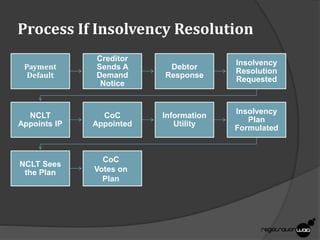
The document outlines the insolvency resolution process in India, emphasizing its quick resolution and creditor payment assurance. The process can be initiated by creditors or corporate debtors under specific conditions, followed by various steps including appointment of an insolvency professional, formation of a creditor committee, and voting on the insolvency plan. Timeframes for the resolution differ based on company size, taking 180 days for large companies and 90 days for small companies, with possible extensions.