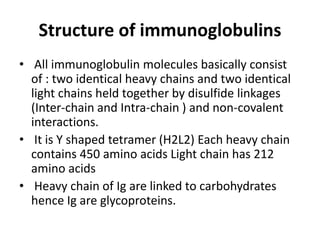
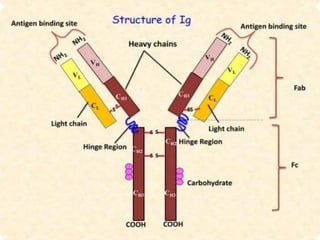
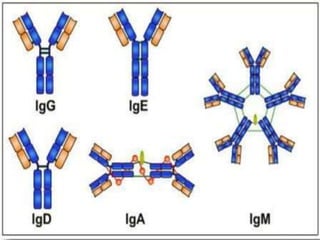
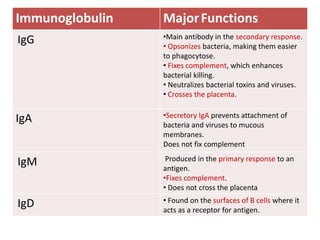
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells in response to antigens. They consist of two heavy chains and two light chains. The variable regions of the light and heavy chains determine antigen binding specificity. There are five major classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE - which differ in structure and function. IgG is the most common antibody and provides primary defense. IgM is the first antibody produced during initial exposure and activates the complement system. IgA protects mucosal surfaces from pathogens.