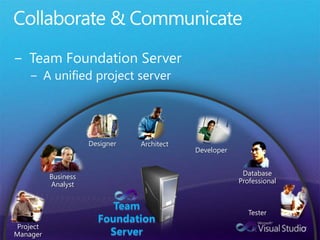
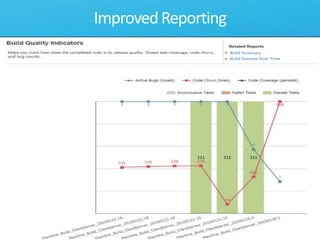
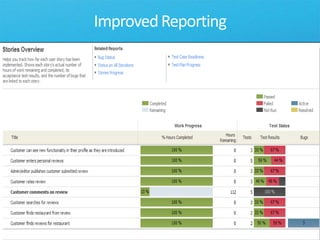
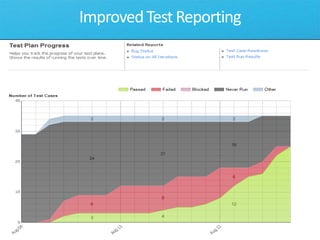
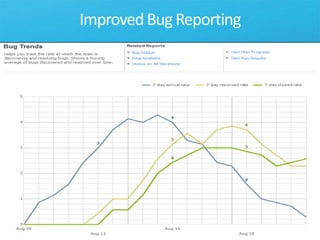
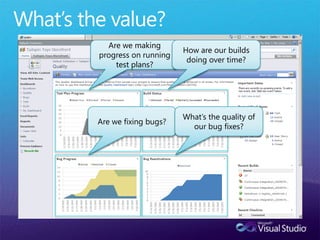
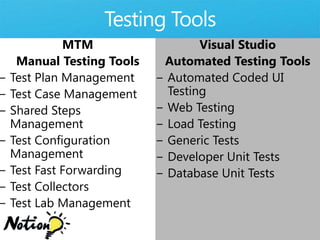
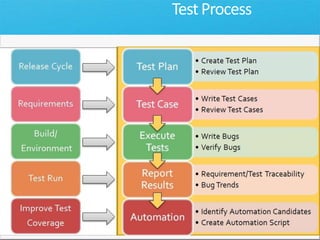
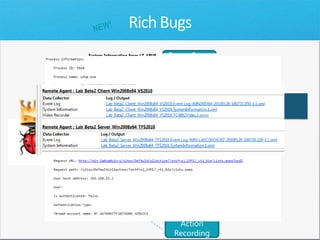
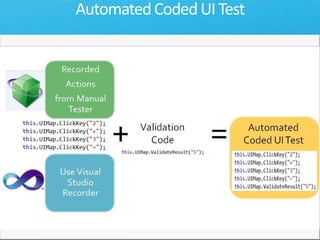
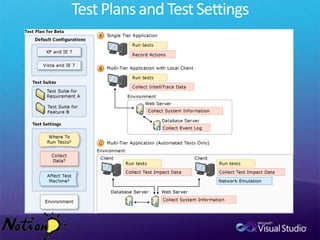
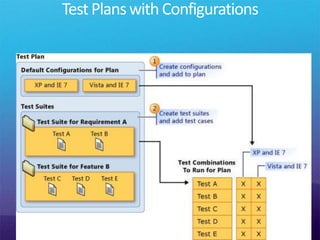
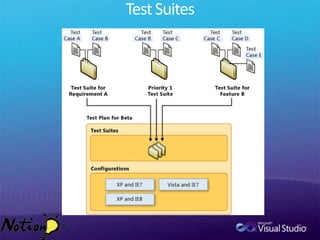
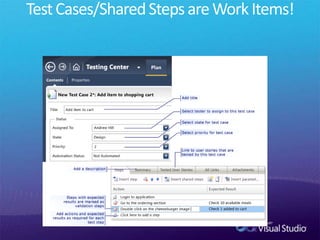
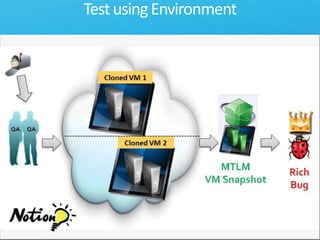
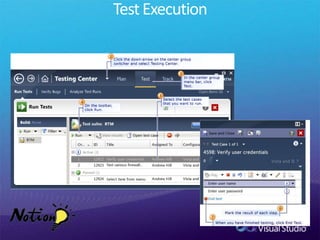
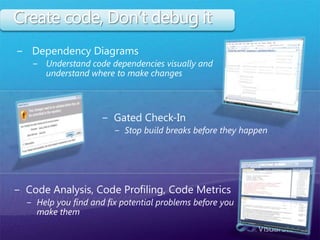
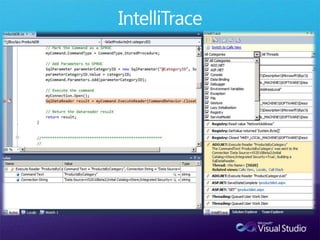
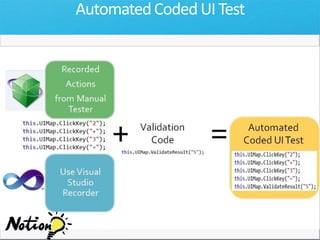
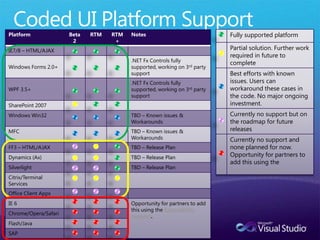
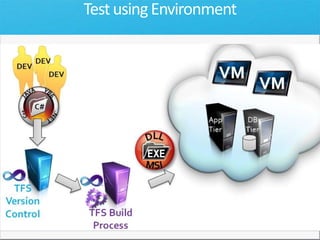
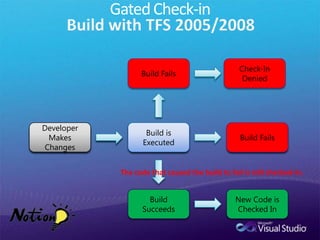
