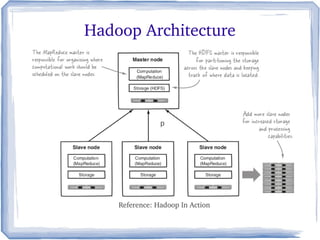
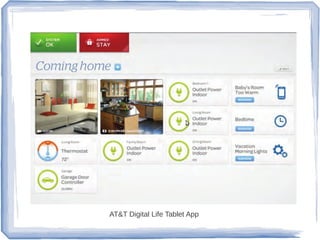
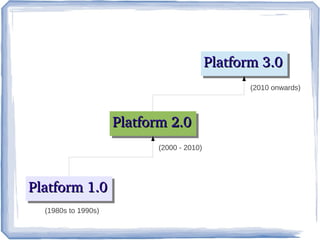
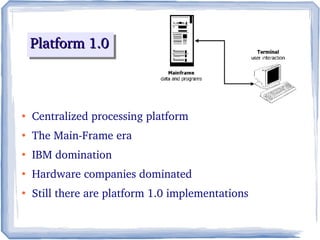
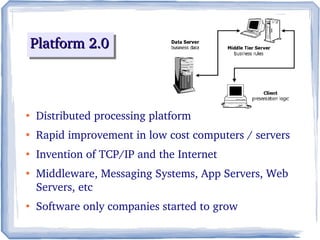
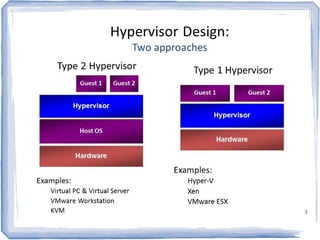
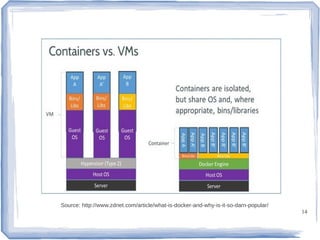
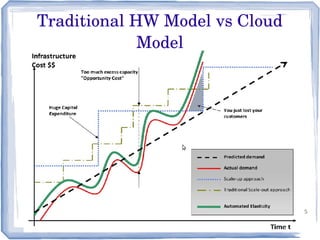
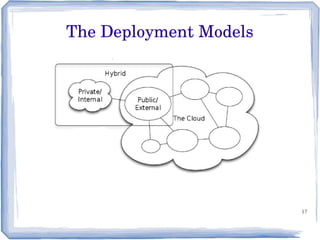
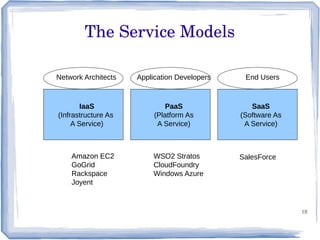
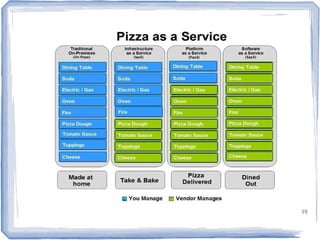
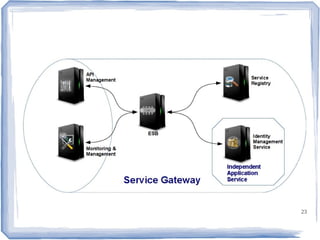
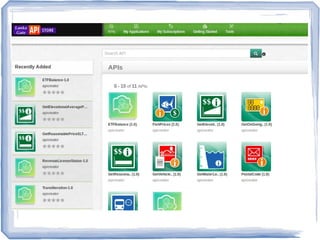
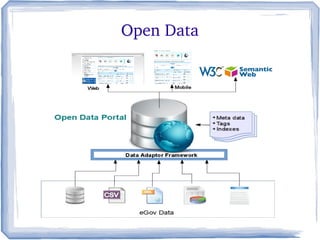
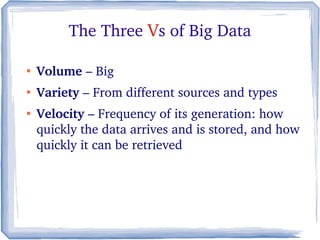
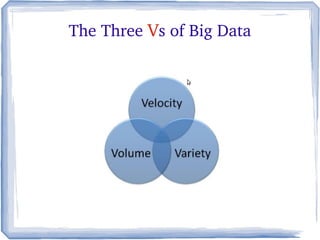
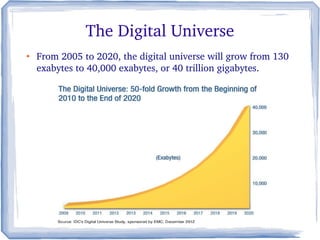
The document discusses the evolution of information technology platforms from Platform 1.0 to Platform 3.0. Platform 1.0 referred to centralized mainframe computing (1980s-1990s). Platform 2.0 introduced distributed processing and the internet (2000-2010). Platform 3.0 is defined by cloud computing, mobile integration, internet of things, big data, analytics and devops (2010-present). Key aspects of Platform 3.0 include cloud infrastructure, application programming interfaces, open data, big data technologies like Hadoop, and the growing internet of things.











![According to IDC, the Big Data technology and service market was about
US$4.8 billion in 2011. The market is projected to grow at a compound annual
growth rate (CAGR) of 37.2% between 2011 and 2015.
By 2015, the market size is expected to be US$16.9 billion.
[Source: IDC. Worldwide Big Data Technology and Services 20122015 Forecast.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edbseminar-150629050600-lva1-app6892/85/Modern-Trends-in-IT-35-320.jpg)
![Gartner reported that more than 65 billion devices were connected
to the internet by 2010. By 2020, this number will go up to 230 billion
[Source: https://www.gartner.com/doc/1799626]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edbseminar-150629050600-lva1-app6892/85/Modern-Trends-in-IT-36-320.jpg)