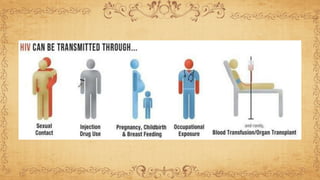
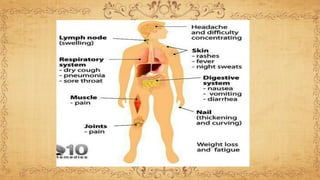
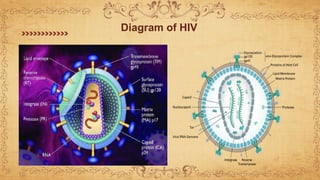
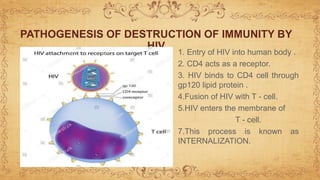
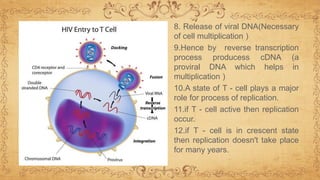
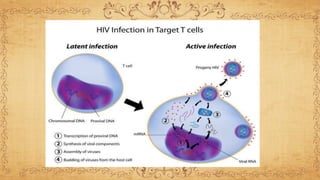
This document summarizes immunodeficiency disorder and HIV/AIDS. It defines AIDS as being acquired, weakening the immune system through CD4+ cell deficiency. HIV is described as a human immunodeficiency virus that infects and attacks human immune cells like CD4+ T cells. The stages of HIV infection are outlined from acute infection with fever and rash, to the chronic phase with falling CD4+ counts and opportunistic infections, and finally AIDS when the immune system has been severely damaged. The pathogenesis of HIV is explained as it binds to CD4+ receptors, integrates into the host cell DNA, and uses the cell's machinery to replicate and infect other cells.