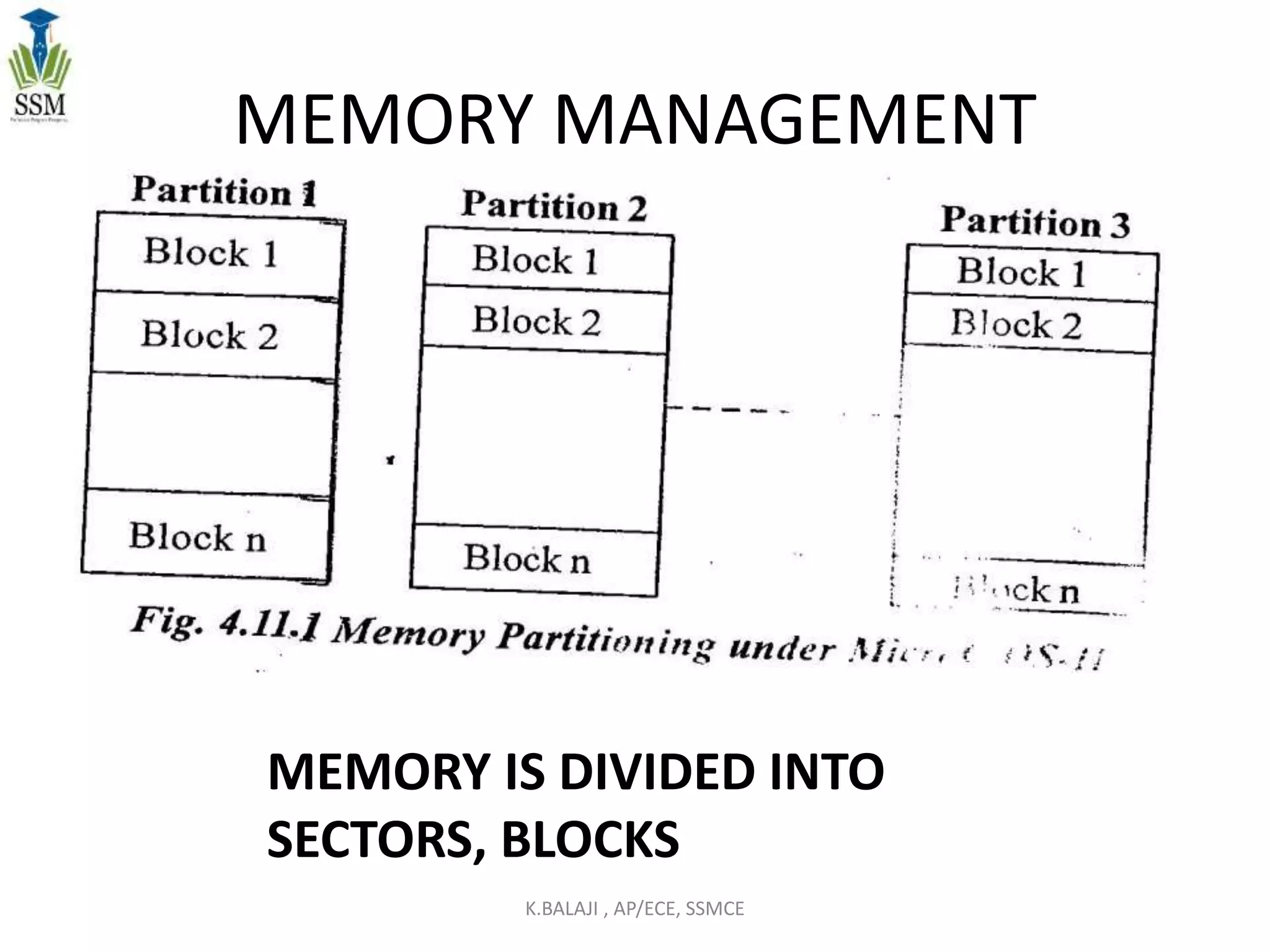
The document compares two real-time operating systems (RTOS): VxWorks and MicroC/OS-II (UC/OS-II). VxWorks is a hard real-time, multitasking RTOS used in applications like aerospace and robotics, featuring POSIX compliance and priority-based task scheduling. In contrast, MicroC/OS-II is a simpler kernel with multitasking and priority scheduling, utilizing a message queue for inter-process communication and capable of handling nested interrupts.