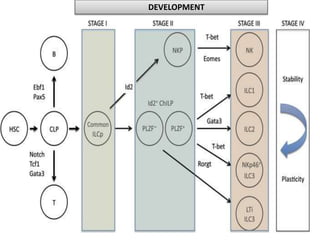
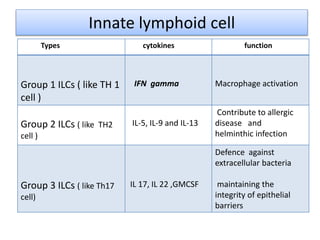
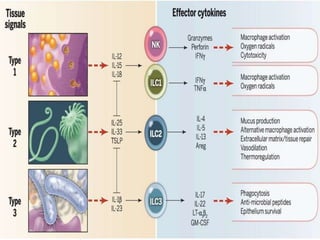
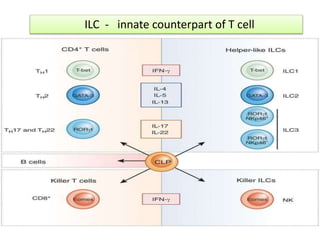
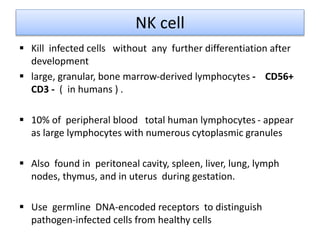
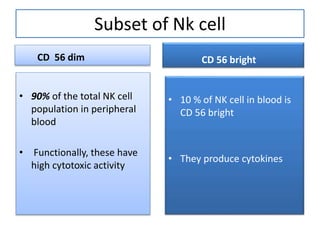
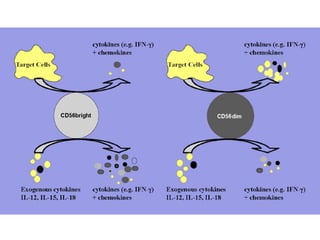
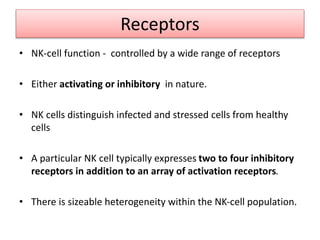
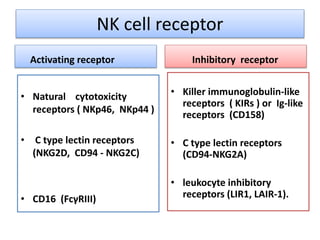
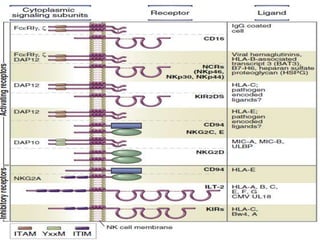
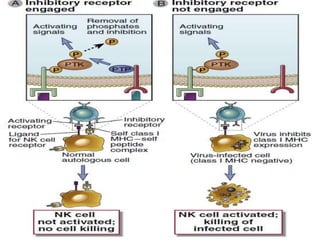
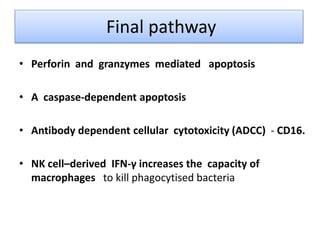
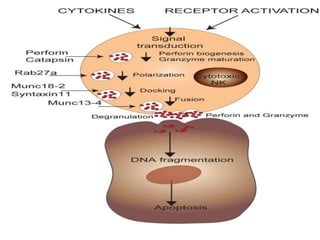
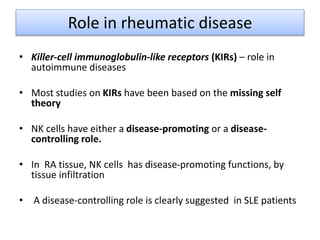
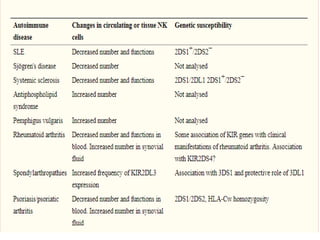
This document discusses innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and natural killer (NK) cells. It covers their development, types and subsets. ILCs are lymphoid cells that lack antigen receptors but play a crucial role in innate immunity against microbes and stressed cells. NK cells are a subset of ILCs that can kill infected cells without further differentiation. The document outlines the activating and inhibitory receptors on NK cells that help them distinguish healthy from infected cells. It also discusses the clinical importance of NK cells and ILCs in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and their potential as therapeutic targets.