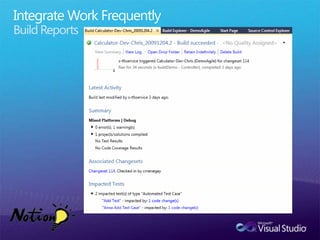
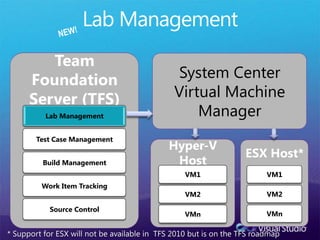
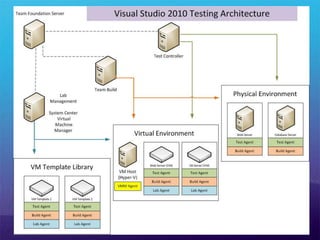
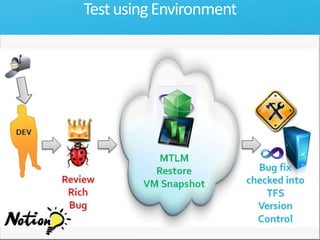
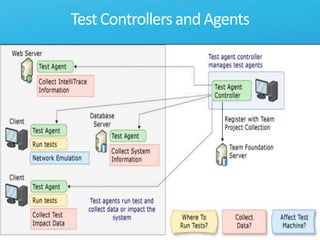
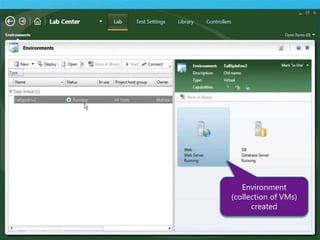
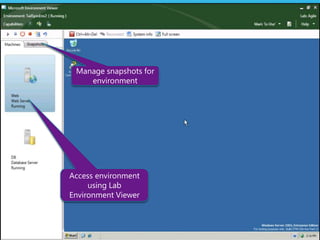
The document discusses how Visual Studio 2010 improves software quality through features that enable better work management, reporting, testing tools, developer quality tools, automated builds, lab management, and collaboration between development and testing teams. Key improvements include hierarchical work tracking, richer bug reporting, automated coded UI testing, IntelliTrace for debugging, and lab management for maintaining virtual test environments. The goal is to align development and testing, break down silos, and improve transparency and integration across the lifecycle.