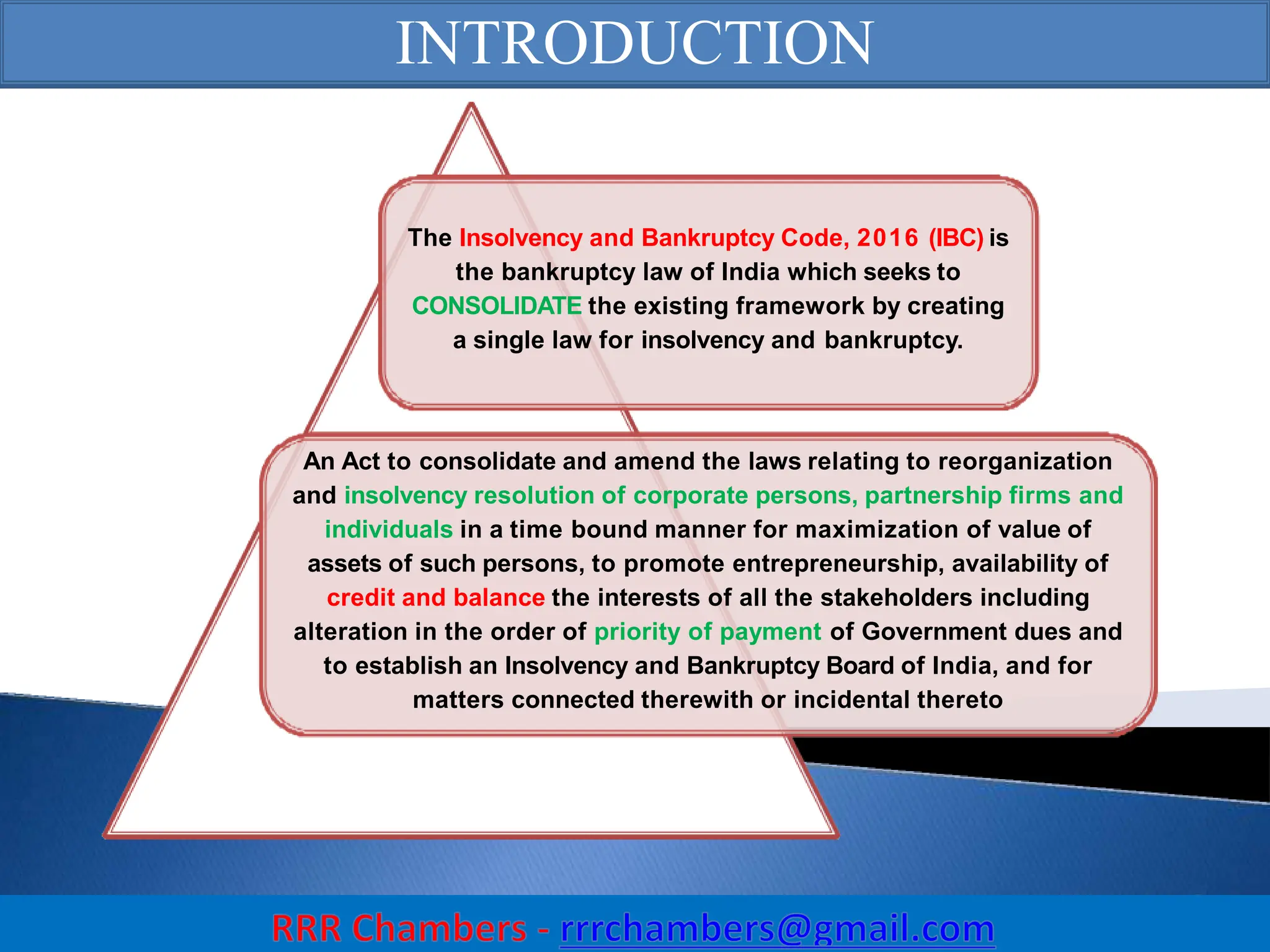
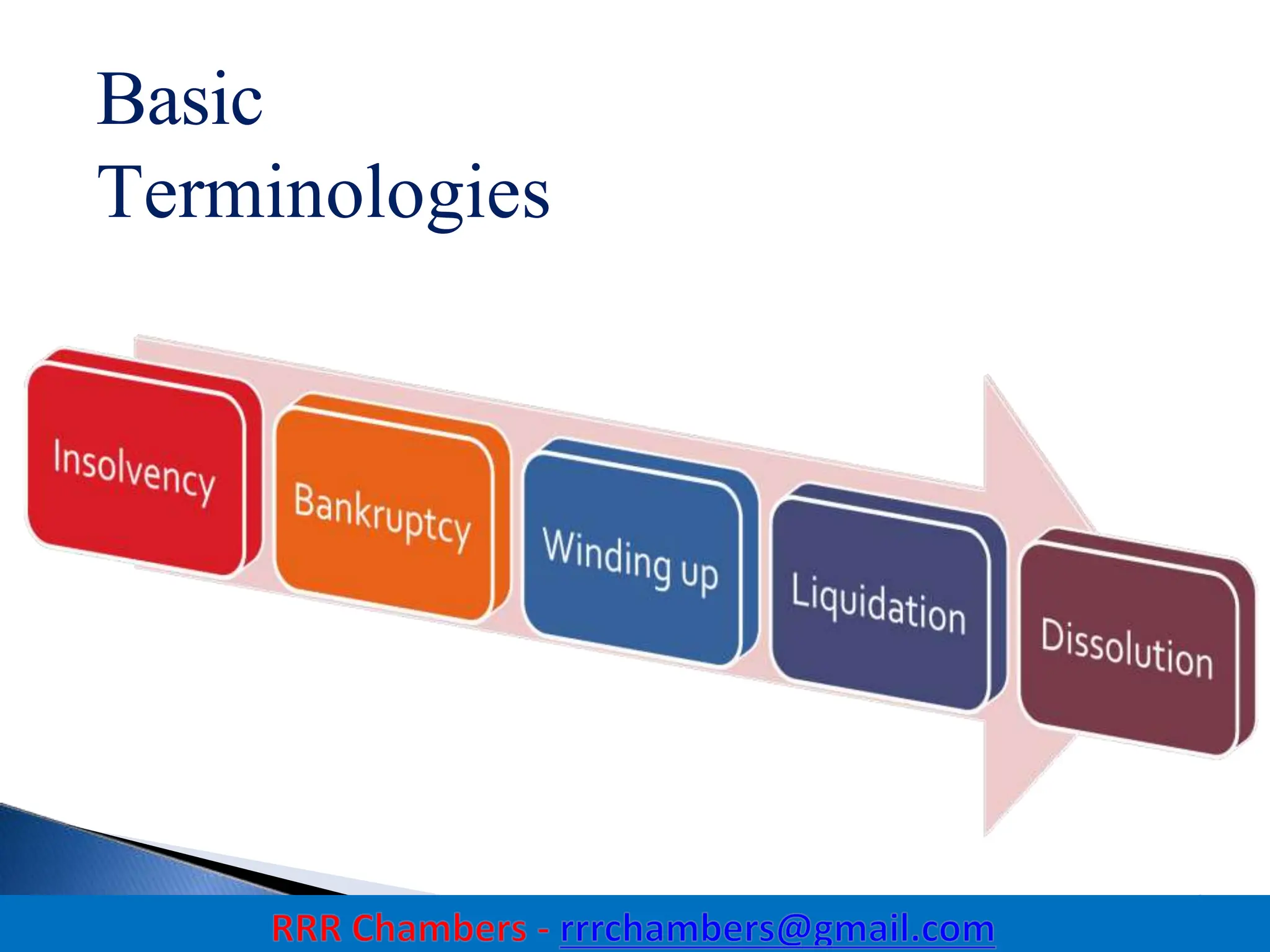
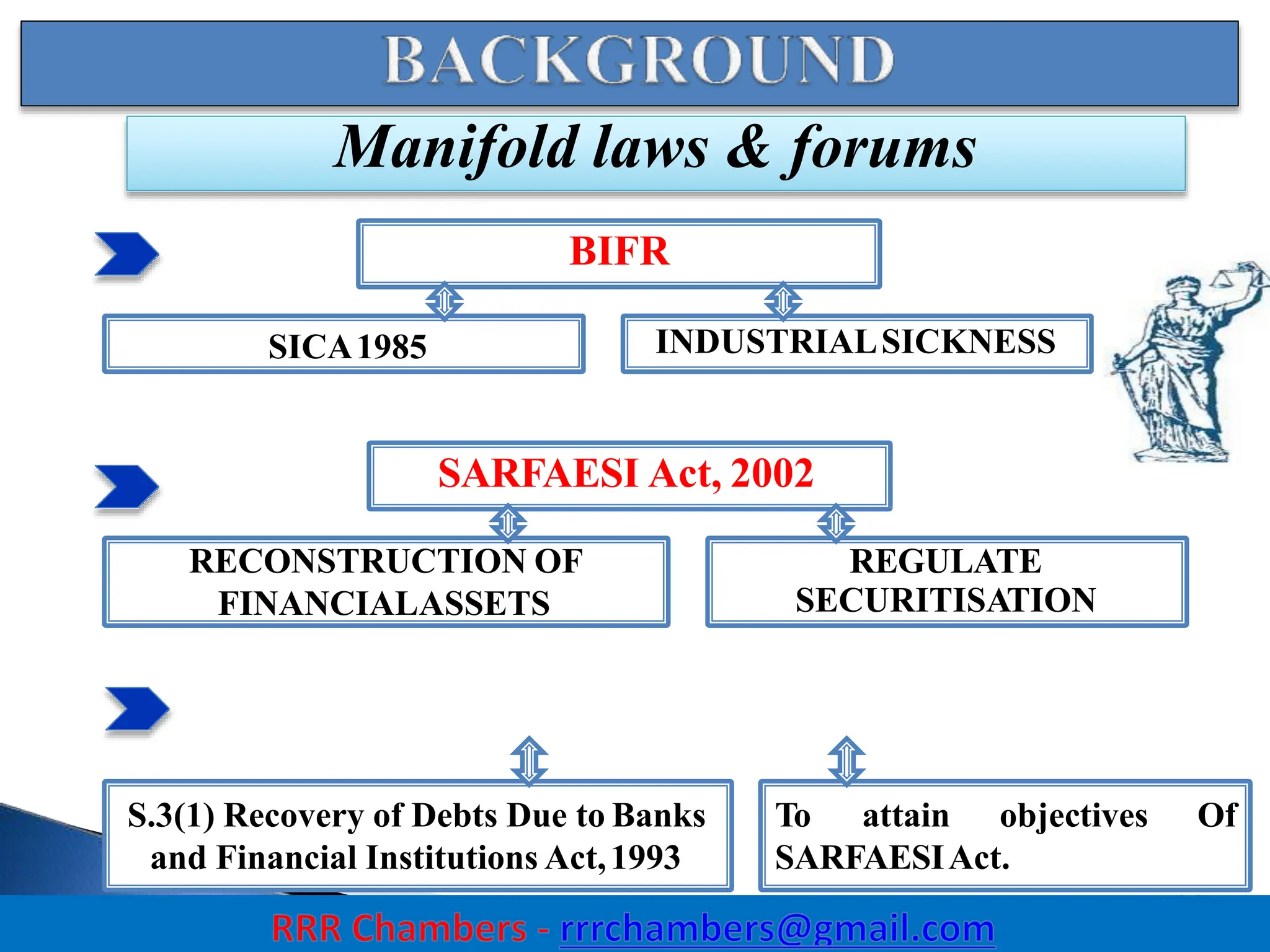
