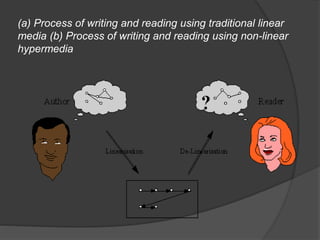
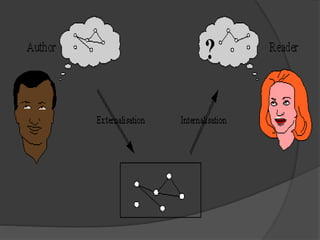
This document discusses hypermedia, which is a nonlinear medium of information that includes graphics, audio, video, text, and hyperlinks. It allows for associative relationships between information and facilitates access to and manipulation of encapsulated data. The World Wide Web is a classic example of hypermedia, while a non-interactive cinema presentation is an example of standard multimedia. Hypermedia development tools include programming languages and multimedia software. Hypermedia is related to how human memory works through associations, and it has applications in education and language learning by offering more control over instructional environments. However, current hypermedia applications have limitations in effectively locating information and understanding user context.