Embed presentation
Download to read offline



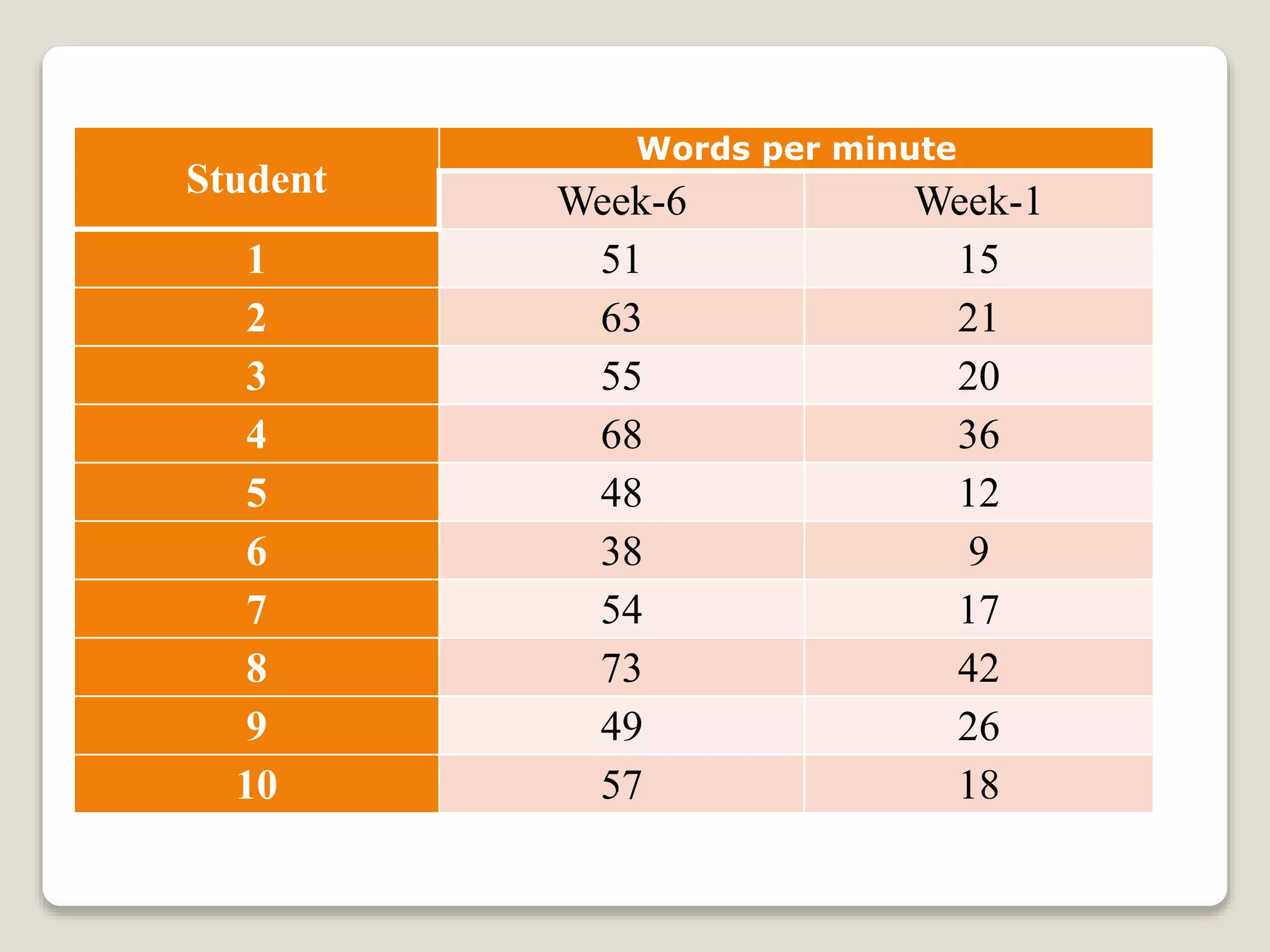
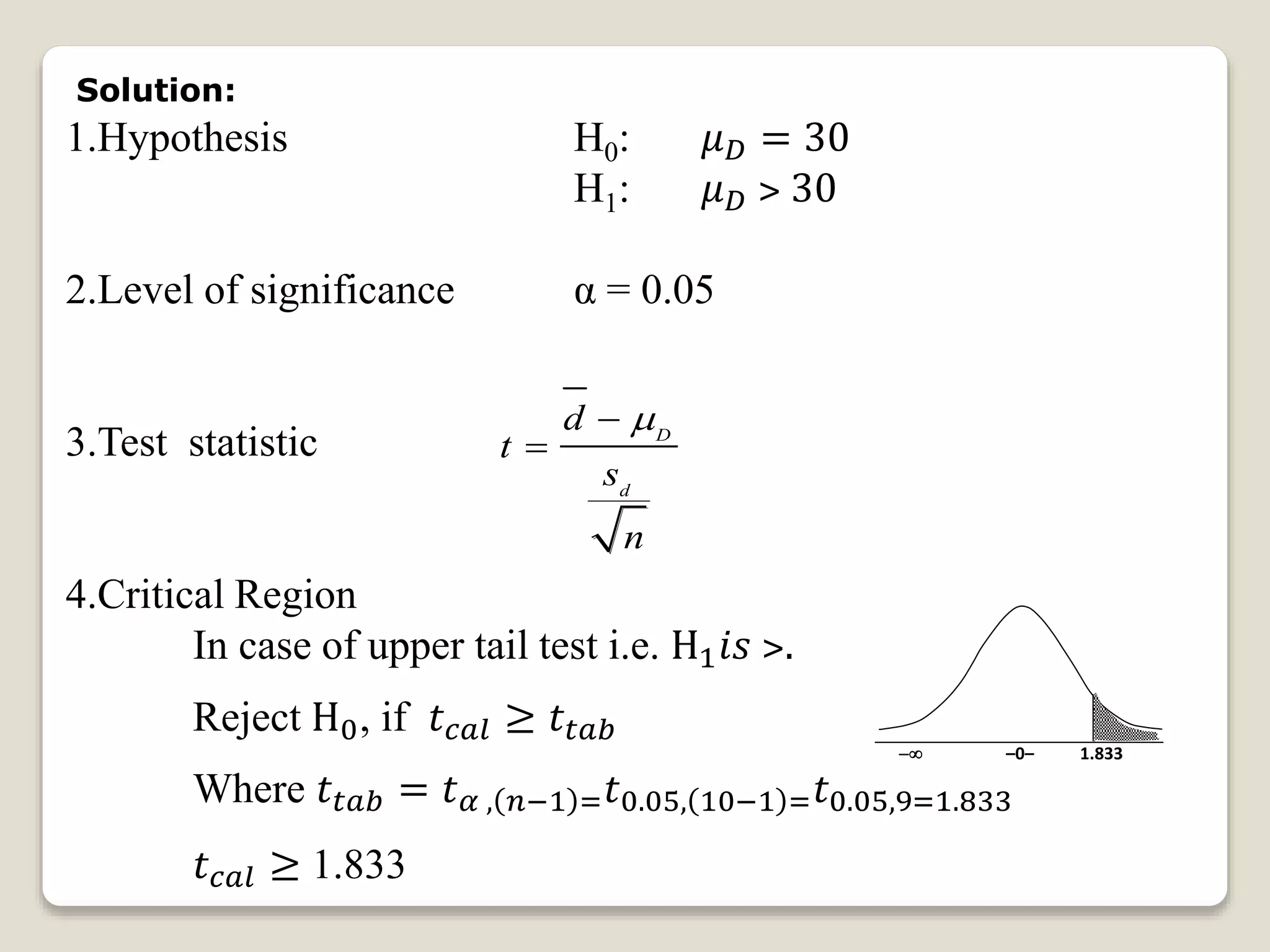
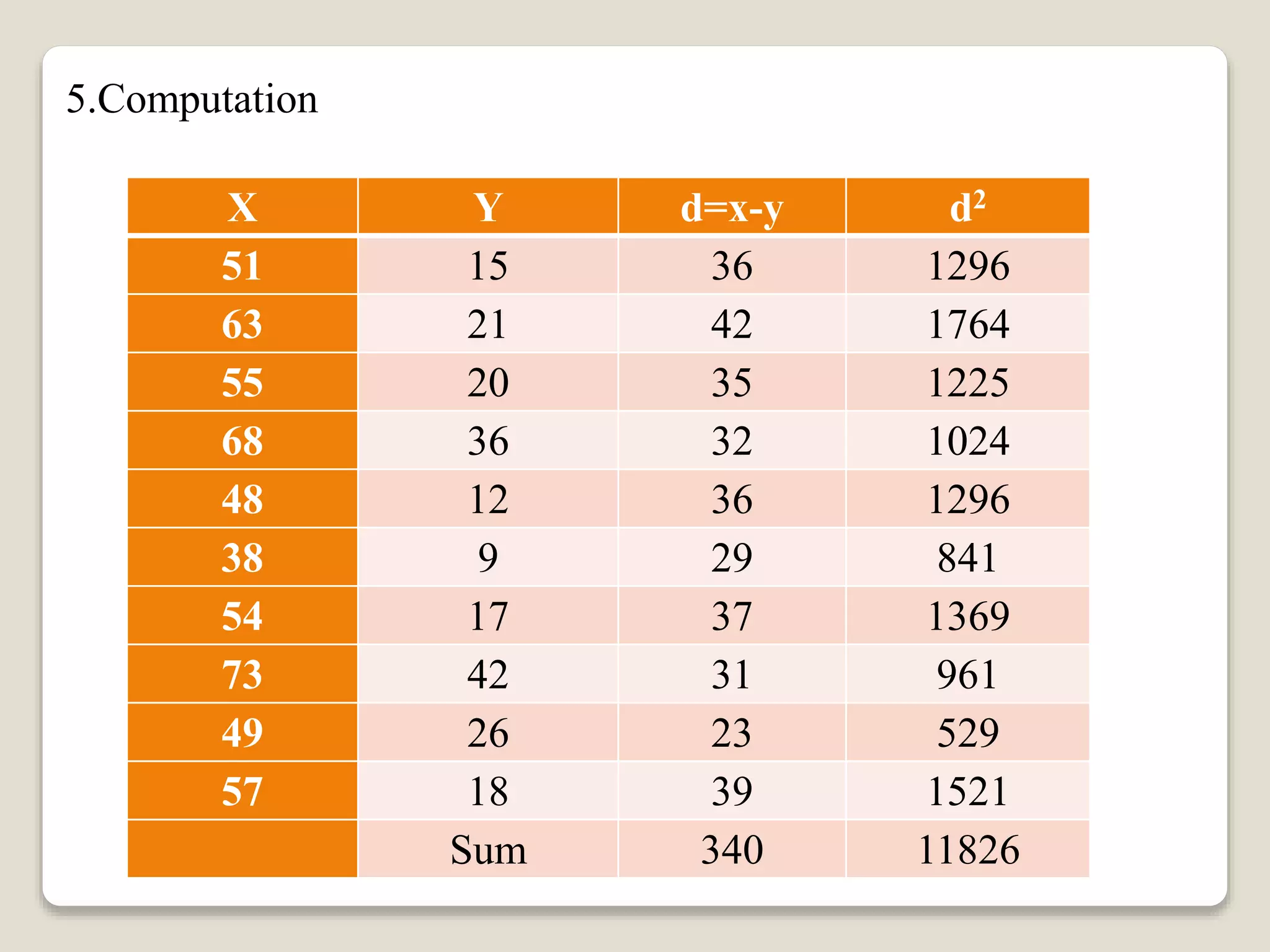
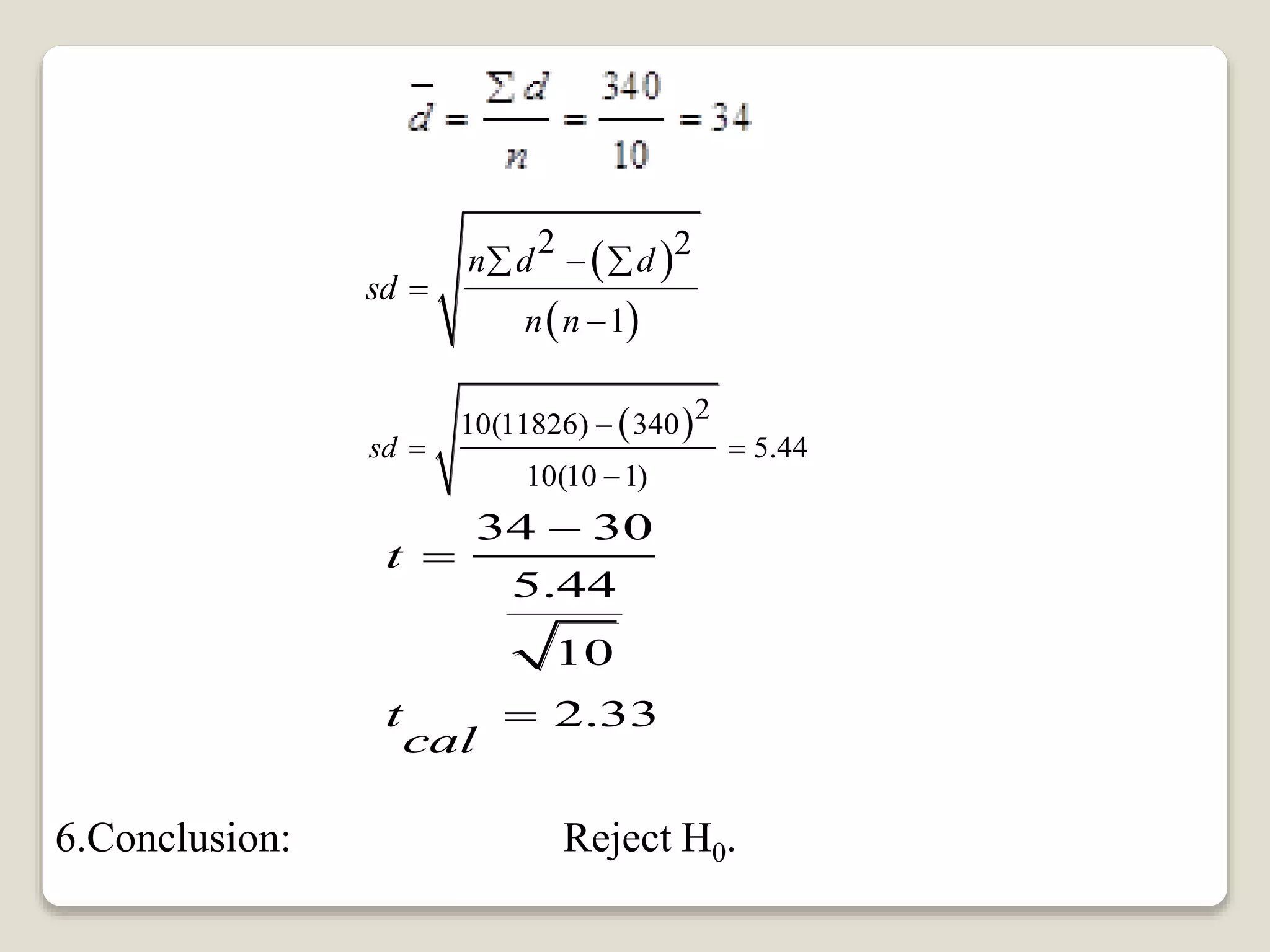

This document discusses paired t-tests and provides an example problem. It introduces paired t-tests as a statistical test used to compare the means of two related groups or measurements on the same item to determine if there is a significant difference. The example problem tests the hypothesis that students' average typing speed increased by over 30 words per minute after completing a typing course, using a paired t-test with a sample of 10 students' pre-and post-course typing speeds. The calculated t value is compared to the critical value to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.






