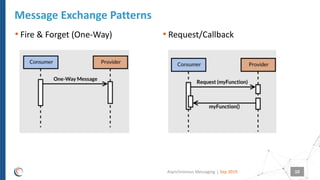
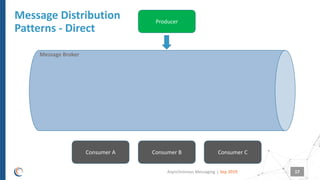
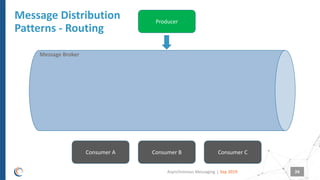
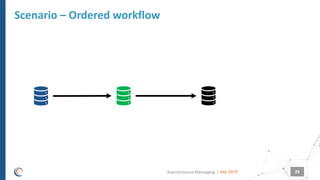
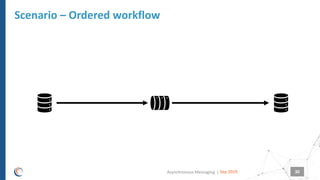
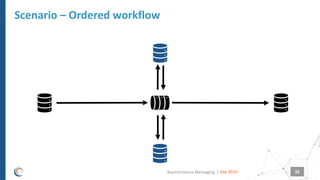
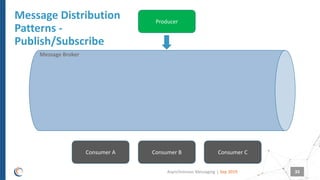
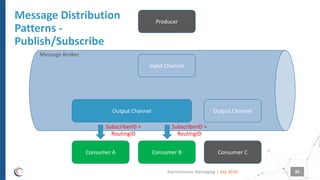
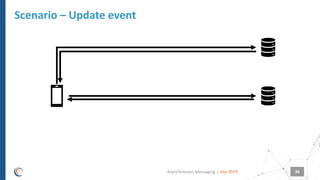
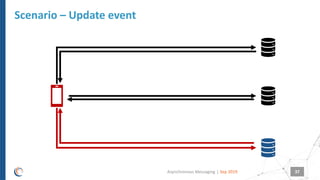
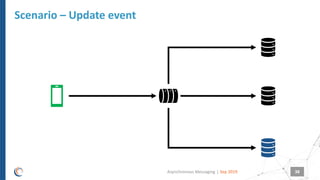
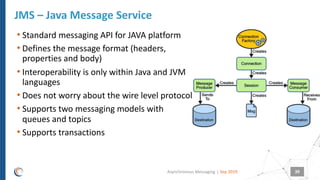
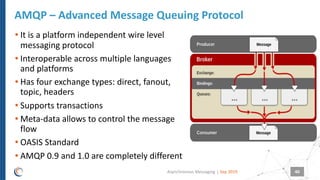
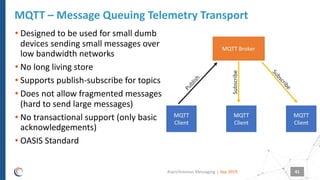
The document discusses asynchronous messaging as a mode of interaction where multiple parties can exchange information without needing simultaneous participation, making it ideal for scenarios with varying event rates. It outlines key benefits, integration architecture, and various messaging patterns such as publisher/subscriber, direct, and broadcast. Additionally, it contrasts different messaging protocols like JMS, AMQP, and MQTT, highlighting their specific use cases and characteristics.