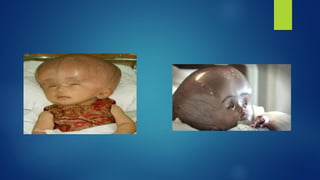
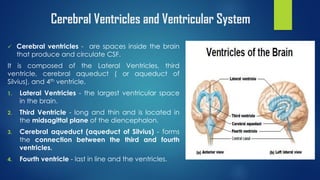
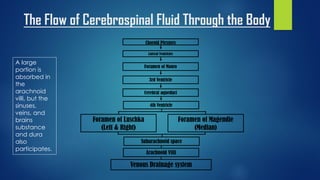
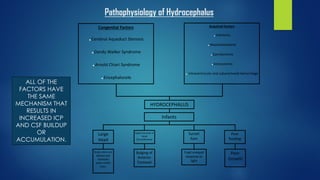
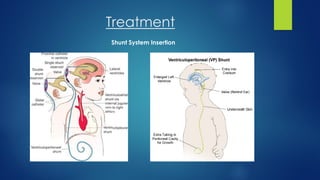
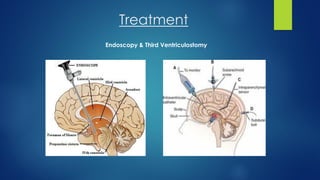
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain ventricles. This buildup of CSF increases intracranial pressure and causes the ventricles to dilate, potentially damaging the brain. Hydrocephalus can be congenital due to genetic factors or acquired later in life due to infections, tumors, or hemorrhages that obstruct CSF flow. Common signs include an abnormally enlarging head size, bulging fontanel, downward eye deviations, and poor feeding in infants. Left untreated, hydrocephalus can cause brain damage or death.