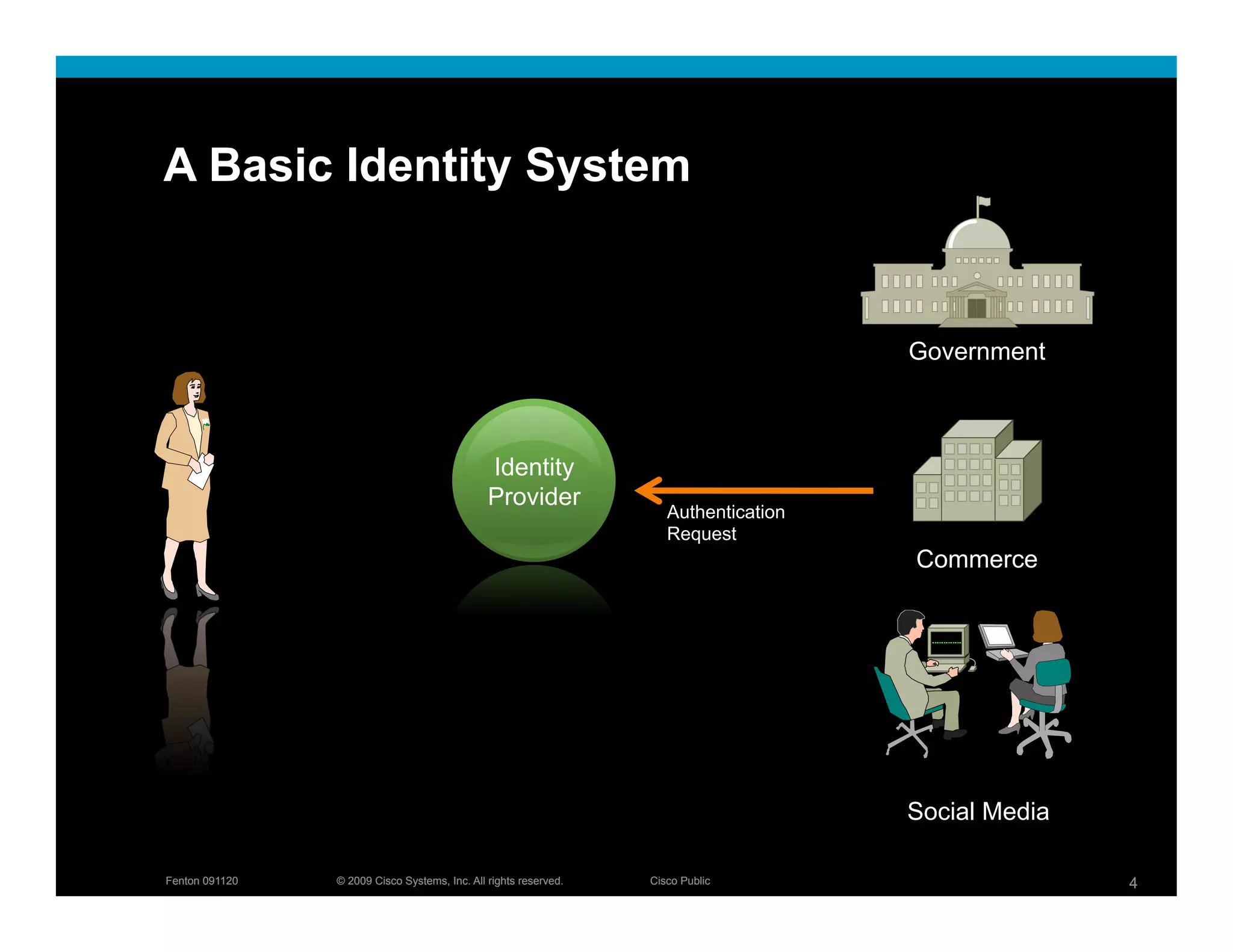
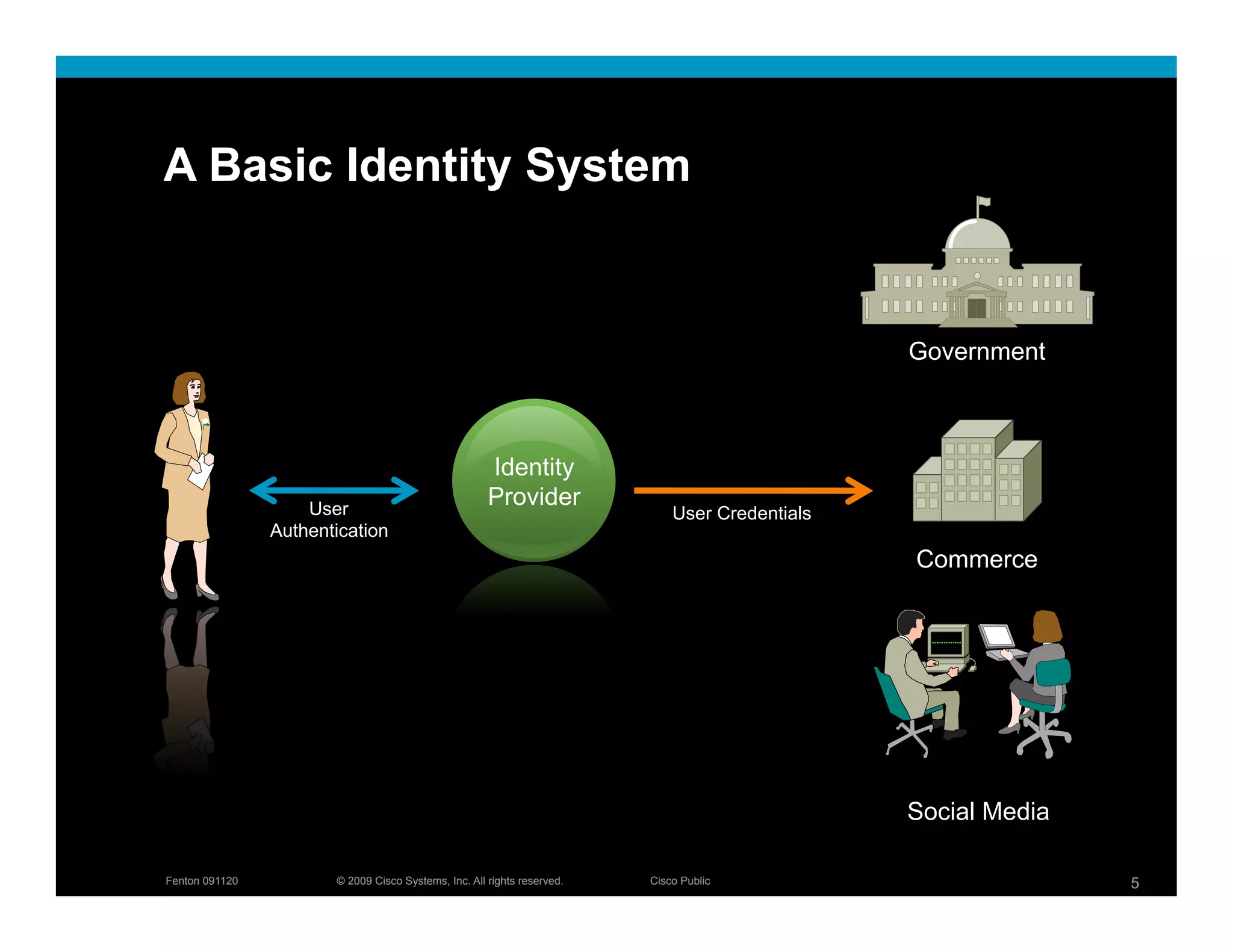
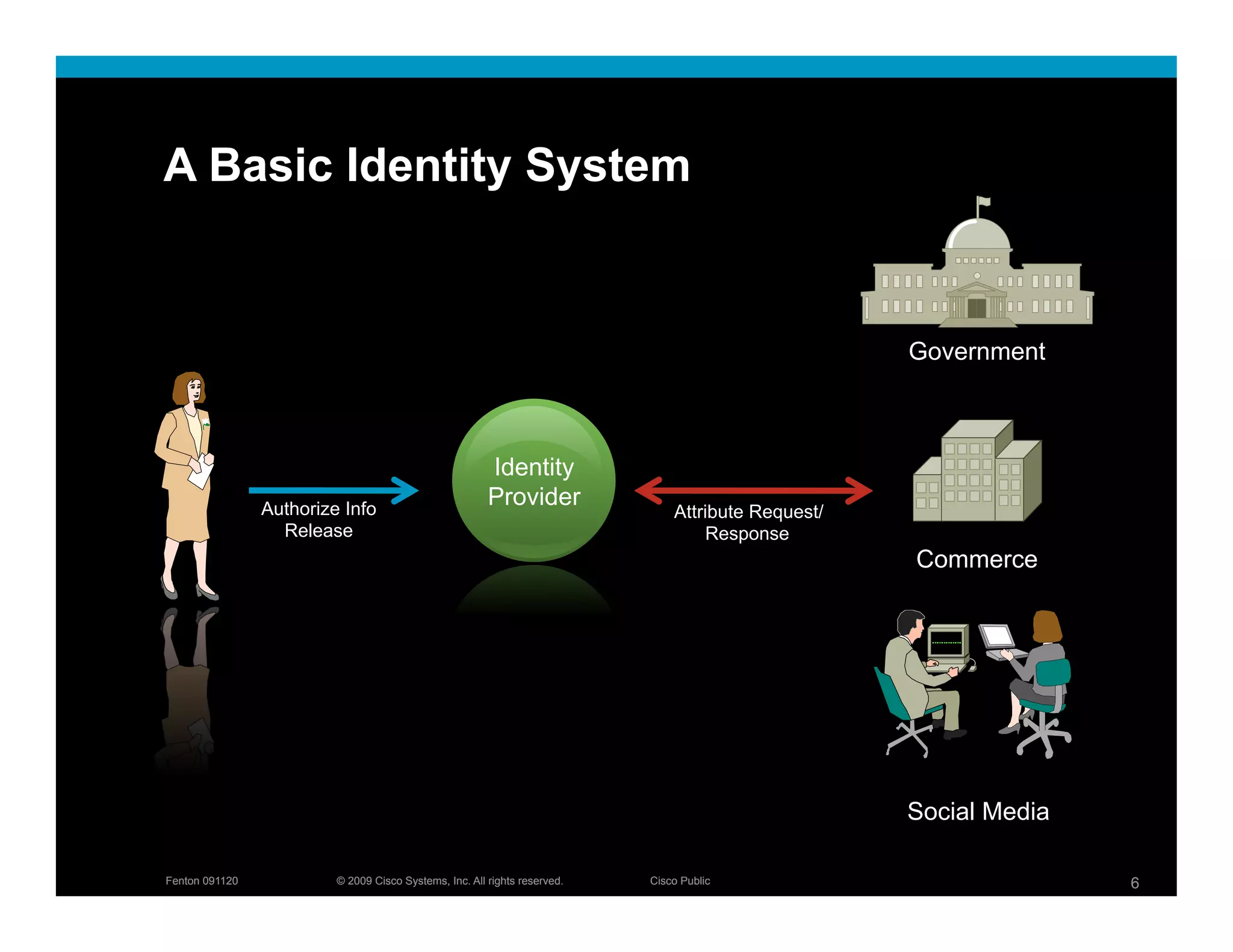
