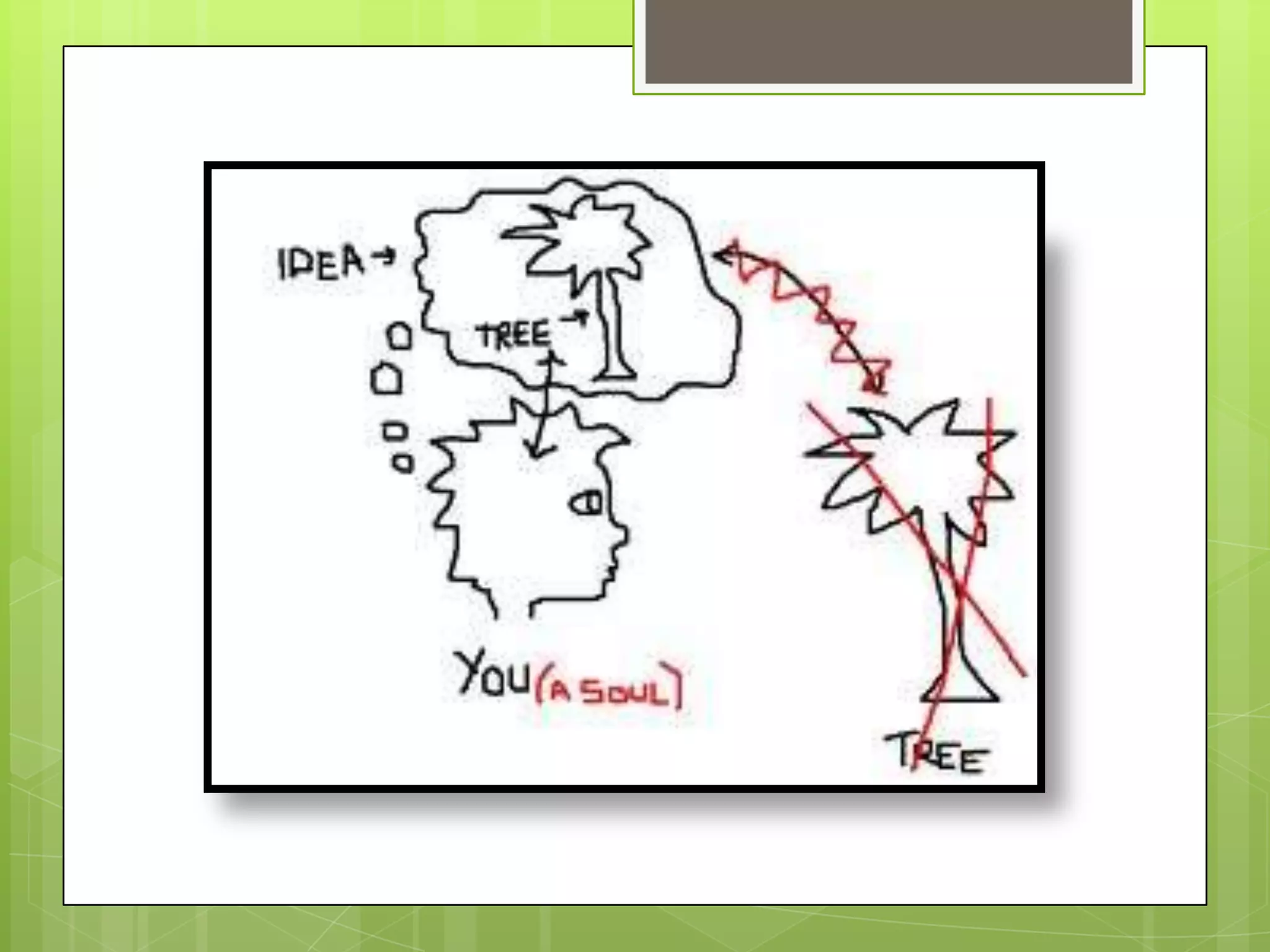
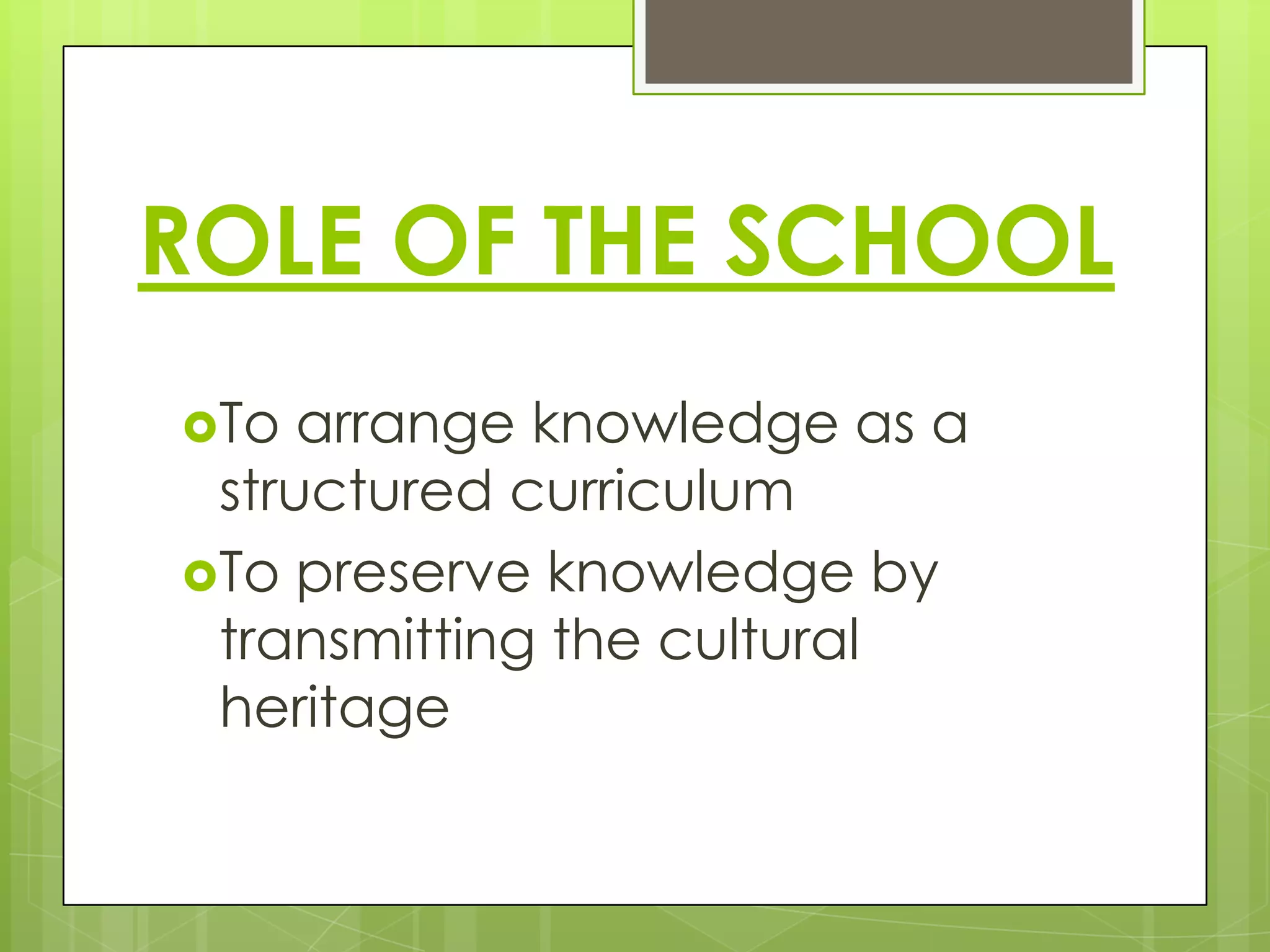
The document discusses the philosophy of idealism and its implications for education. It provides background on idealist philosophers like Hegel, Emerson, and proponents of American Transcendentalism. Idealism views reality as existing primarily in the mind rather than the physical world. Education under idealism aims to lead students to truth and cultural heritage. It favors a liberal arts curriculum organized in a hierarchy. Teaching methods involve lectures and recitation with the teacher as the authority and model transmitting knowledge. The teacher-student relationship sees the teacher as perfecting students' character and cultural understanding.