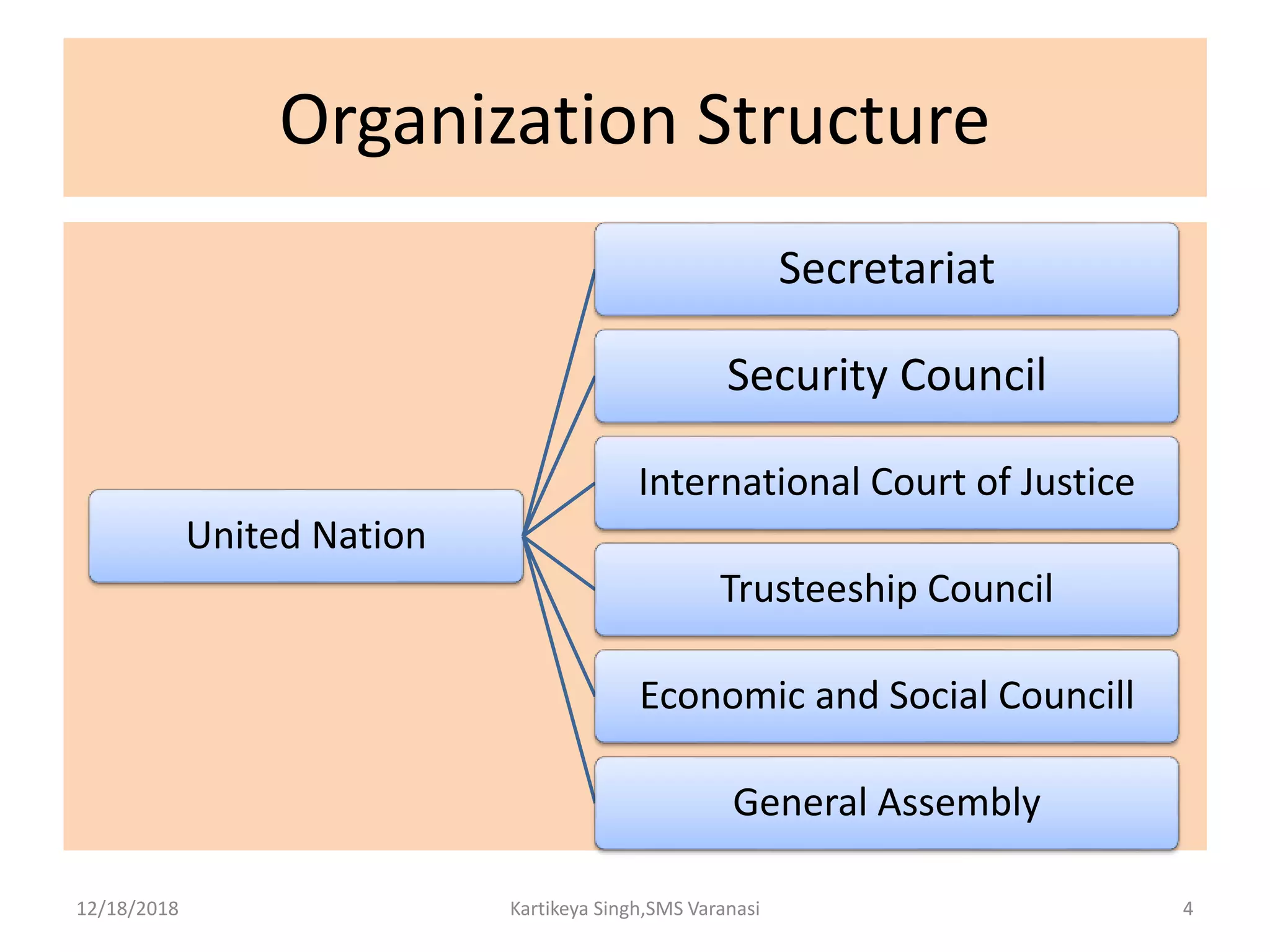
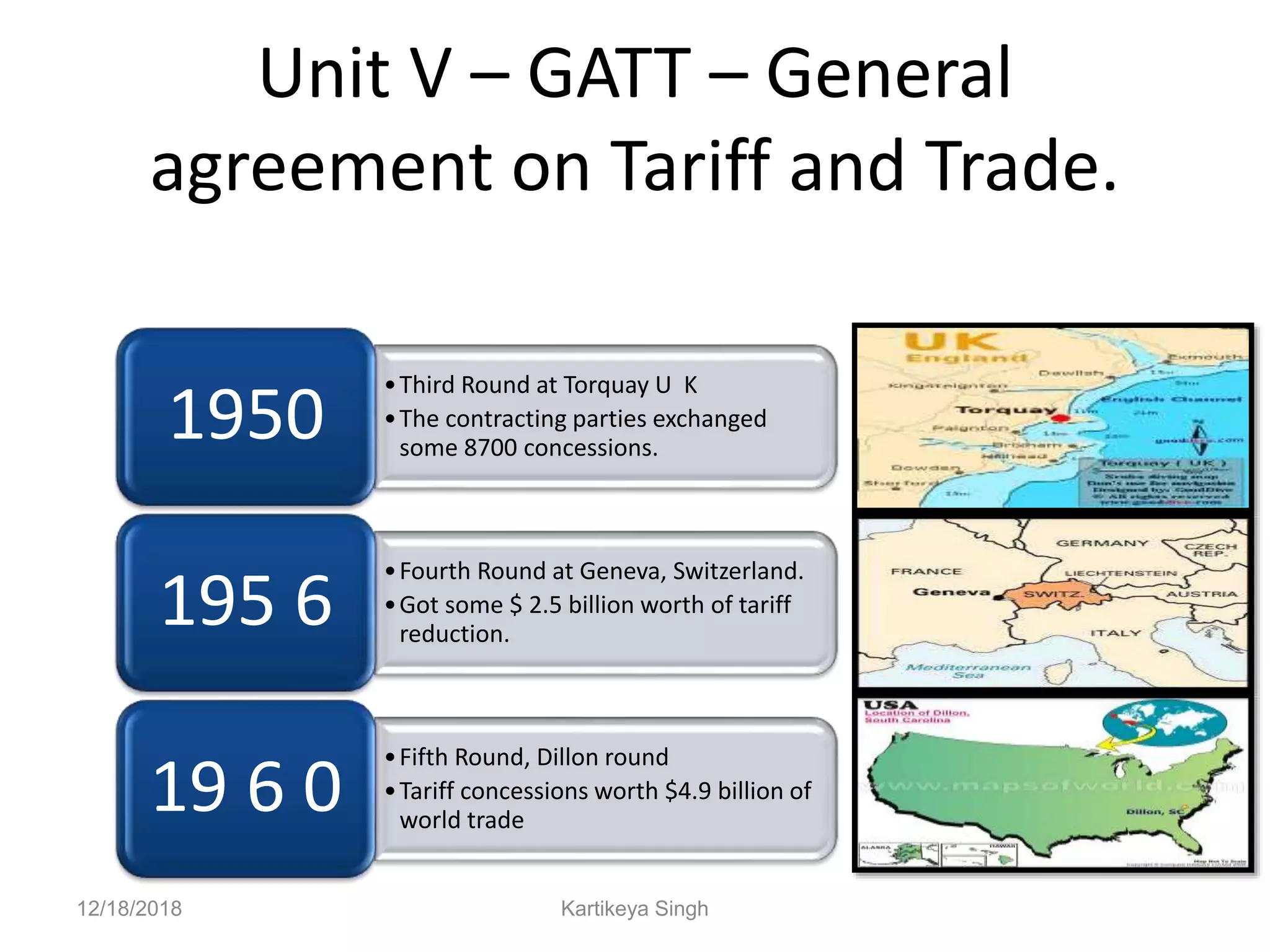
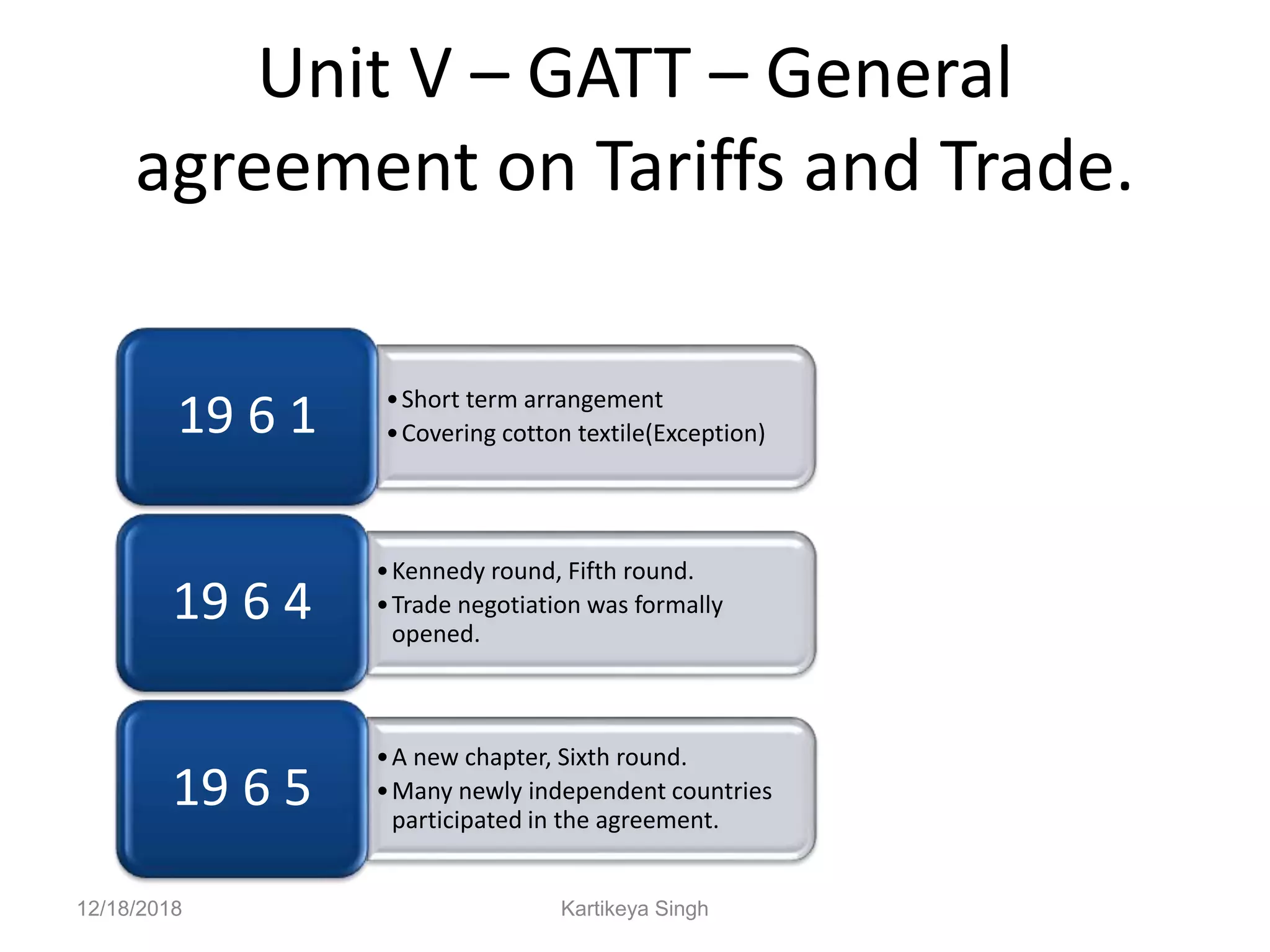
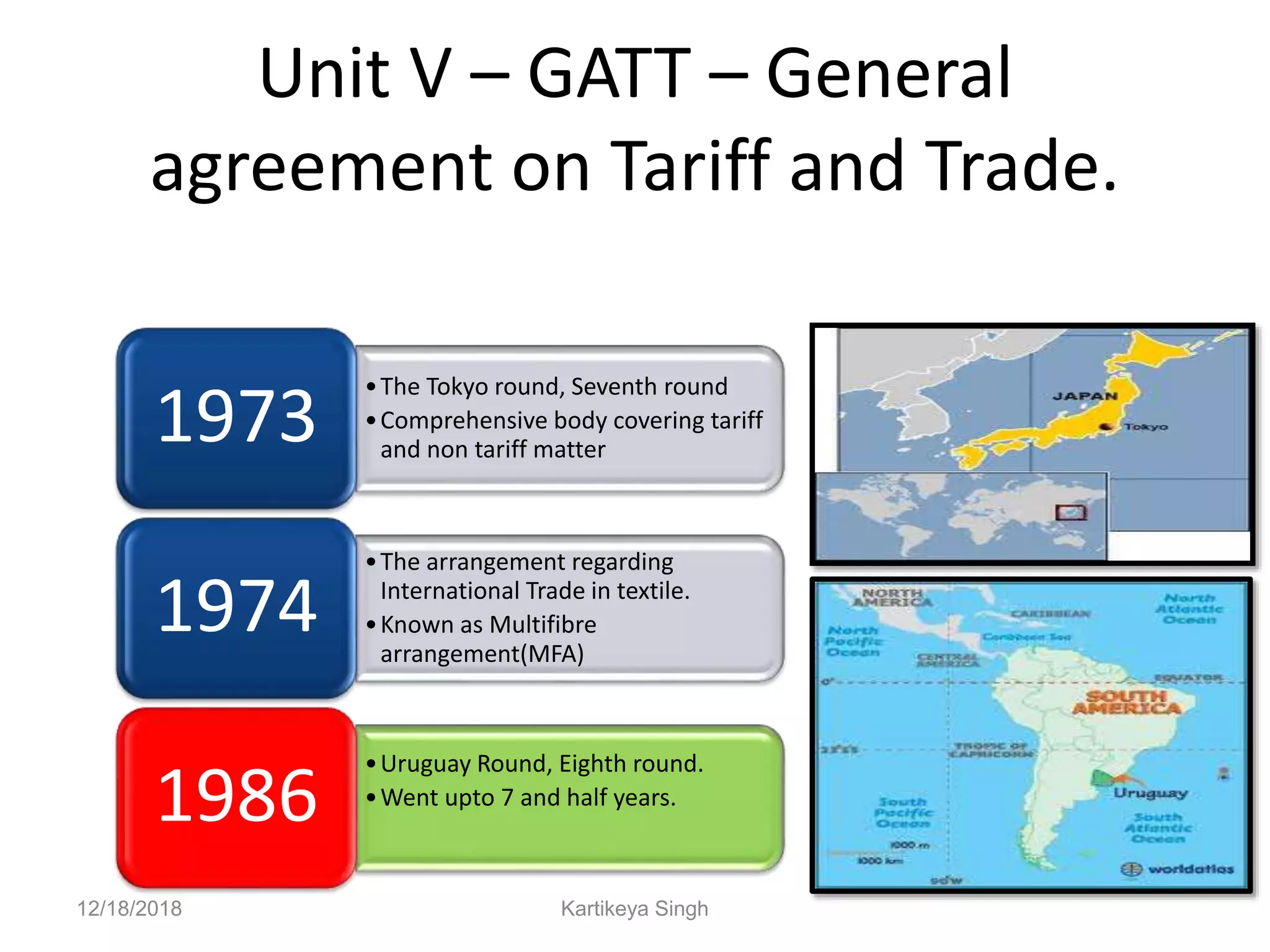
