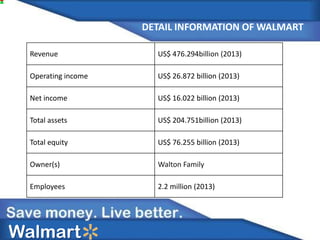
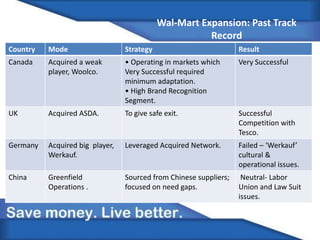
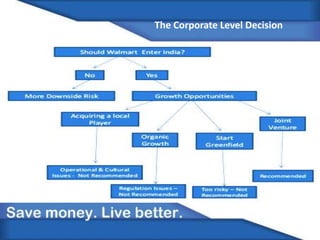
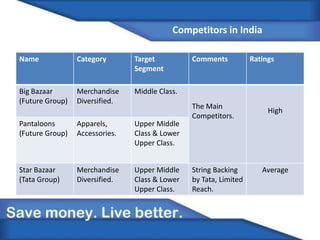
Walmart is expanding into India through a joint venture formed in 2006 with Bharti Enterprises. India represents a major growth opportunity for Walmart due to India's growing middle class and changing consumption patterns leading to rapid retail sector growth. Walmart aims to leverage its low price strategy and supply chain expertise to gain market share in India's retail market from large competitors like Big Bazaar. However, Walmart must also adapt to India's diverse local markets and customer preferences to find success.