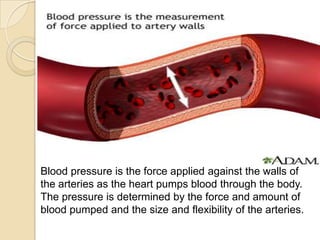
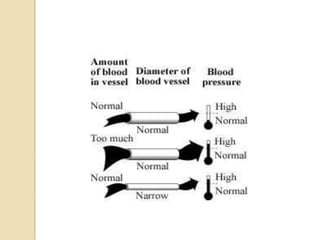
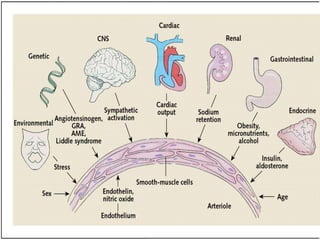
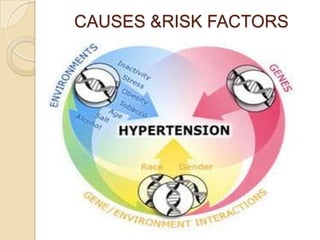
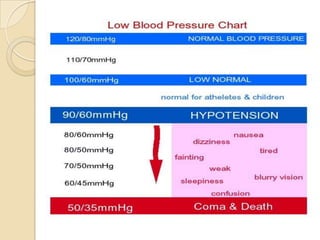
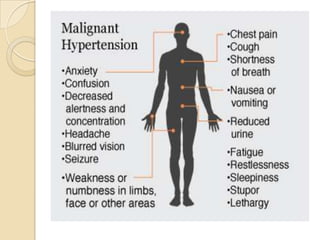
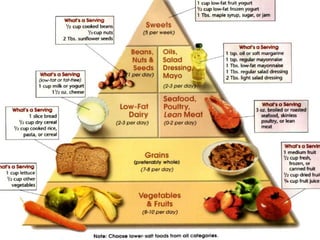
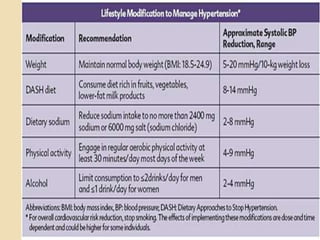
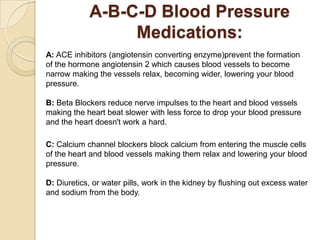
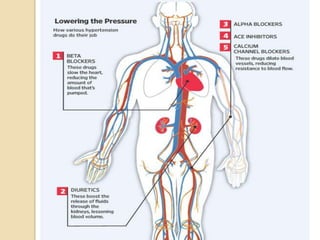
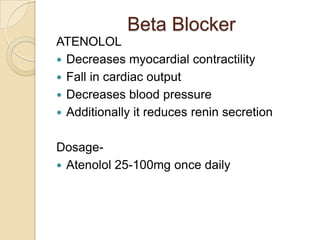
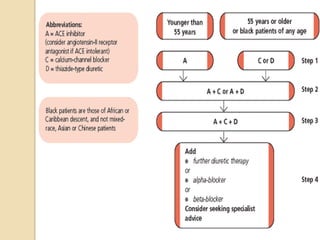
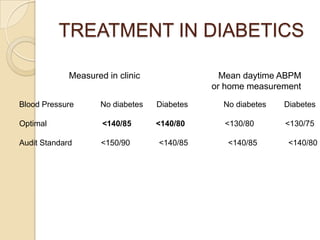
This document discusses hypertension (high blood pressure) including its definition, causes, risk factors, types, symptoms, investigations, management, medications, treatment for diabetics, and follow up. Hypertension is defined as blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg and is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. It has no symptoms in most cases, making it difficult for patients to accept the diagnosis. Lifestyle modifications and medications are used to treat it. Common medication classes include ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. Strict control of blood pressure is important, especially for diabetics, to prevent complications.