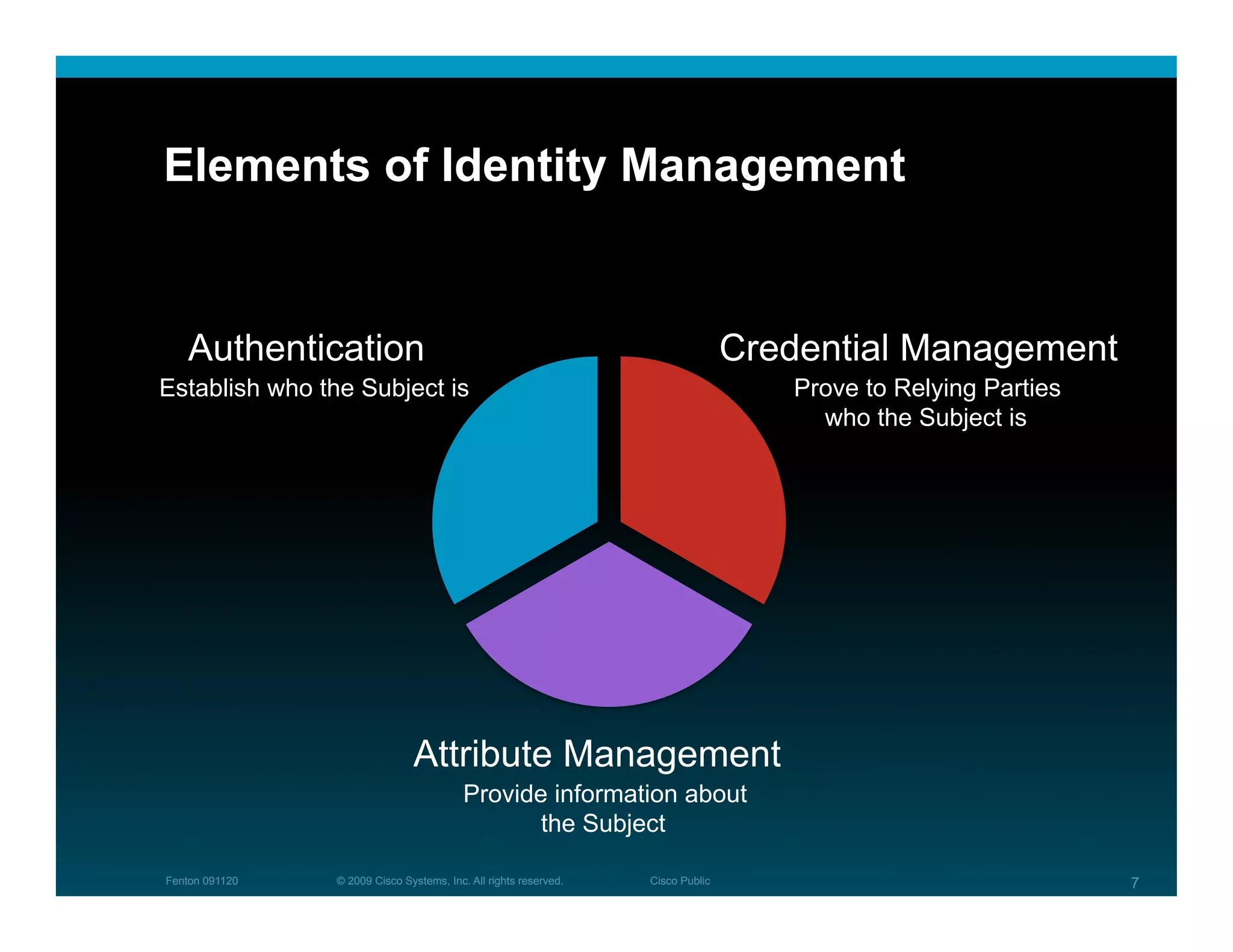
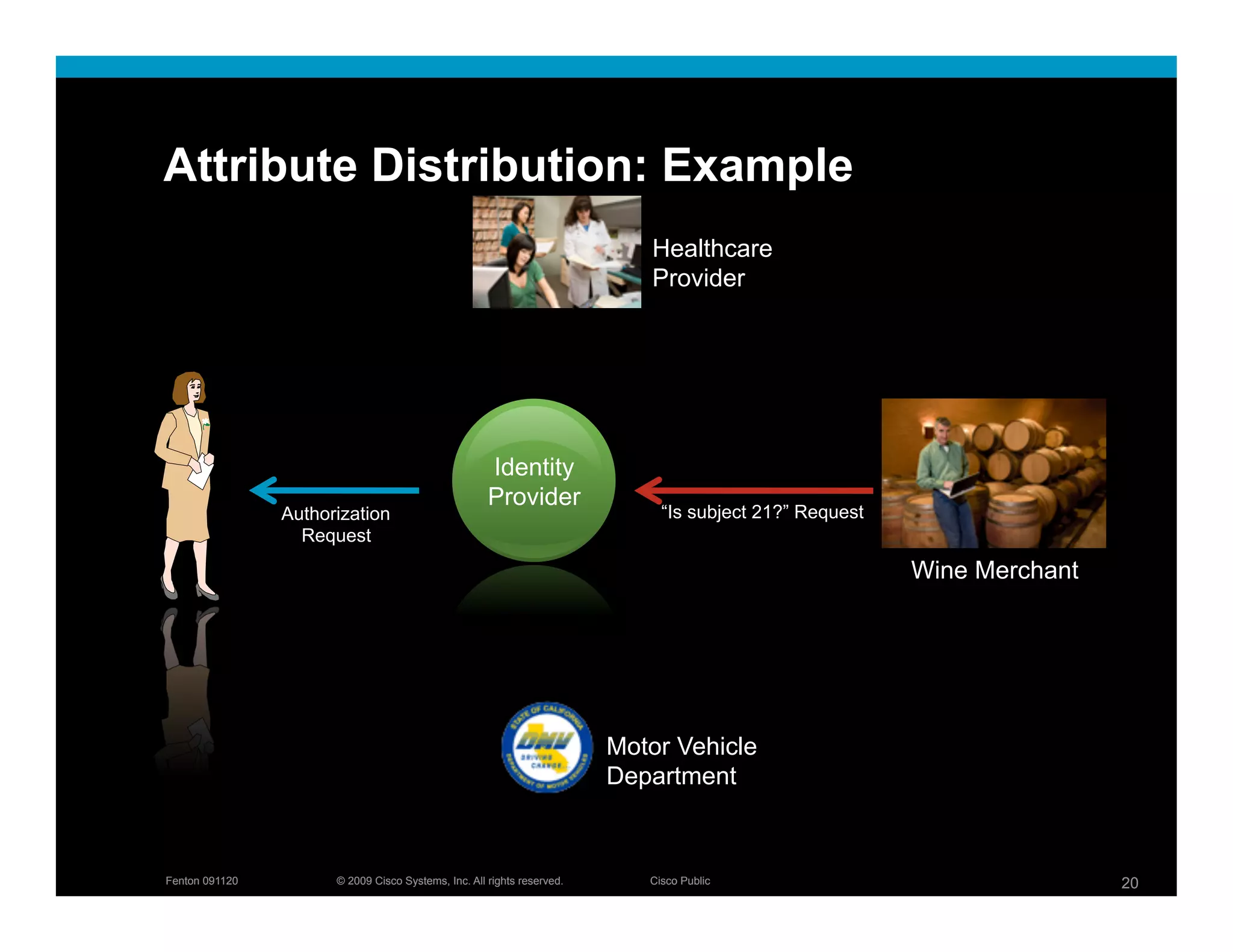