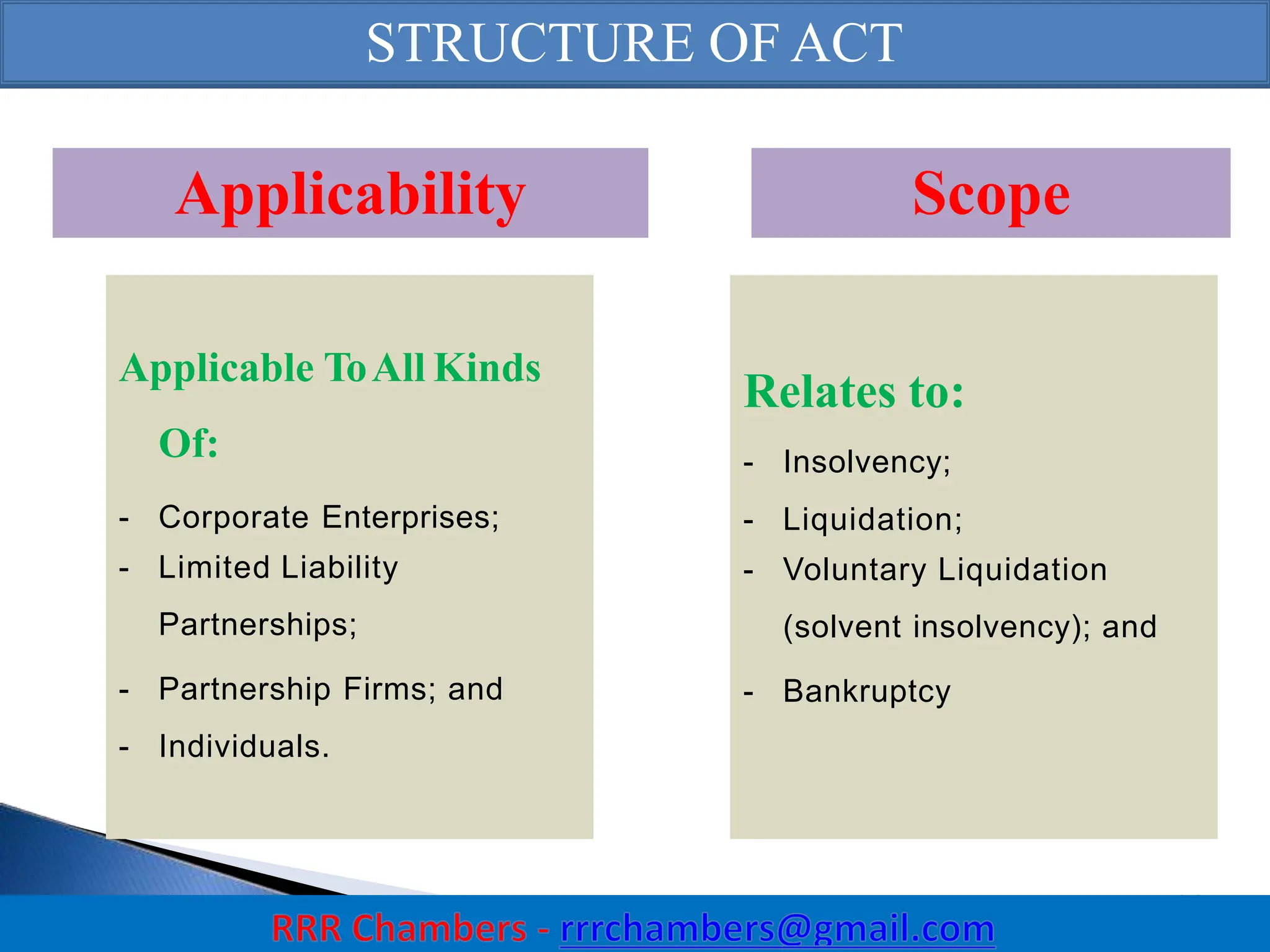
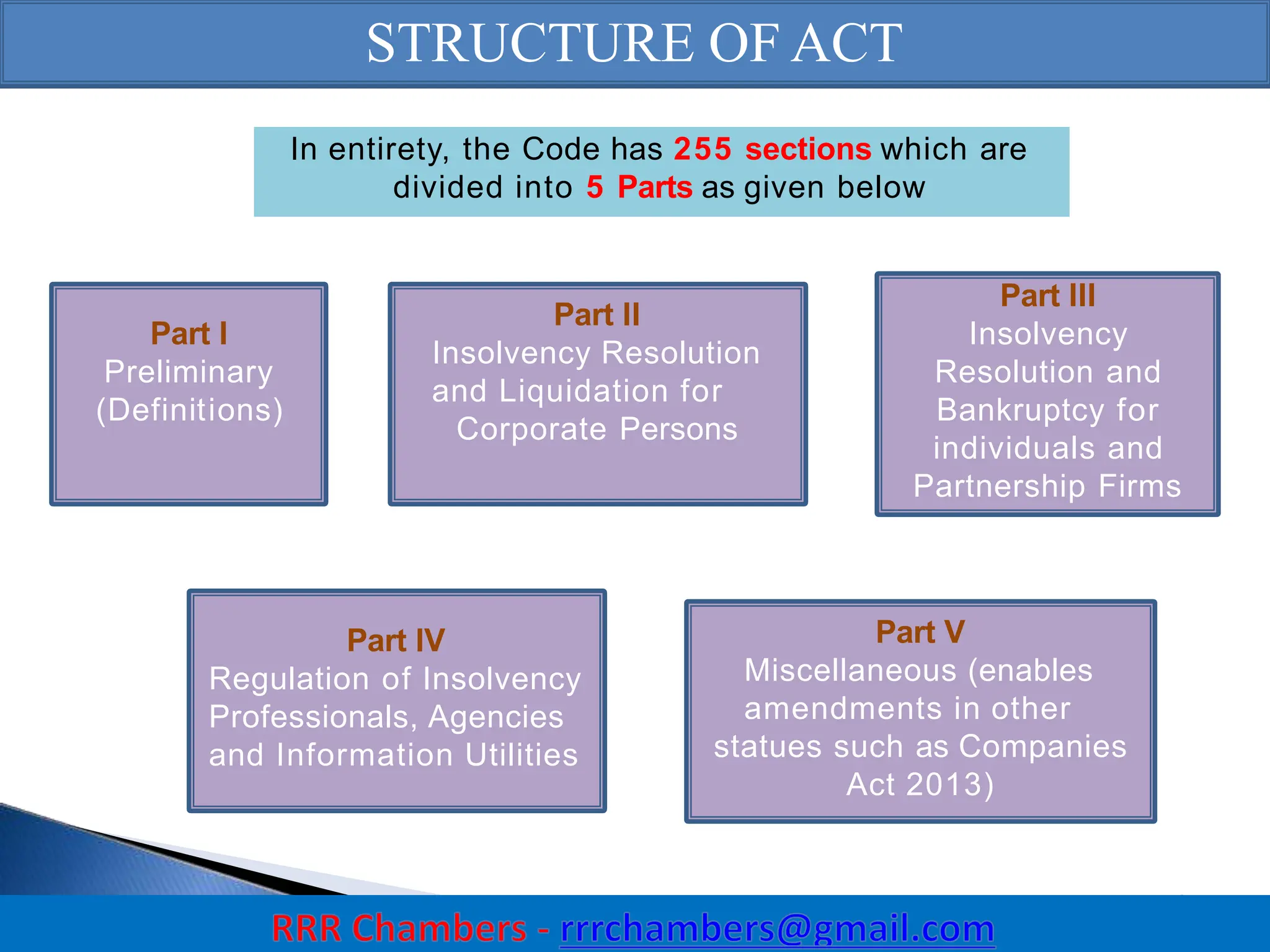
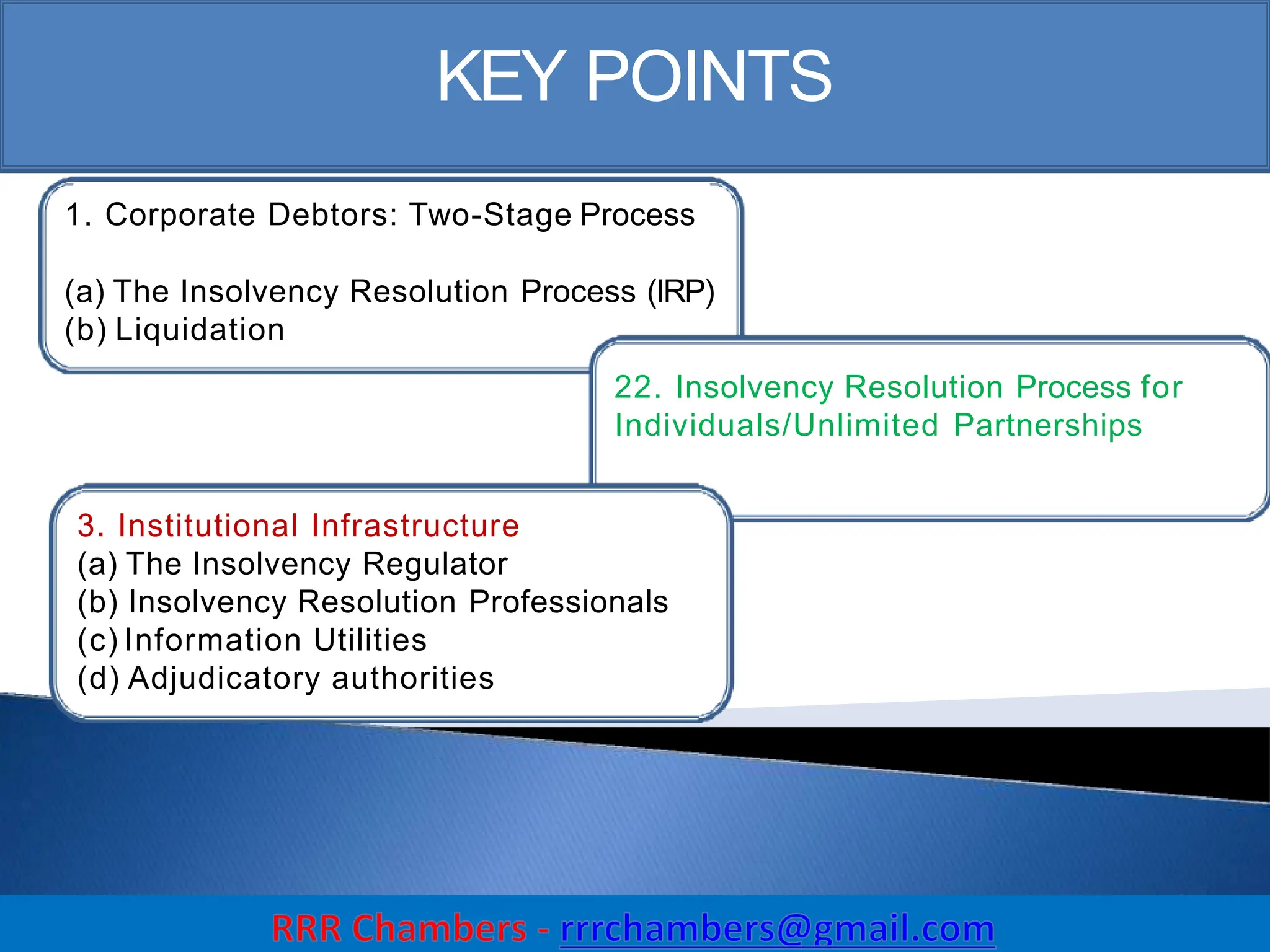
