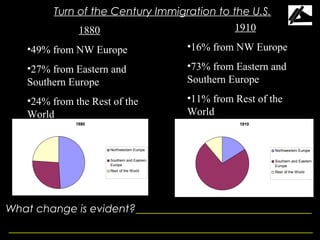
The document summarizes immigration trends and characteristics between 1880-1921. It shows that immigration to the US shifted from being majority northwestern European to majority southern and eastern European over this period. The new immigrants tended to be young, unskilled males from Catholic and Jewish backgrounds with little money or education. Push factors in Europe and pull factors in the US influenced immigration levels and destinations. Immigrants faced hardships but also gradually assimilated into American society, though nativism and restrictions on immigration increased over time.