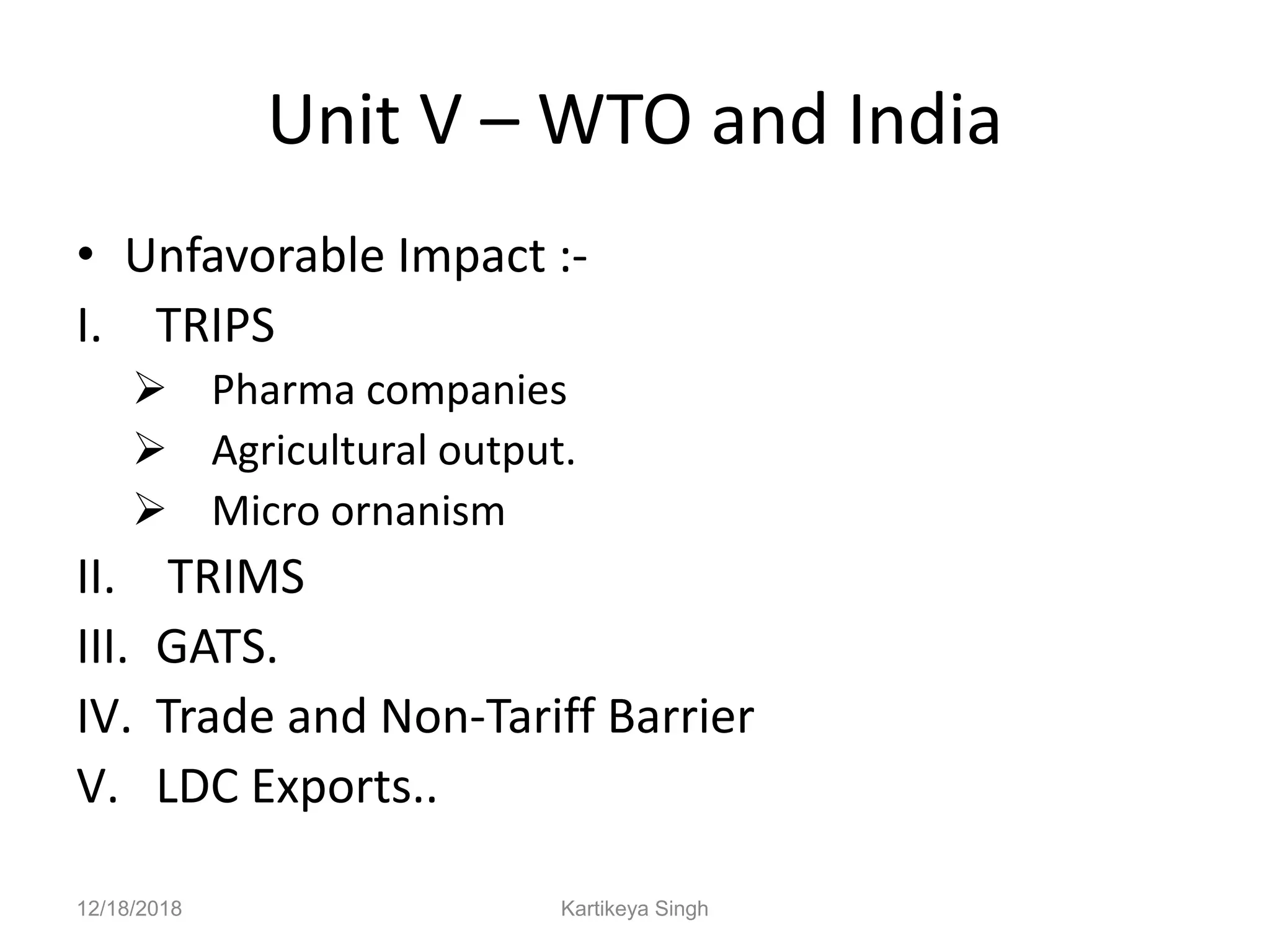
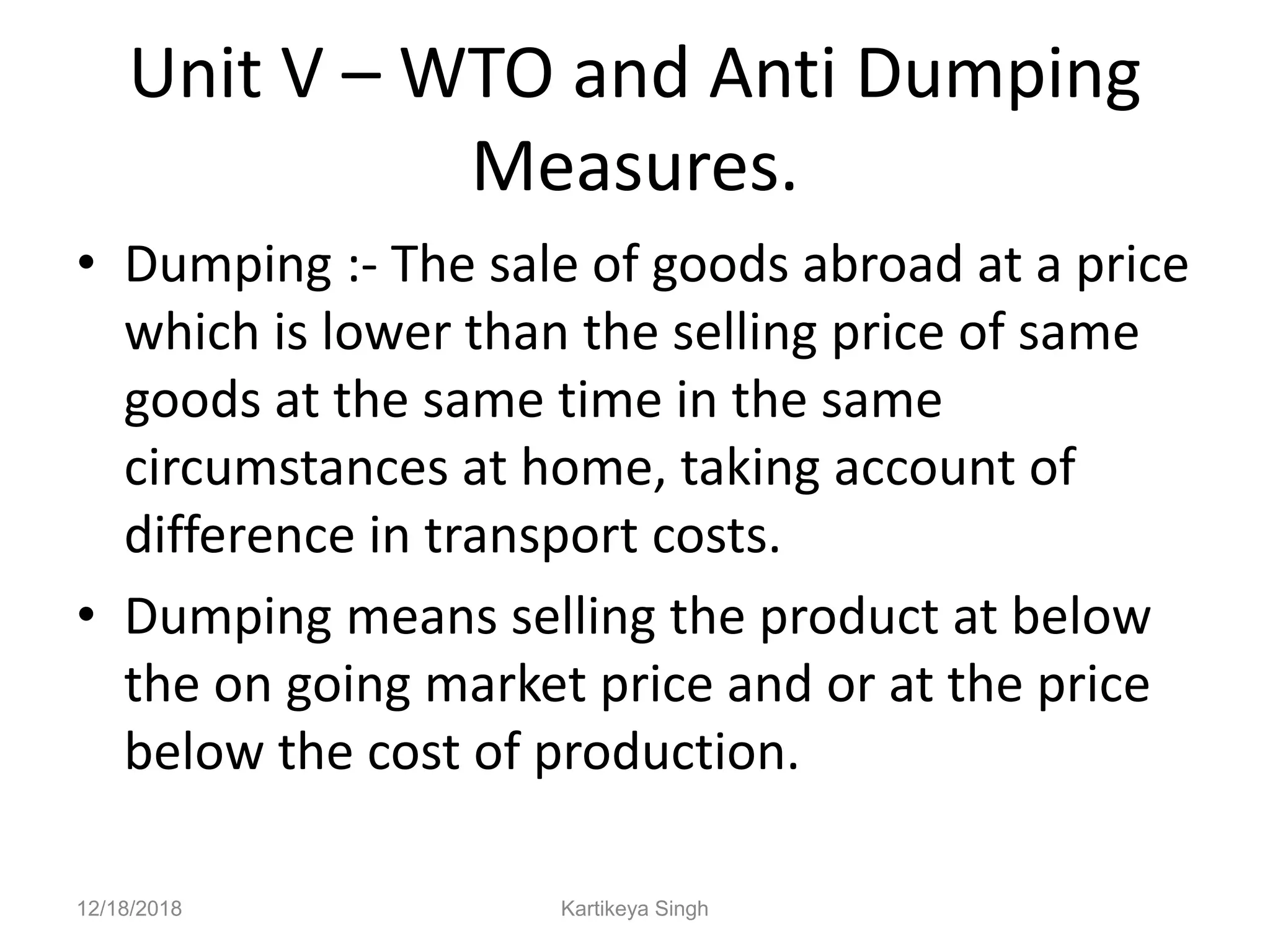
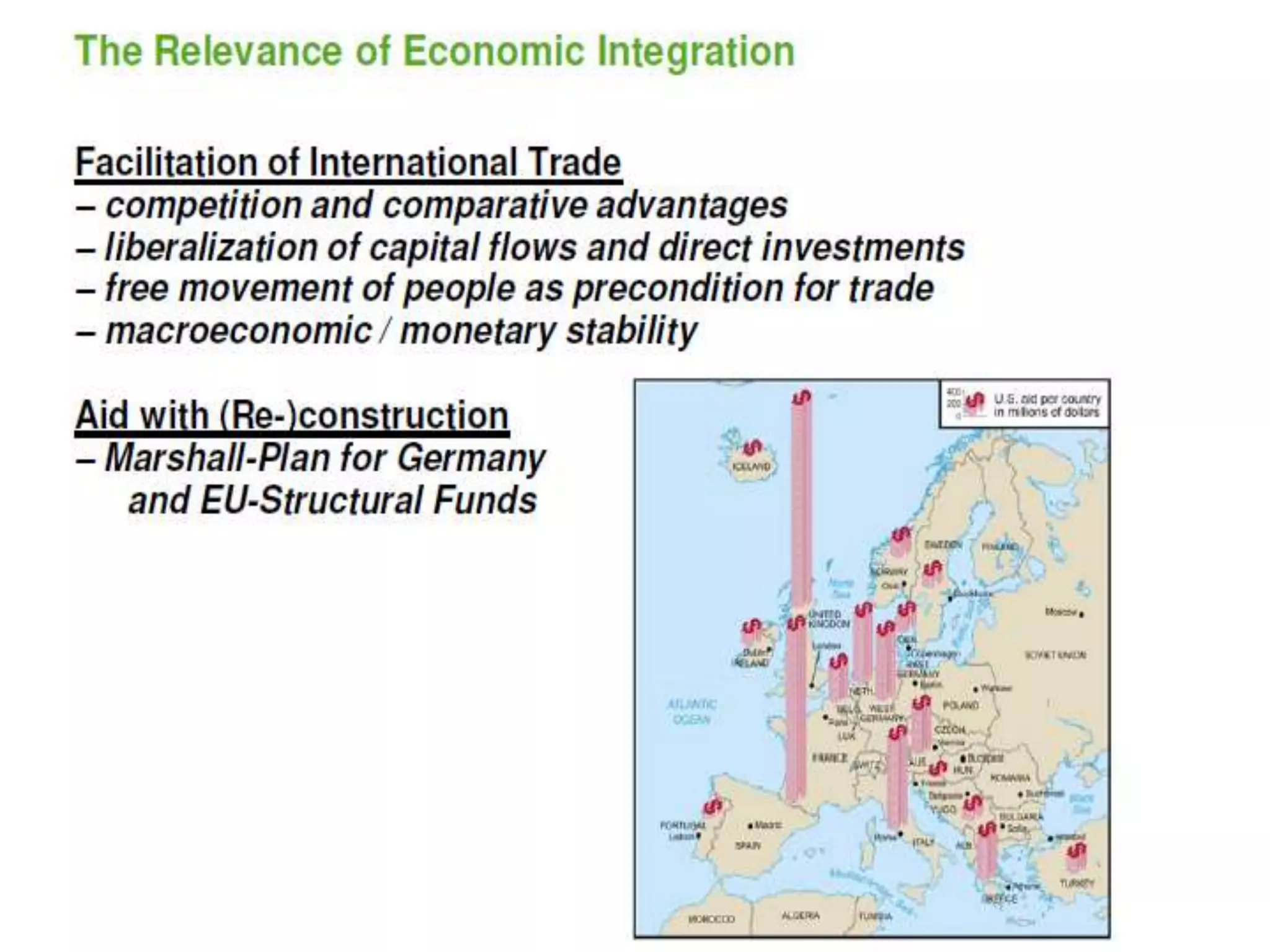
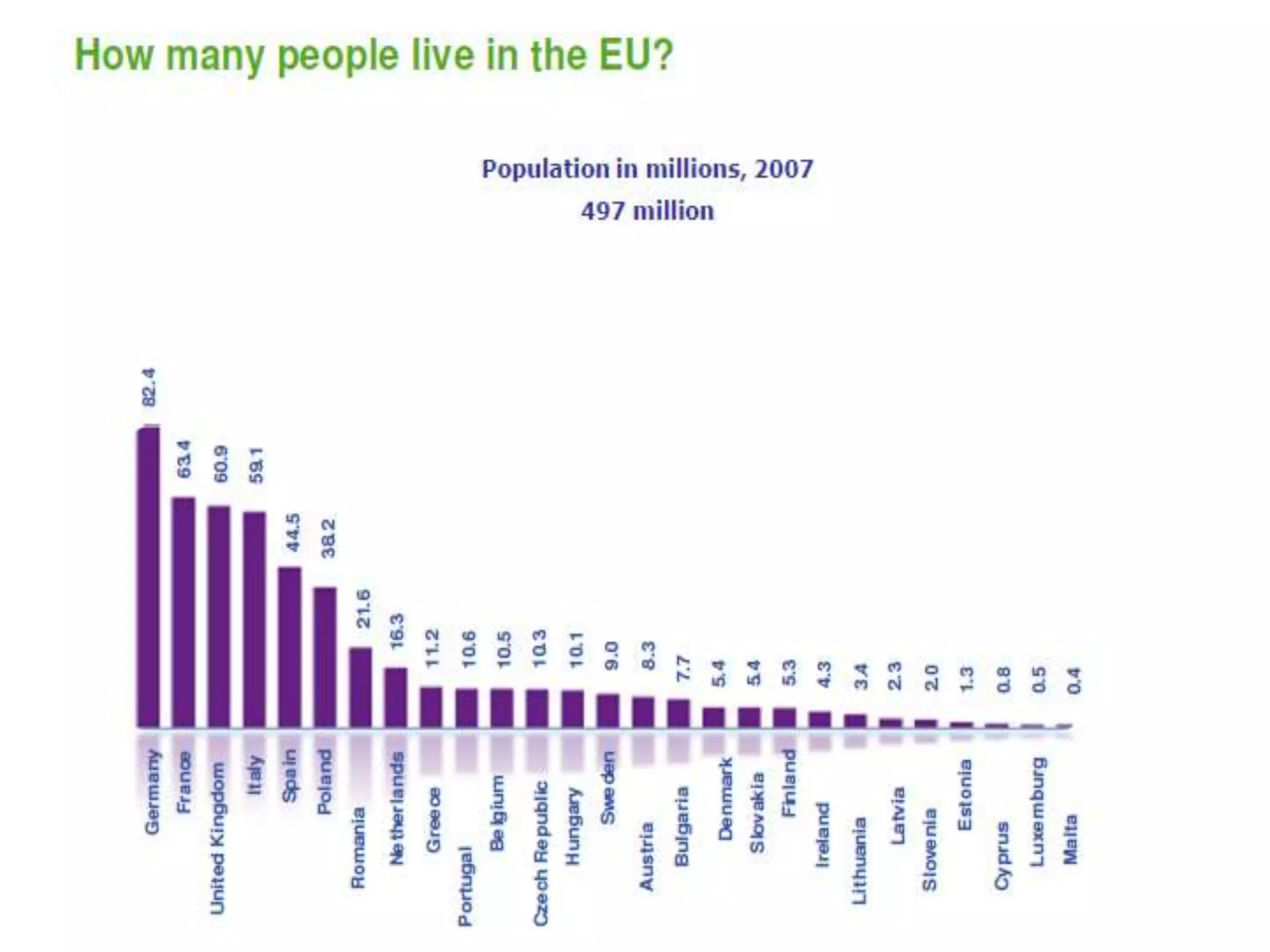