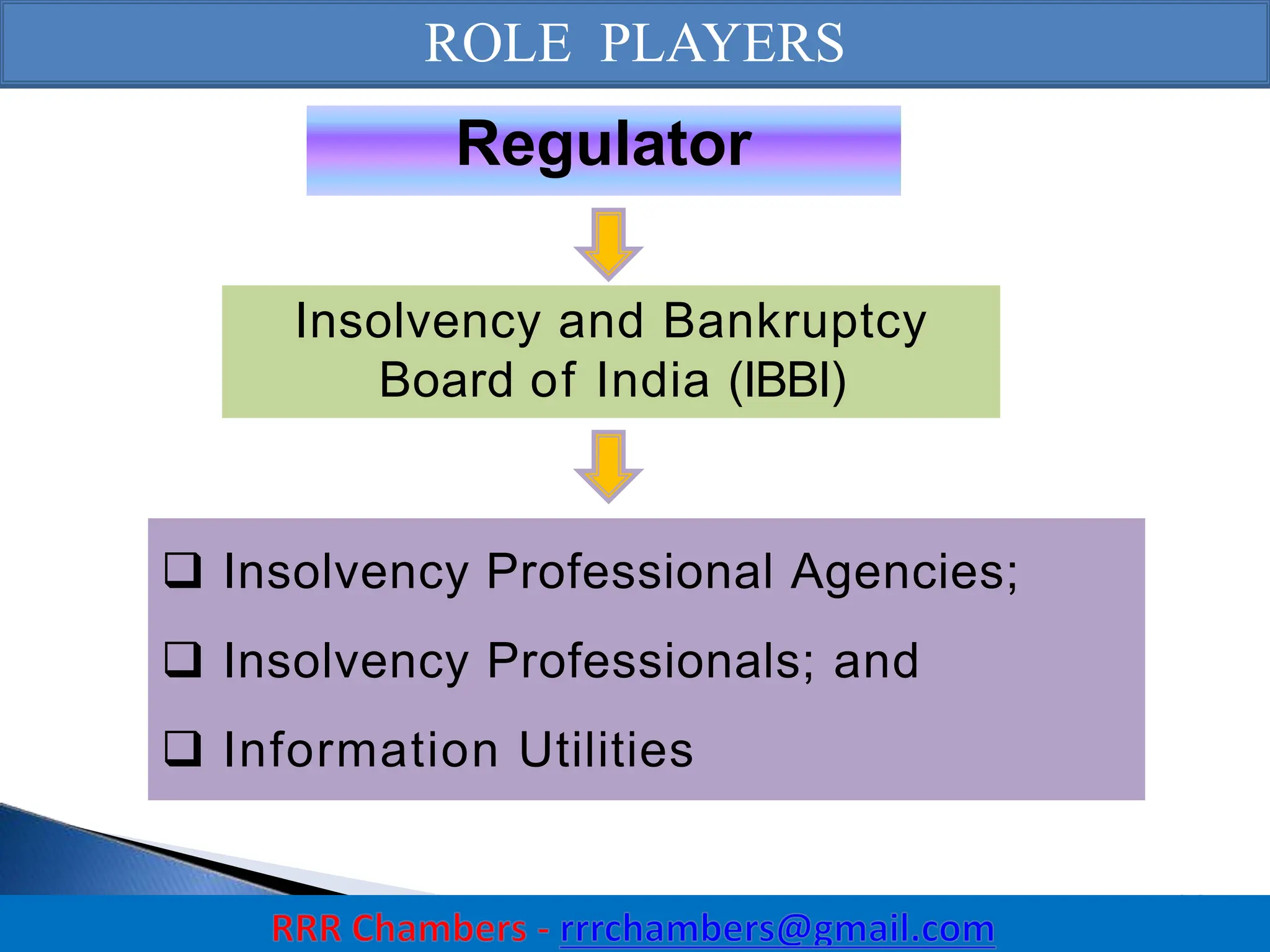
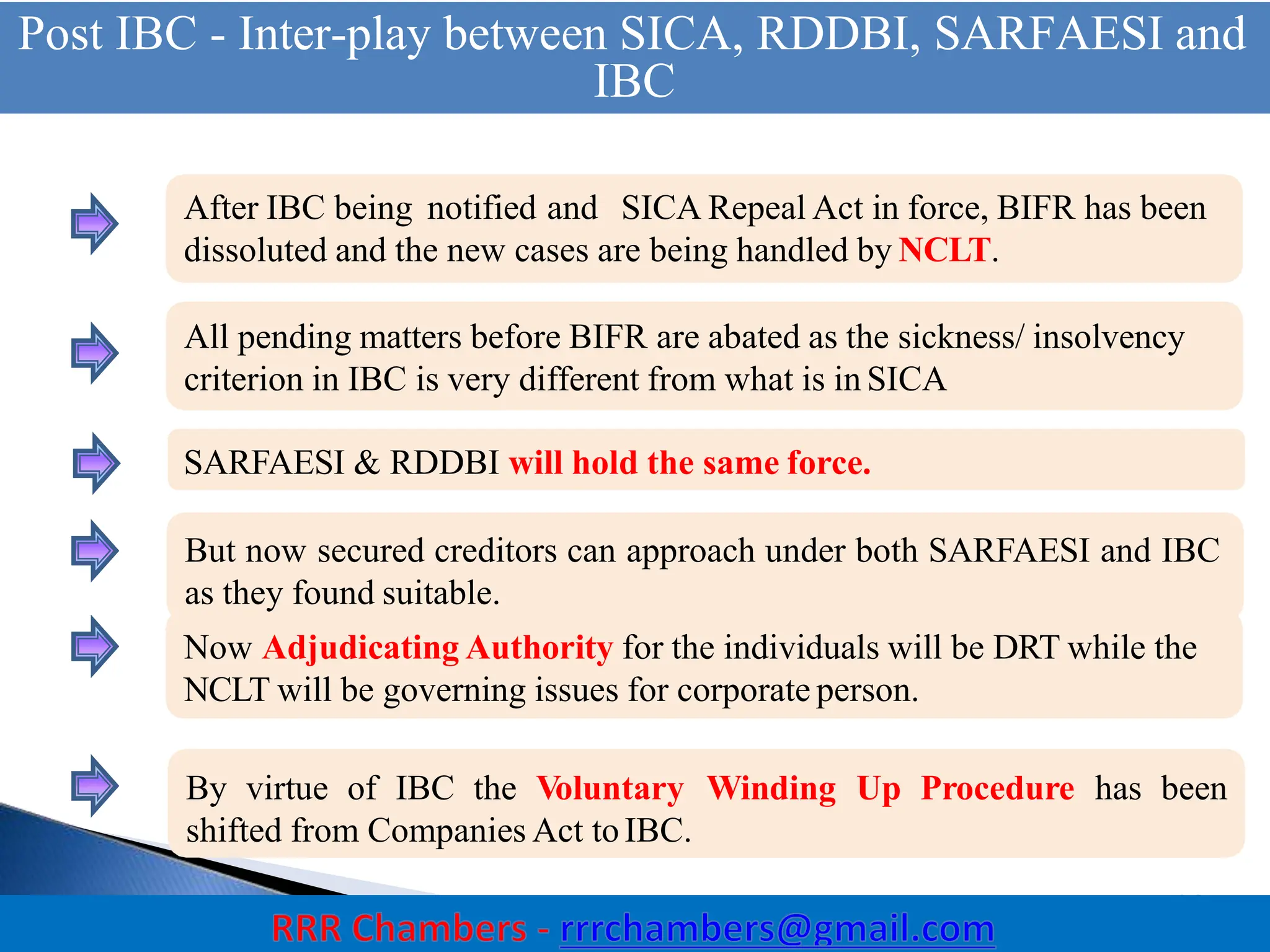
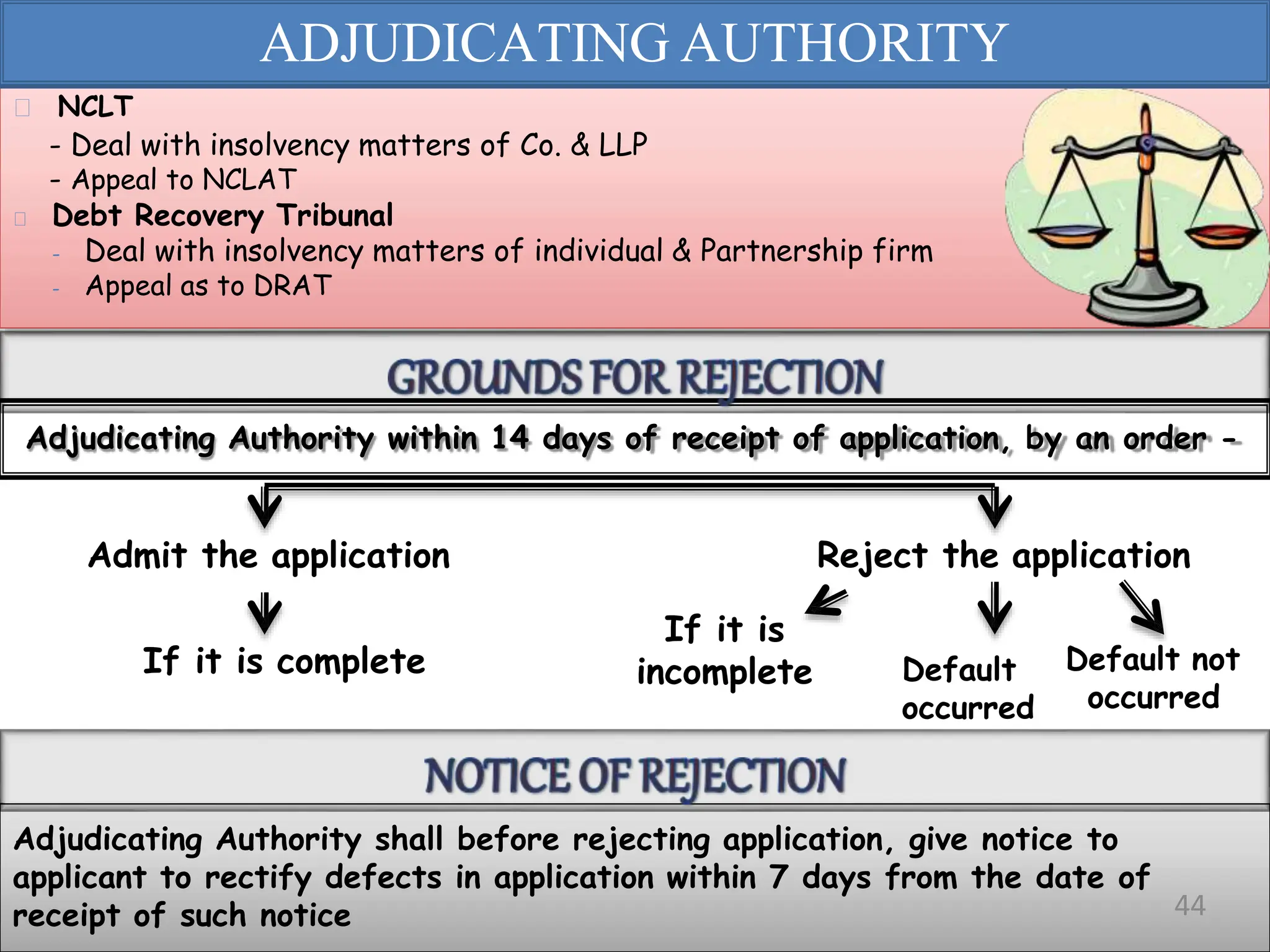
