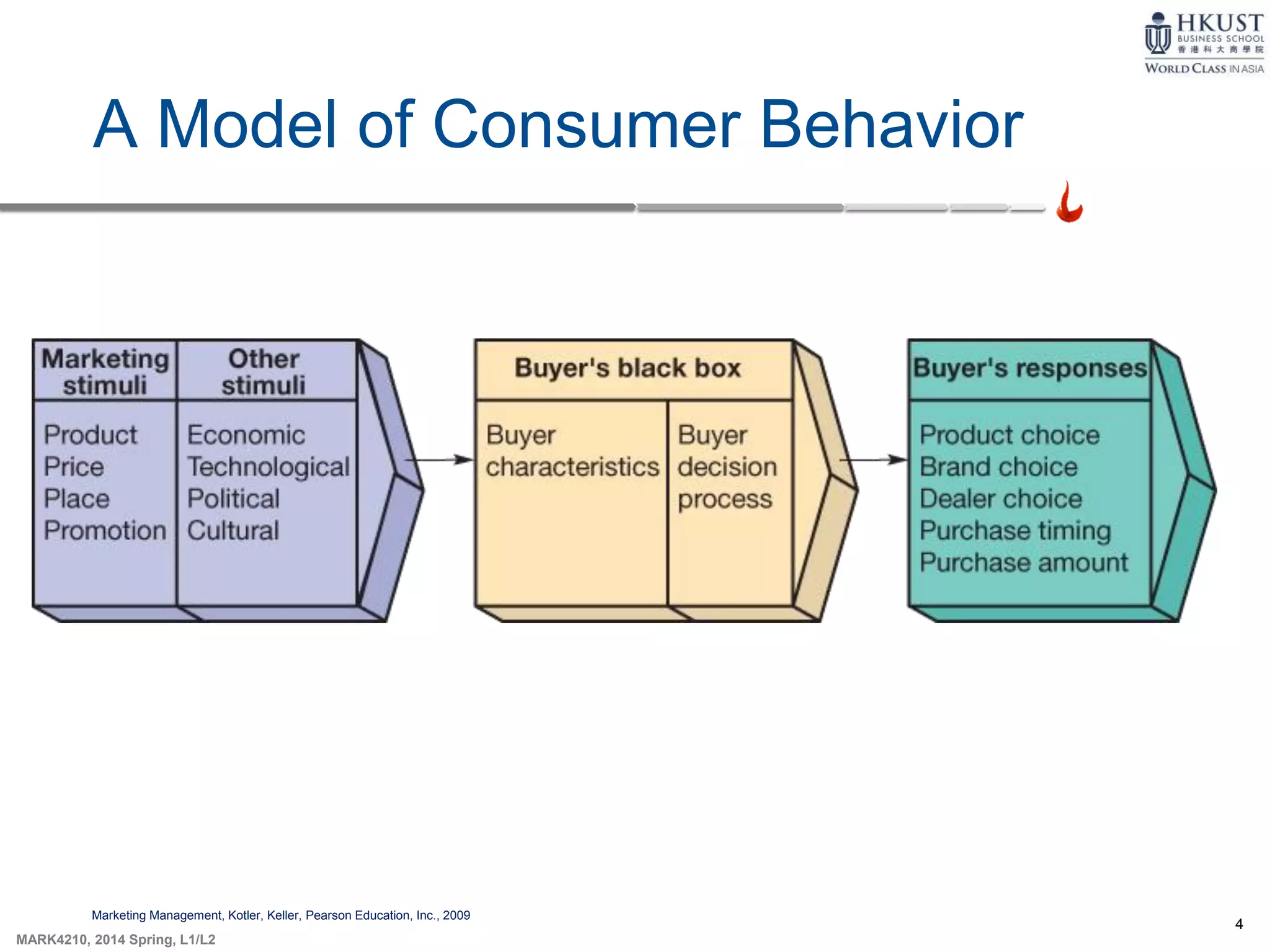
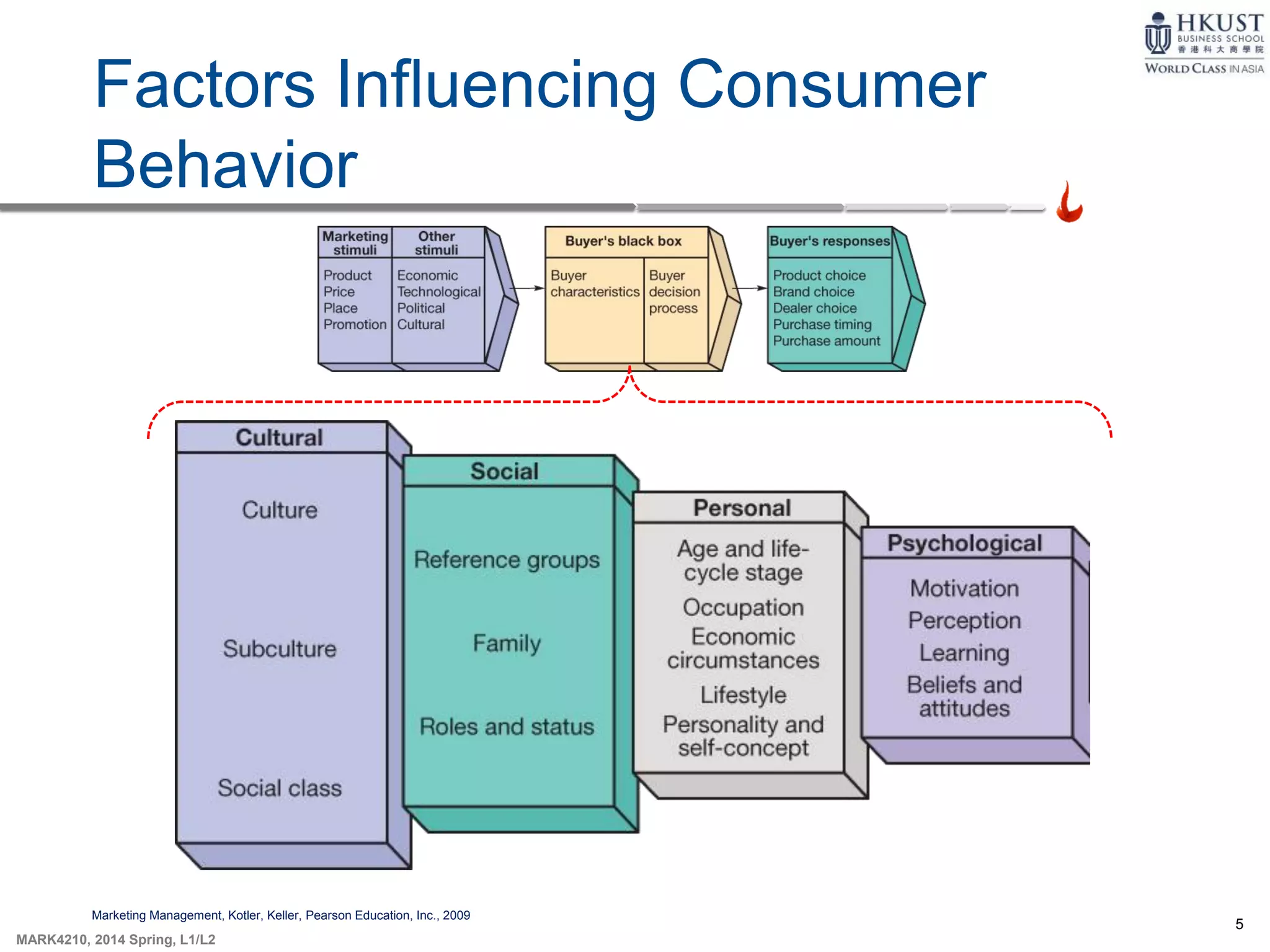
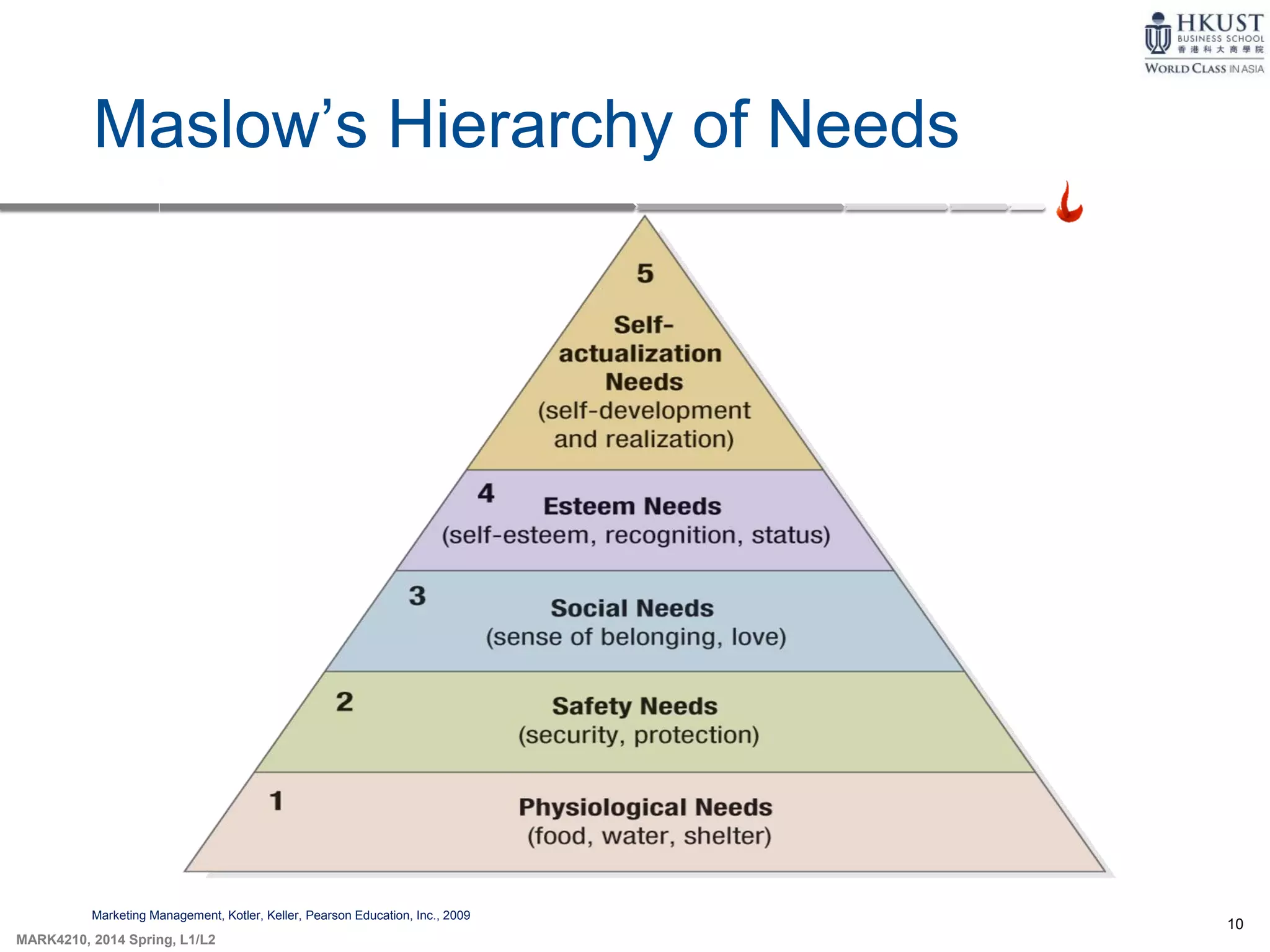
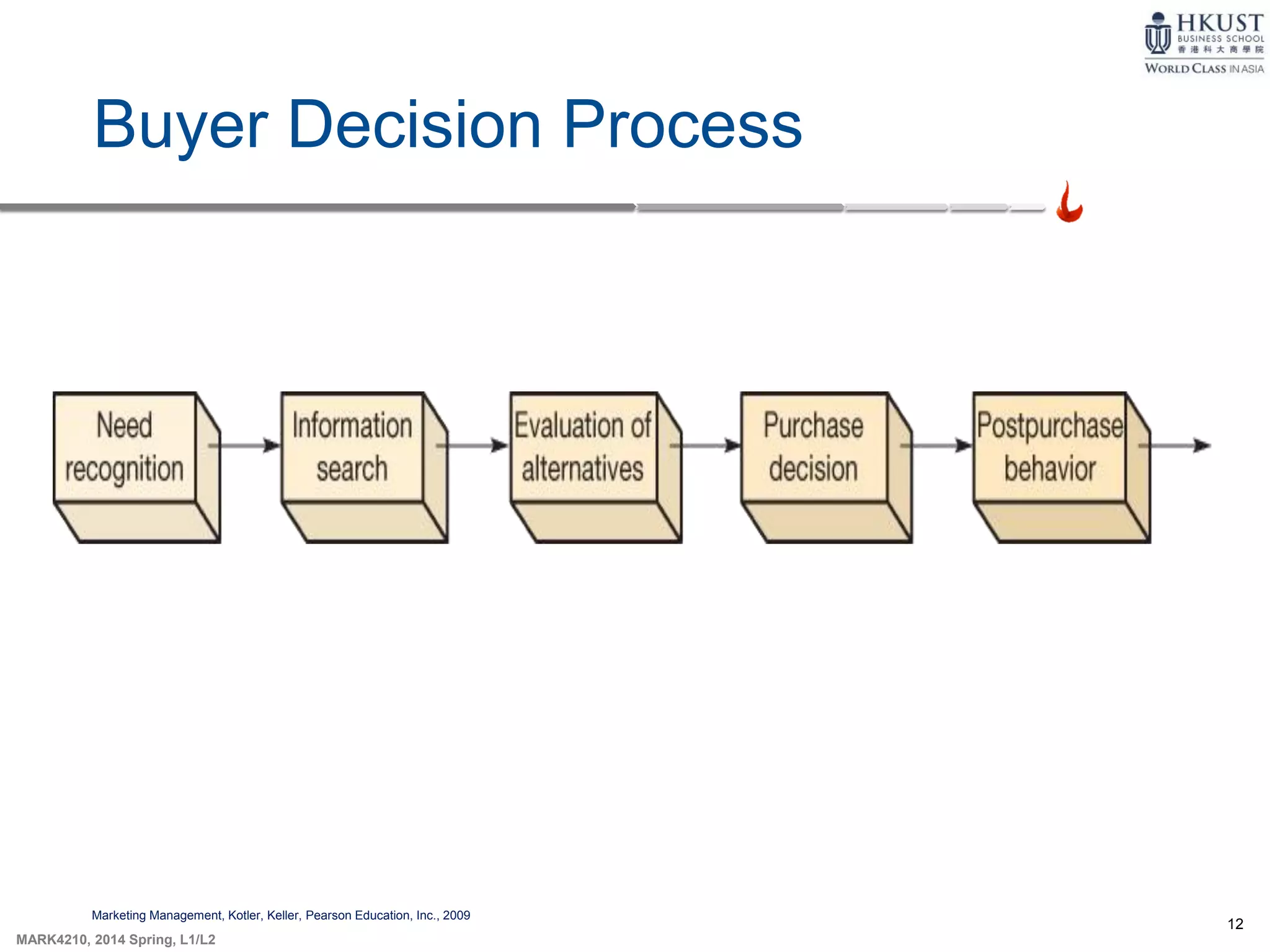
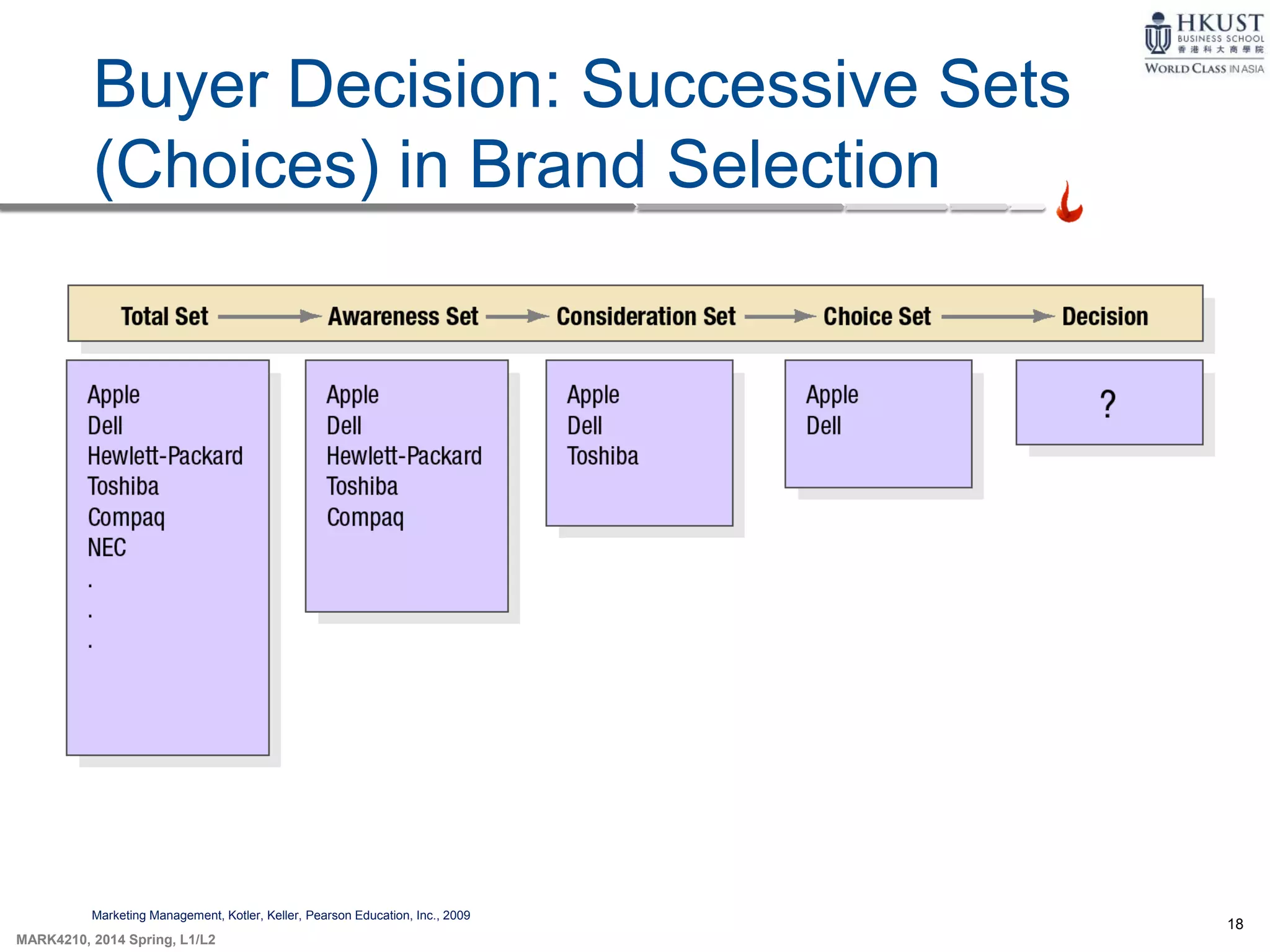
This document outlines key concepts about consumer behavior from marketing textbooks. It discusses factors that influence consumer behavior such as cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. A model of consumer behavior is presented involving need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Maslow's hierarchy of needs and theories of motivation from Freud and Herzberg are also summarized. The document provides an overview of the consumer decision process.
![MARK4210, 2014 Spring, L1/L2
MARK4210: Strategic Marketing
2014 Spring, Section L1/L2
[Class #24]
Consumer Behavior](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iclass24-consumerbehaviorv20140507finalposting-140605023609-phpapp02/75/consumer-behavior-4210-1-2048.jpg)