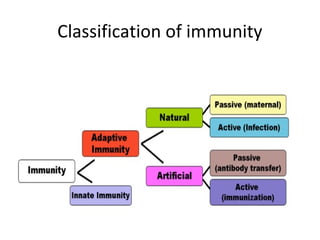
This document summarizes different types of immunity. It describes passive immunity as the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another, providing short-term protection but no immunological memory. Active immunity is induced within an individual through exposure to an antigen, resulting in long-lasting immunological memory. Immunity can be naturally acquired through exposure to pathogens or artificially acquired through vaccination. Vaccines include inactivated, live attenuated, toxoid, and subunit vaccines.