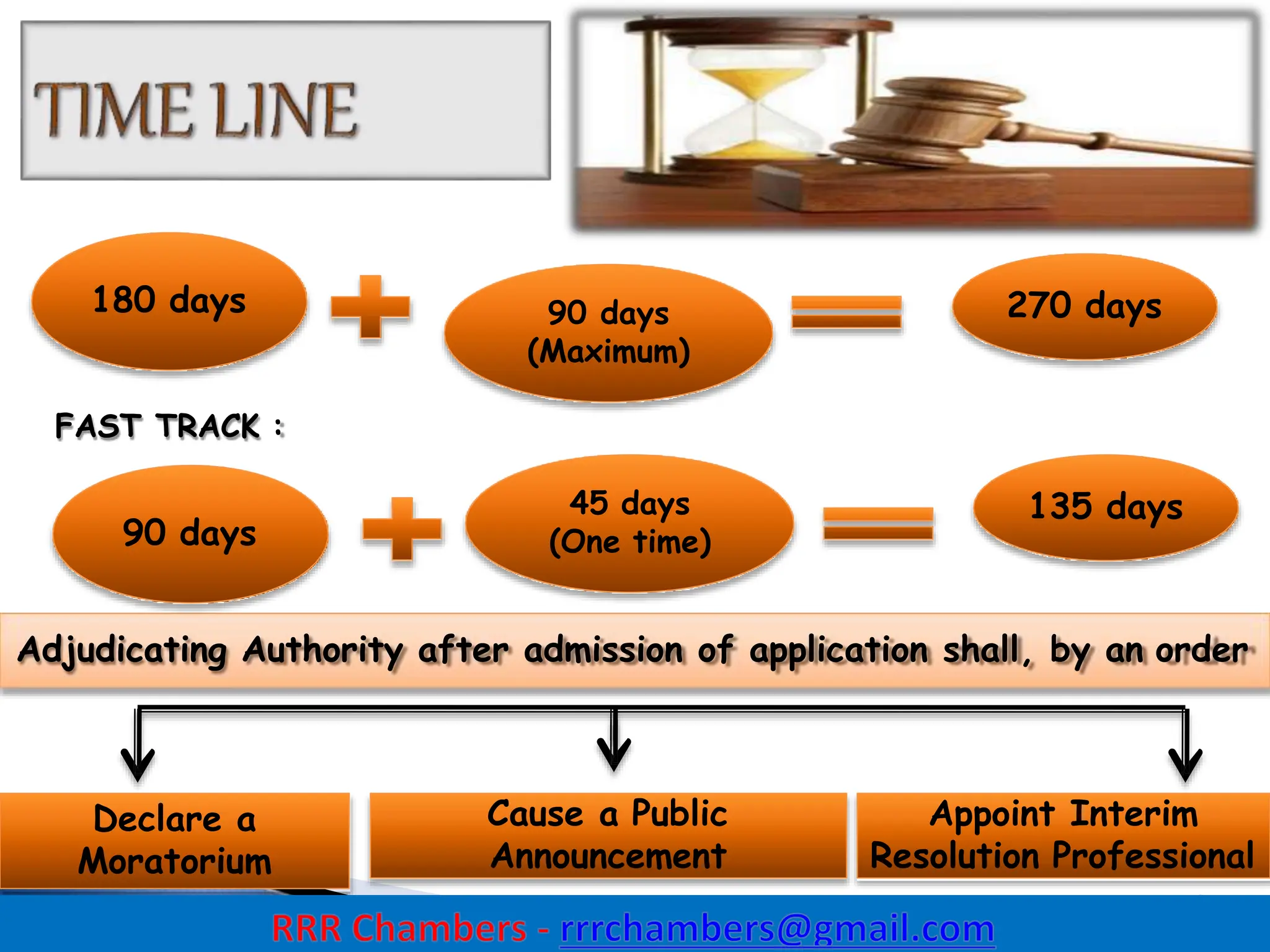
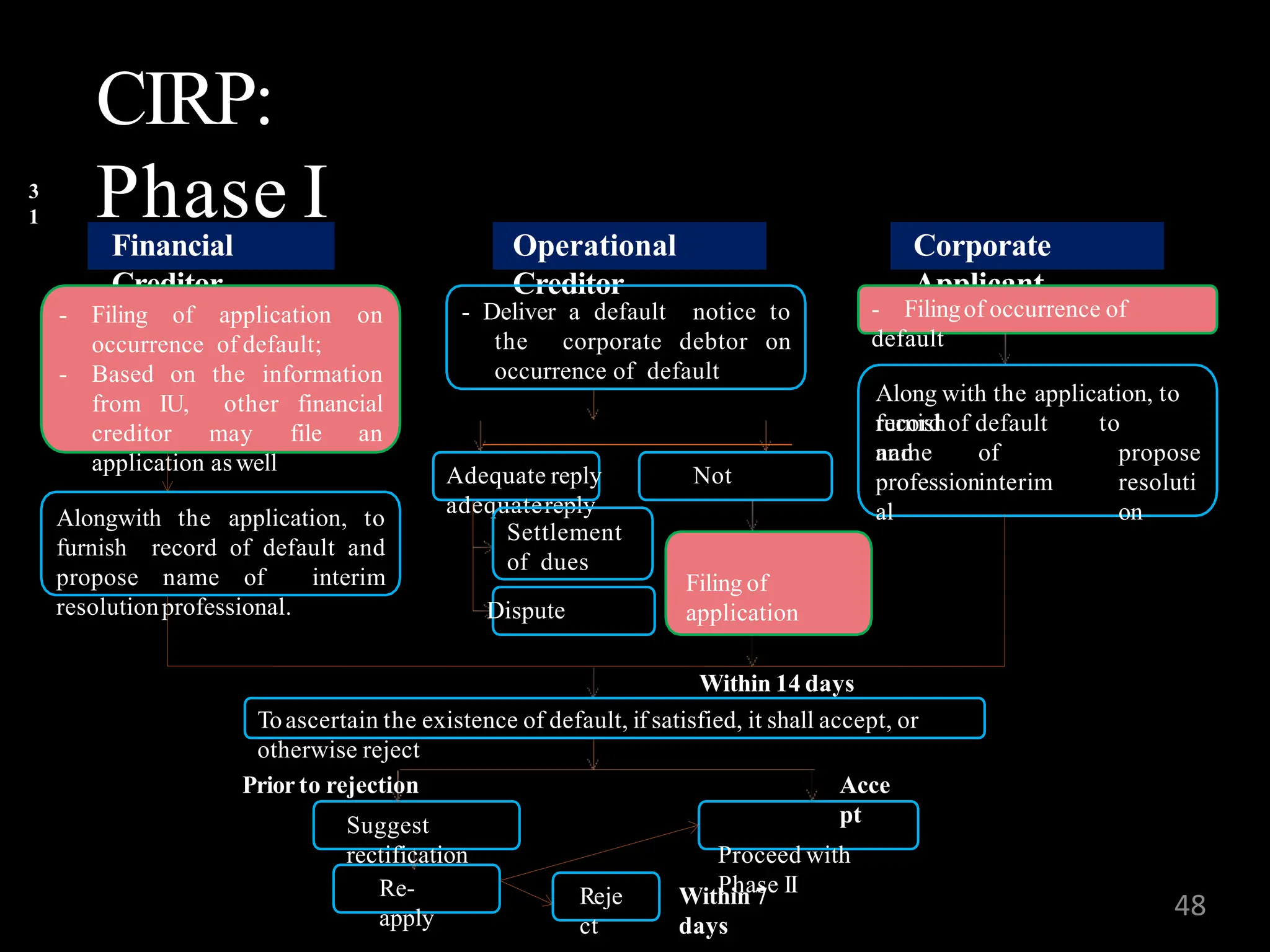
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) of 2016 aims to consolidate existing laws in India related to insolvency and bankruptcy, promoting timely reorganization and resolution of debts for corporate entities, partnerships, and individuals. It introduces a creditor-driven framework and a strict timeline for the insolvency process, with an emphasis on improving India's ease of doing business and maximizing asset value. Key features include a new regulatory structure, roles of various stakeholders, and provisions for resolution and liquidation processes.