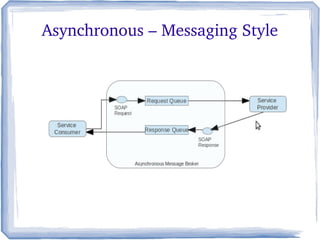
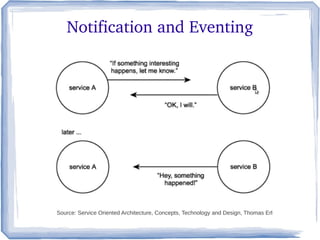
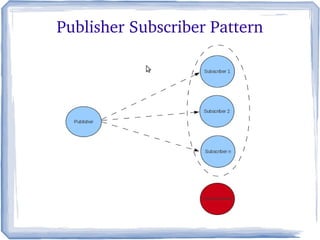
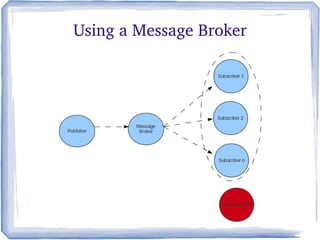
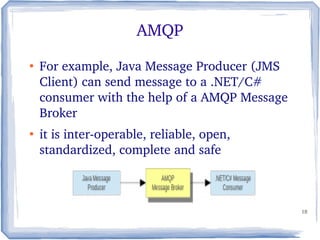
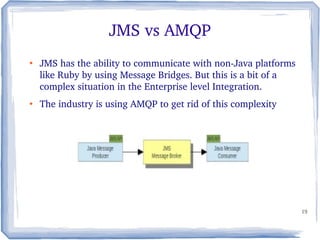
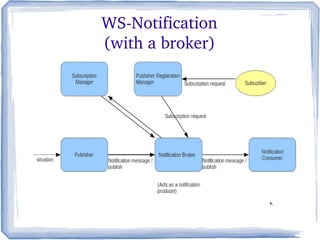
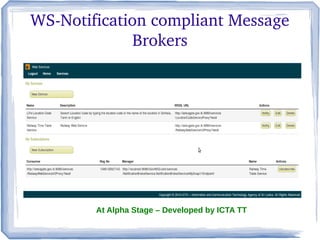
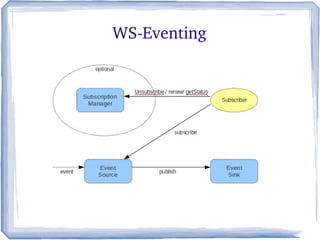
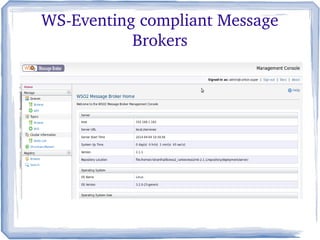
The document discusses the concepts and implementation of message brokers in service-oriented architecture, detailing synchronous and asynchronous service invocations. It covers the publisher-subscriber pattern, the benefits of decoupling, and various message broker standards like JMS, MSMQ, and AMQP. The document also compares JMS and AMQP, highlights two WS specifications (WS-Eventing and WS-Notification) used for implementing the publisher-subscriber model, and addresses potential differences between ESB and message brokers.