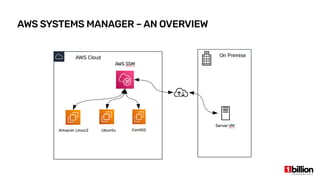
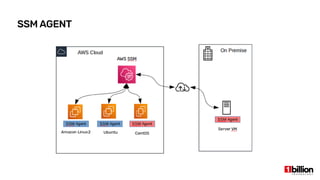
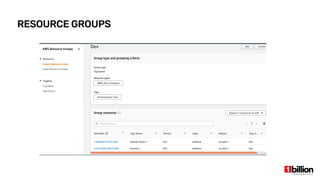
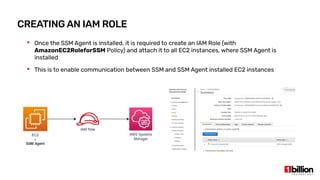
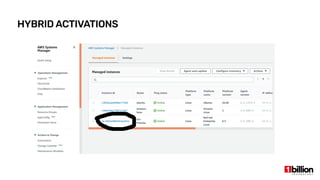
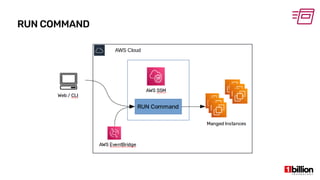
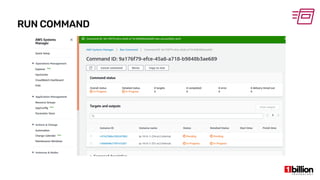
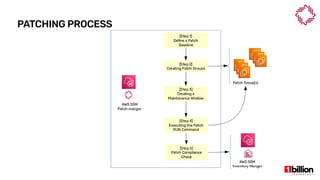
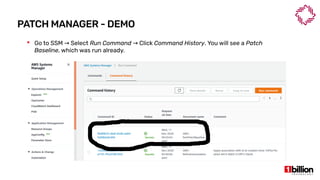
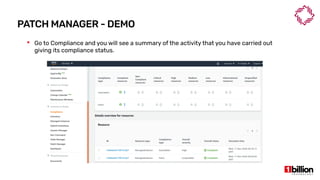
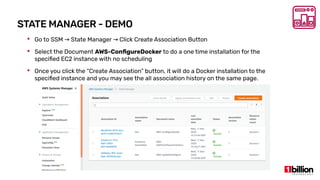
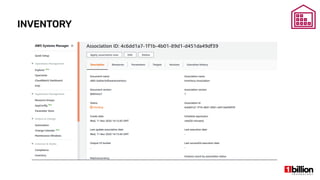
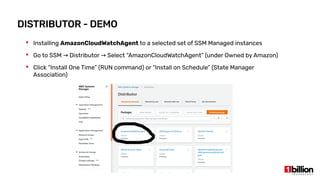
This document provides an overview and agenda for an AWS Systems Manager November 2020 meetup. It discusses the key capabilities of AWS Systems Manager including SSM documents, managed instances, resource groups, RUN commands, hybrid activations, patch manager, inventory, session manager, automation, parameter store, distributor, and OpsCenter/Explorer. It also includes demonstrations of creating RUN commands, hybrid activations, patching processes, state manager associations, and installing software using distributor.