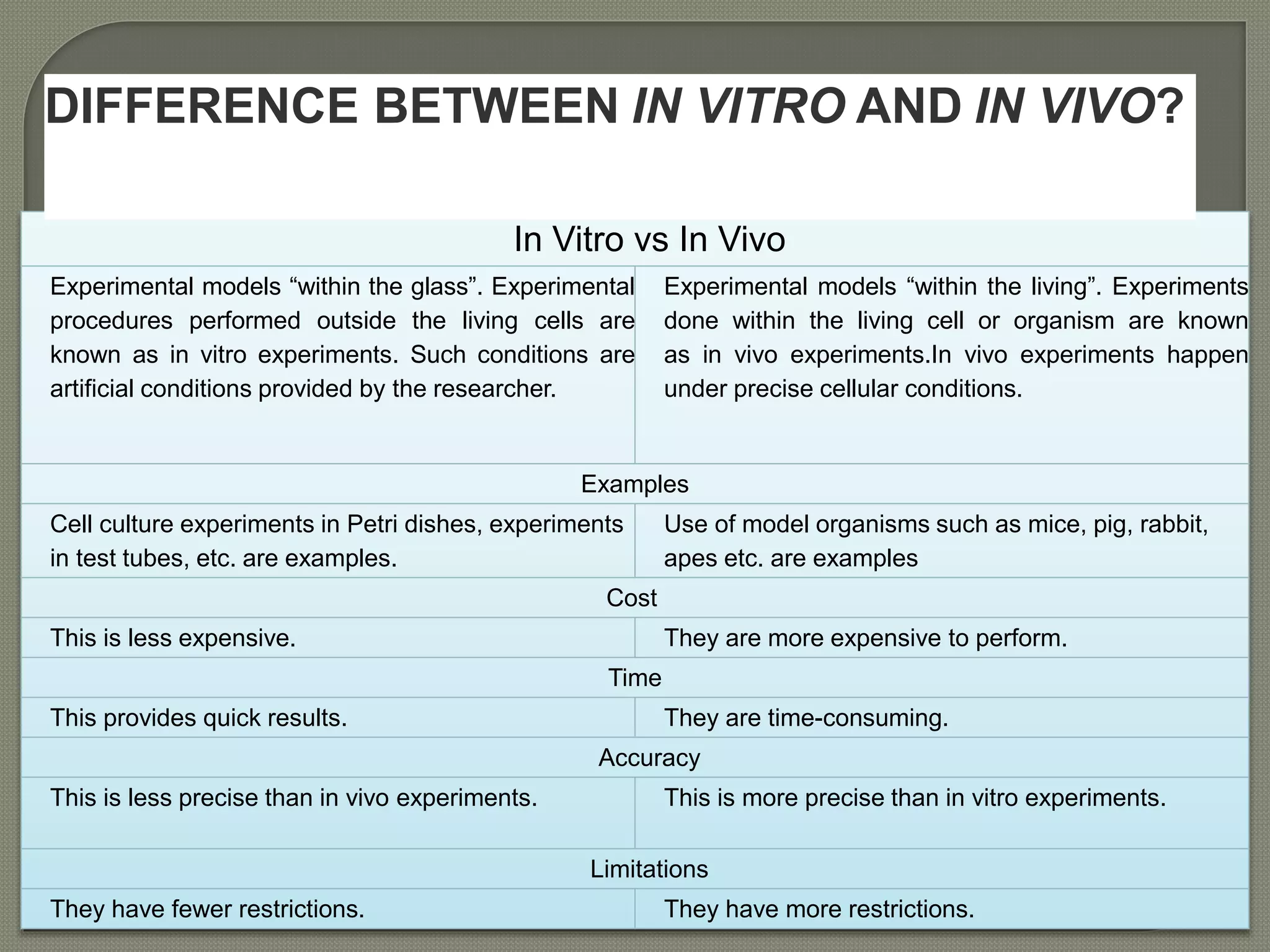
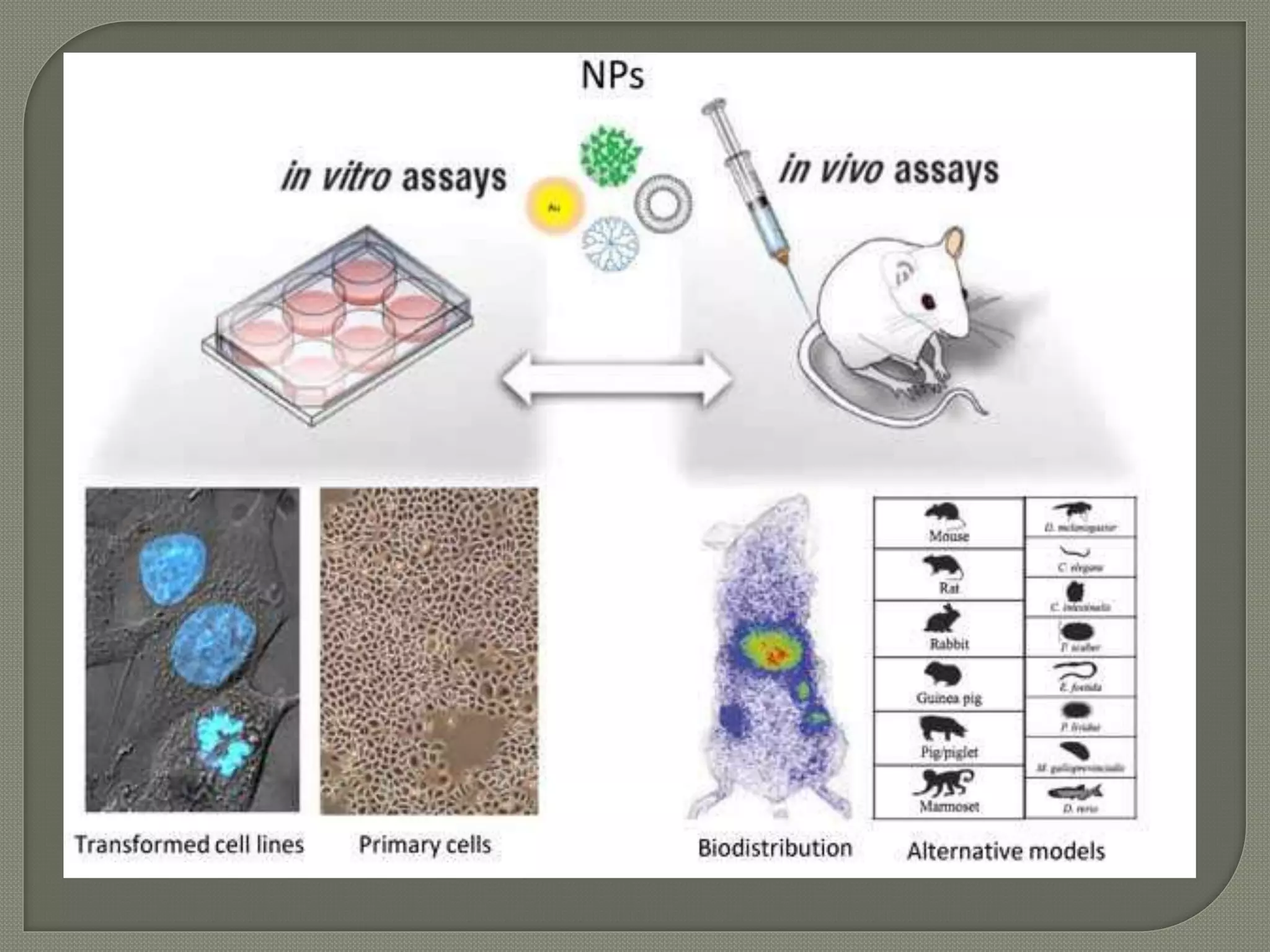
This document summarizes the key differences between in vitro and in vivo experiments. In vitro refers to experiments performed outside of a living organism in artificial laboratory conditions, such as cell cultures or test tubes. In vivo experiments are conducted within living organisms under natural physiological conditions. Some key differences highlighted are that in vitro experiments are less expensive and faster but also less precise, while in vivo can provide more accurate results but are more time-consuming and costly. Examples of each type of experiment are also provided.