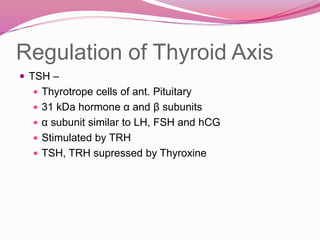
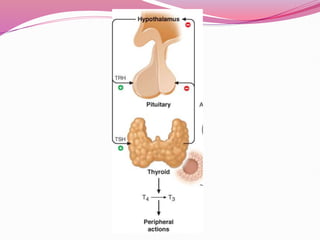
The document discusses the thyroid gland and thyroid disorders. It provides details on:
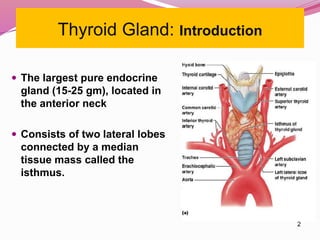
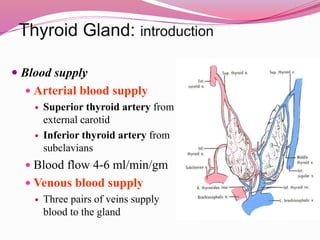
- The anatomy and blood supply of the thyroid gland.
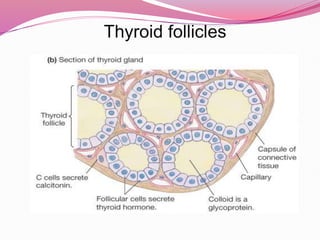
- Thyroid follicles which are the functional units that secrete thyroid hormones like T4 and T3.
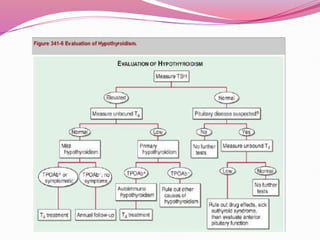
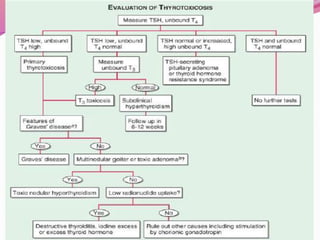
- The two main thyroid disorders - hypothyroidism which is an underactive thyroid, and hyperthyroidism which is an overactive thyroid.
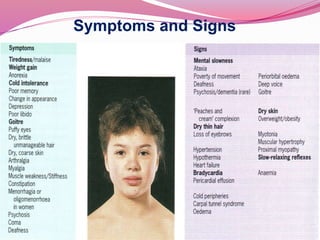
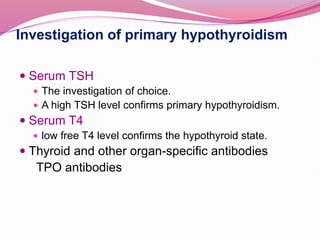
- The most common causes of hypothyroidism including Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and the signs, symptoms, and treatment which involves thyroid hormone replacement.
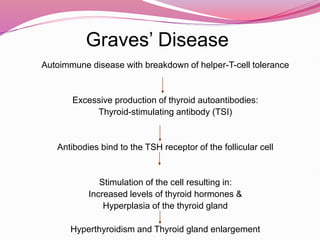
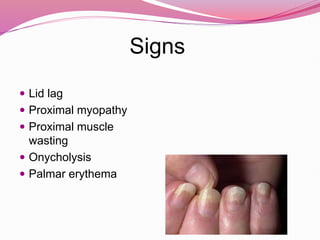
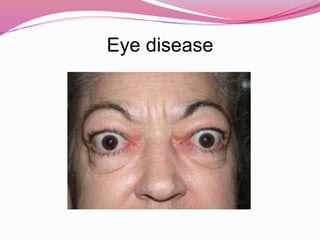
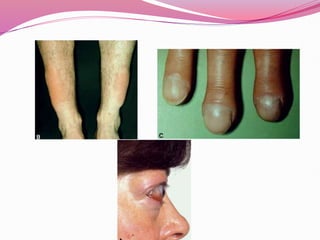
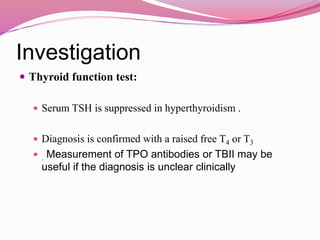
- Graves' disease as the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, along with its autoimmune pathogenesis and associated signs and