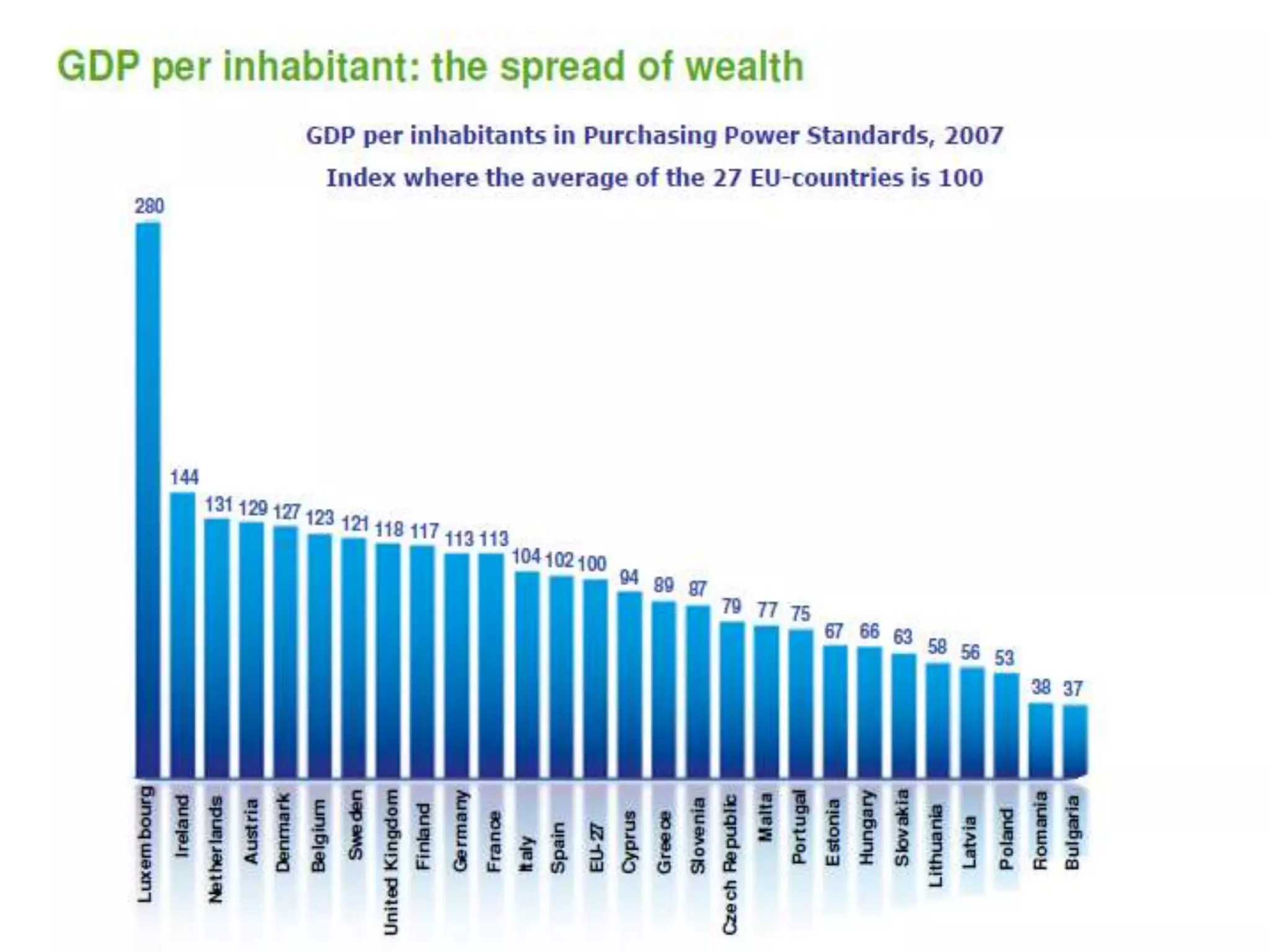
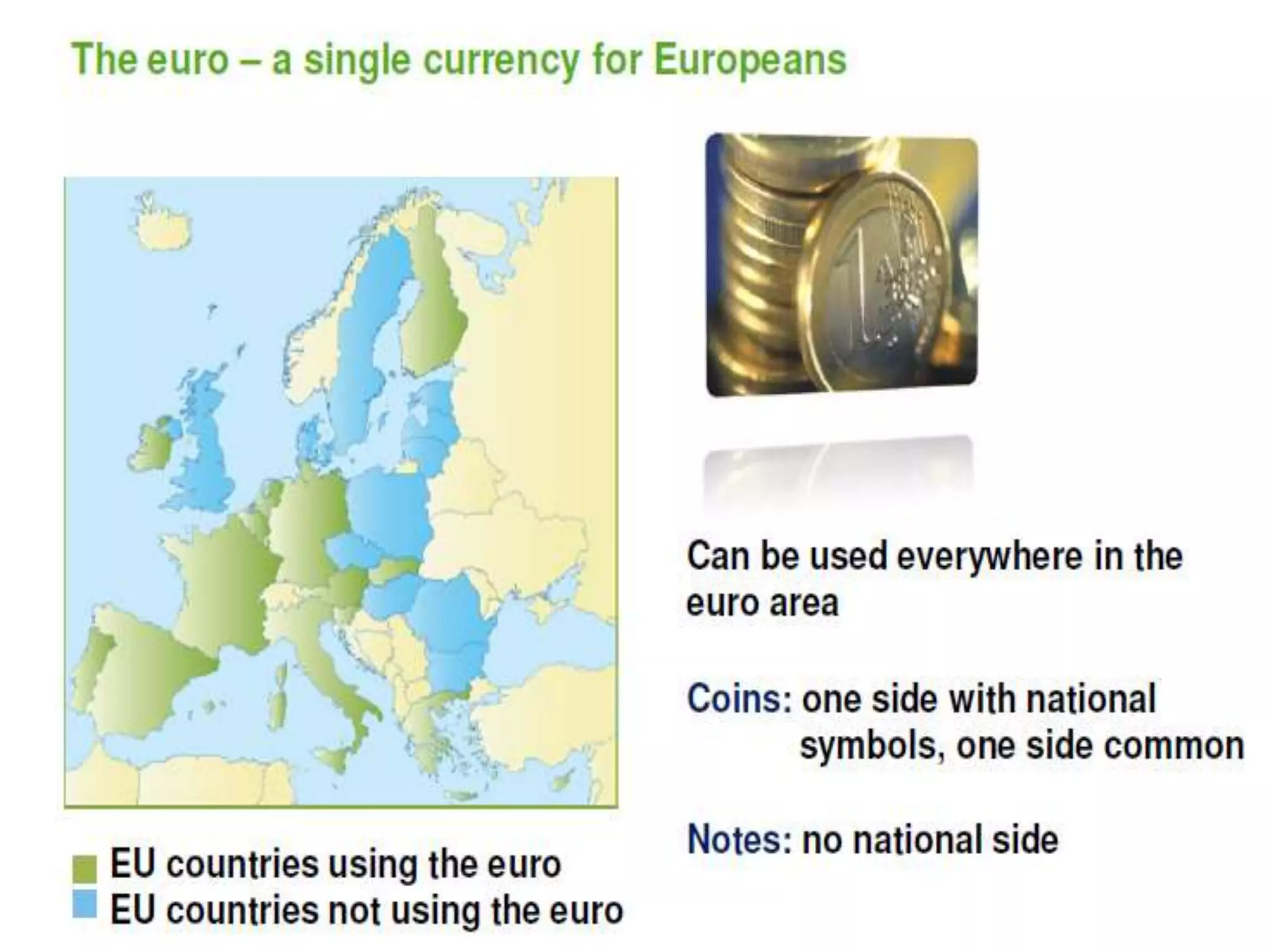
The document discusses the history and structure of the United Nations. It begins with the formation of the UN in 1945 with 51 original member states aimed to prevent future wars. It describes the main UN organs including the Secretariat, Security Council, General Assembly, Economic and Social Council, International Court of Justice, and Trusteeship Council. It provides details on the roles and functions of these organs. For example, it states the Secretariat serves the other UN organs and informs the media about UN work, while the Security Council aims to maintain international peace and can enforce binding resolutions. The document also looks at UNCTAD and its role in promoting trade and development issues for developing countries.

































































