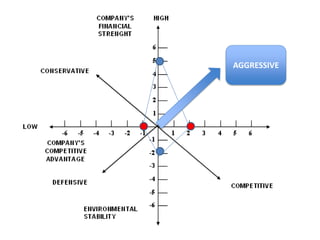
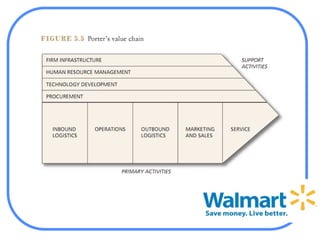
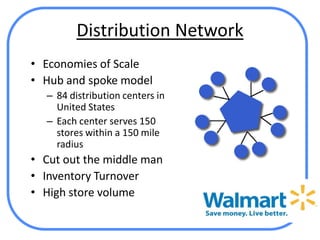
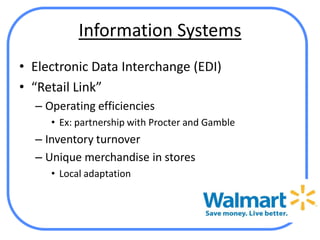
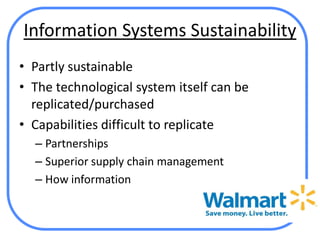
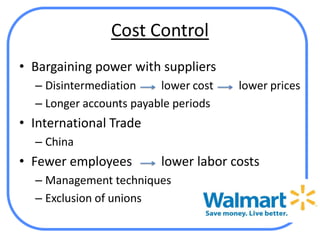
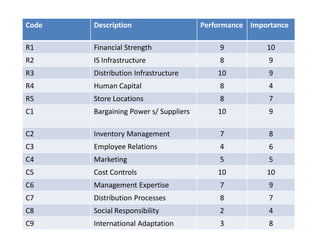
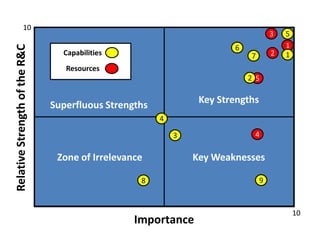
The document analyzes Walmart's strategic management, emphasizing its competitive advantages and sustainability in the retail sector. It highlights Walmart's significant financial figures and examines the impact of industry attractiveness alongside competitive advantages on its performance. Recommendations for sustaining growth include enhancing distribution infrastructure, navigating global markets, and addressing social issues to improve corporate image.

















![References
• Bradley et al. (2003). Walmart Stores in 2003. Harvard Business Review.
• Djeddour, M. (2011). Strategic Management Lecture. [Handout], Strategic
Management Module. Grenoble Graduate School of Business.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/walmartsm-110617053208-phpapp01/85/Wal-Mart-Analysis-Strategic-Management-30-320.jpg)