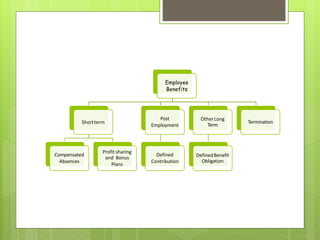
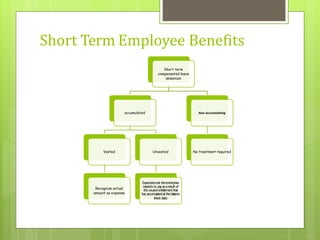
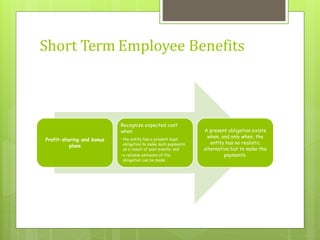
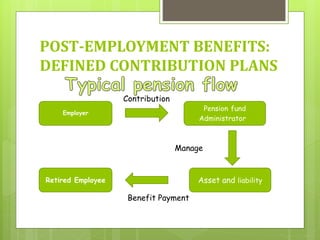
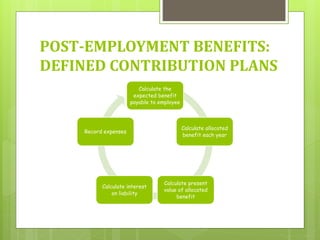
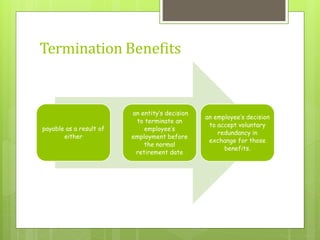
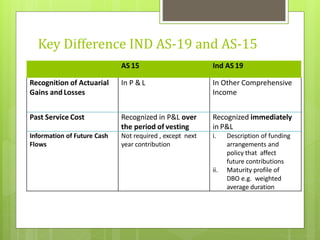
This document discusses the key requirements of Ind AS 19 on employee benefits. It covers the accounting for short-term employee benefits such as compensated absences, profit sharing and bonus plans. For post-employment benefits, it discusses the treatment for defined contribution plans which are expensed as incurred, and defined benefit plans which require actuarial valuation using the projected unit credit method. The document also discusses other long term benefits and termination benefits. Key disclosure requirements under Ind AS 19 are provided.