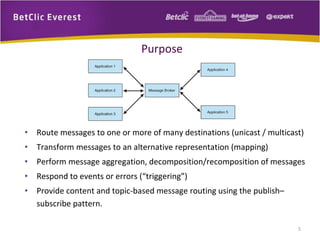
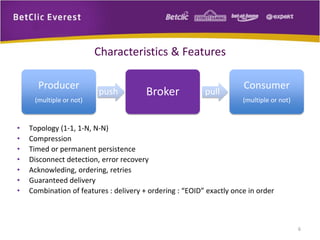
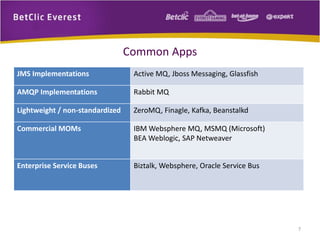
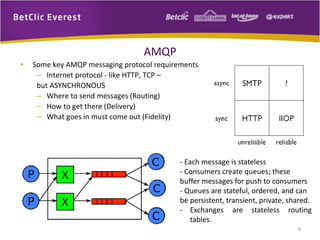
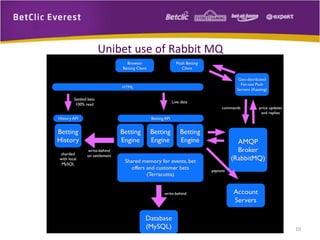
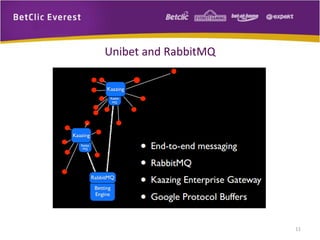
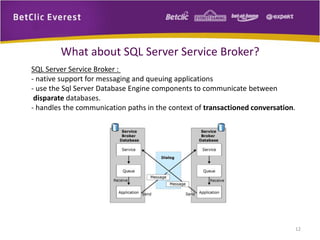
The document provides an overview of message brokers, highlighting their definitions, features, and usage in messaging systems, emphasizing the importance of decoupling applications. It discusses popular message-oriented middleware (MOM) implementations, the AMQP protocol, and specifically details RabbitMQ's functionality and its applications in various organizations. Additionally, it touches on SQL Server Service Broker for messaging within database systems and includes links for further reading.