![12/18/2018 Kartikeya Singh,SMS Varanasi 88
Headquarters Kathmandu, Nepal
Official languages English
Membership
8 members[show]
9 observers[show]
Leaders
Directors:
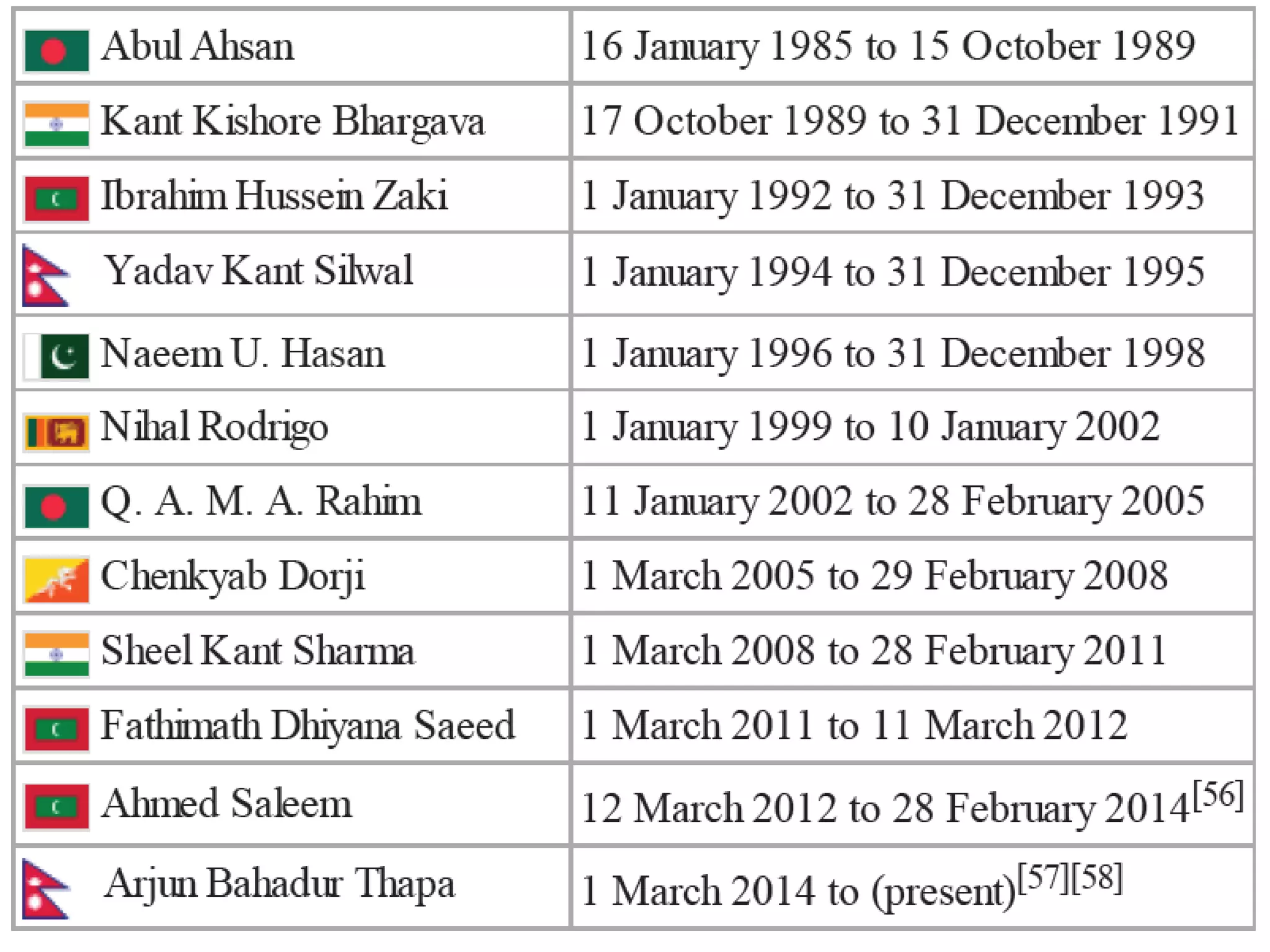
Afghanistan Md Ibrahim Ghafoor
Bangladesh MJH Jabed
Bhutan Singye Dorjee
India L. Savithri
Maldives
a
Fathimath Najwa
Nepal Harpal Sing Nepali
[
Pakistan Ahmar Ismail
Sri Lanka Prasanna Gamage
Establishment 8 December 1985
GDP (PPP) 2014 estimate
Total US$ 9.05 trillion
GDP (nominal) 2014 estimate
Total US$ 2.599 trillion
Website
www.saarc-sec.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ibmrmb302-unitv-181218160036/75/IBM-RMB302-Unit-V-88-2048.jpg)