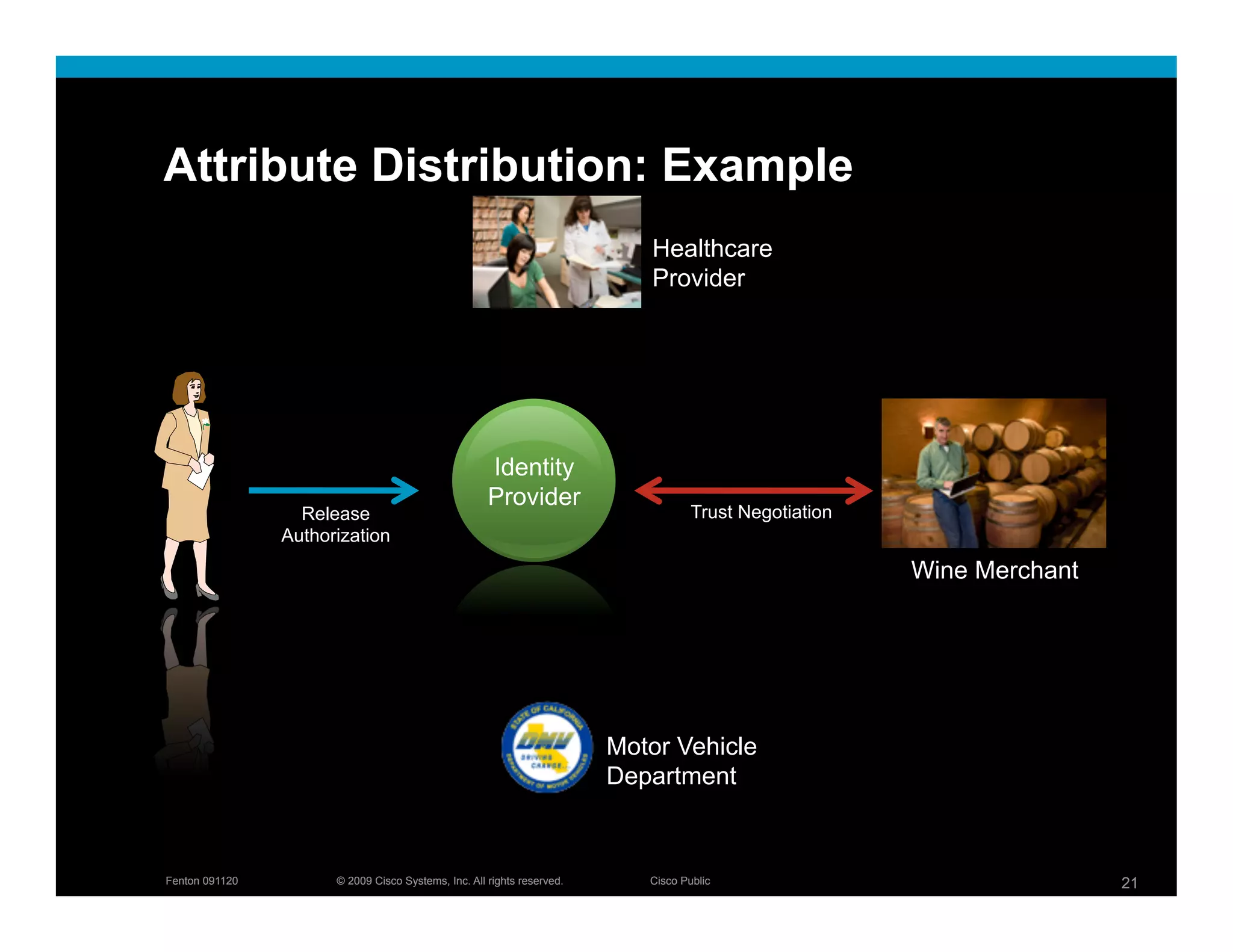
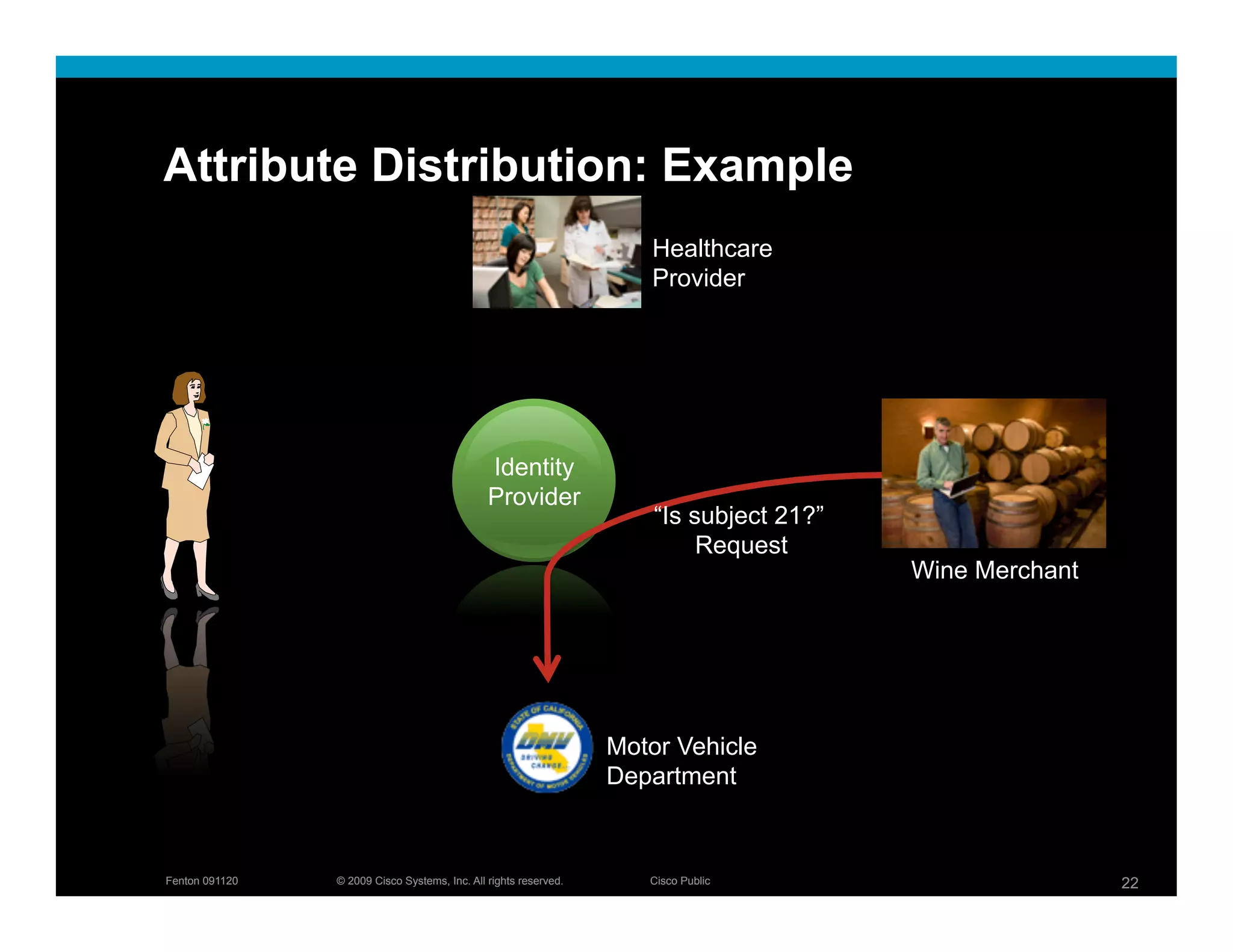
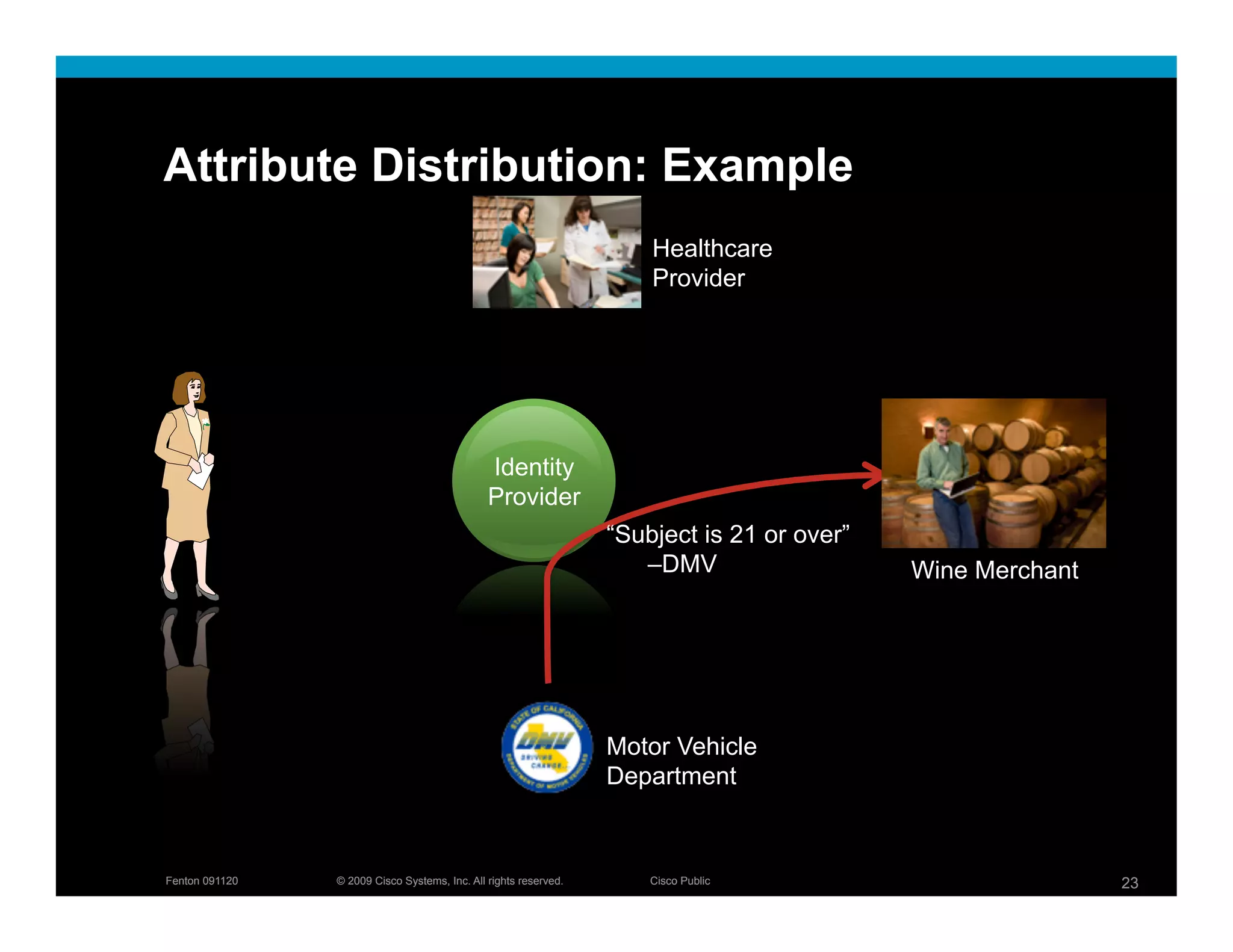
The document discusses key concepts related to identity systems, including subjects, relying parties, attributes, and the basic functions of an identity provider. It outlines a basic identity system model where the identity provider authenticates the user and authorizes the release of attributes to relying parties. It also covers important topics such as user trust, authentication methods, credential management, directed identity, attribute sources, and security and availability challenges.