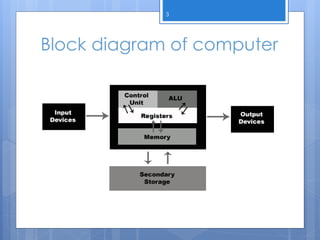
This document discusses the history of computers through their generations of development. It begins by defining a computer and its basic components like the CPU, memory, and input/output devices. It then outlines the four main generations of computers, describing the underlying technologies used and examples for each generation from vacuum tubes to integrated circuits to microprocessors. The generations progressed from machine-dependent to machine-independent languages and from bulky to more compact sizes. It concludes by mentioning a potential 5th generation involving artificial intelligence and parallel processing.