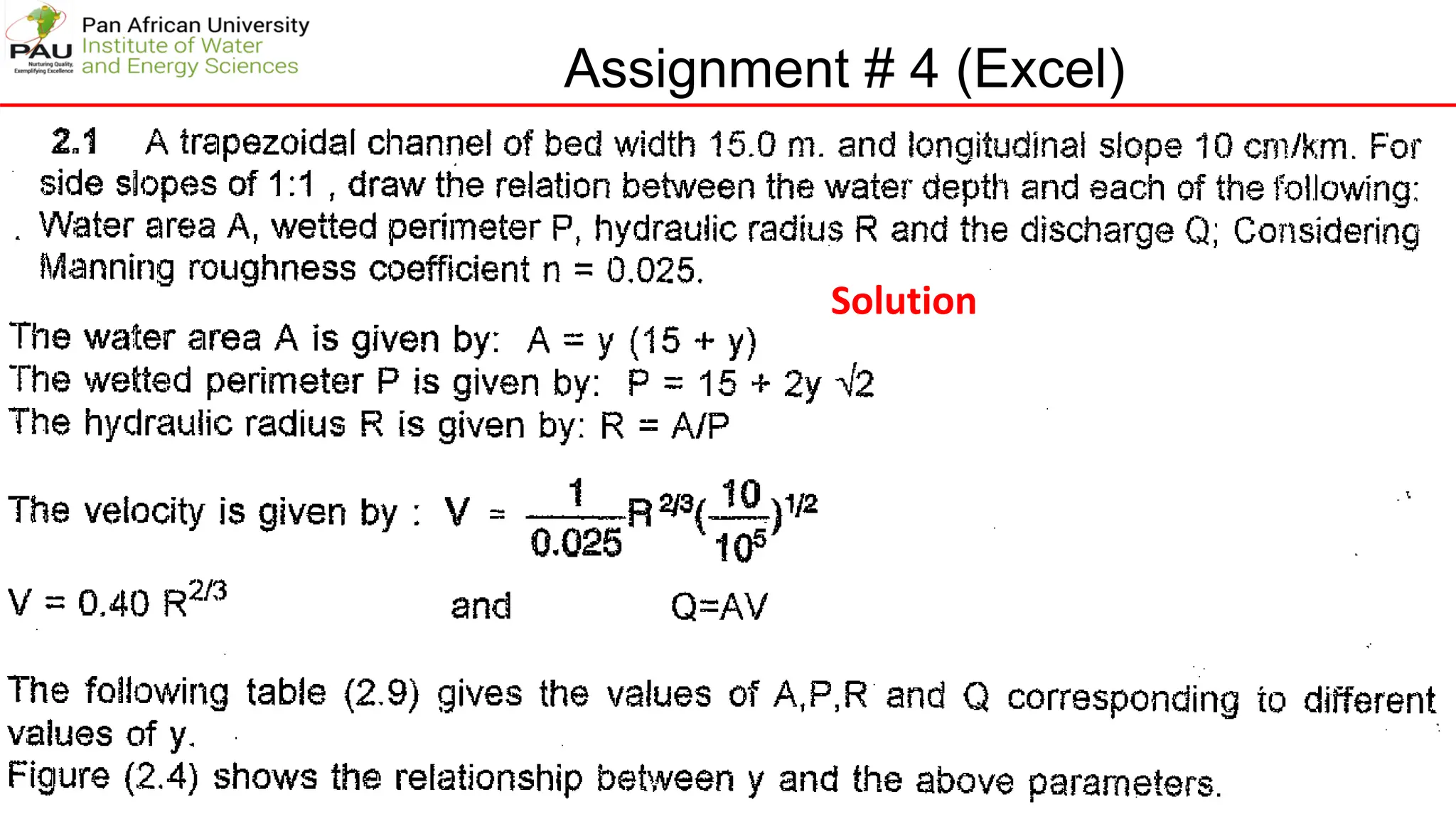
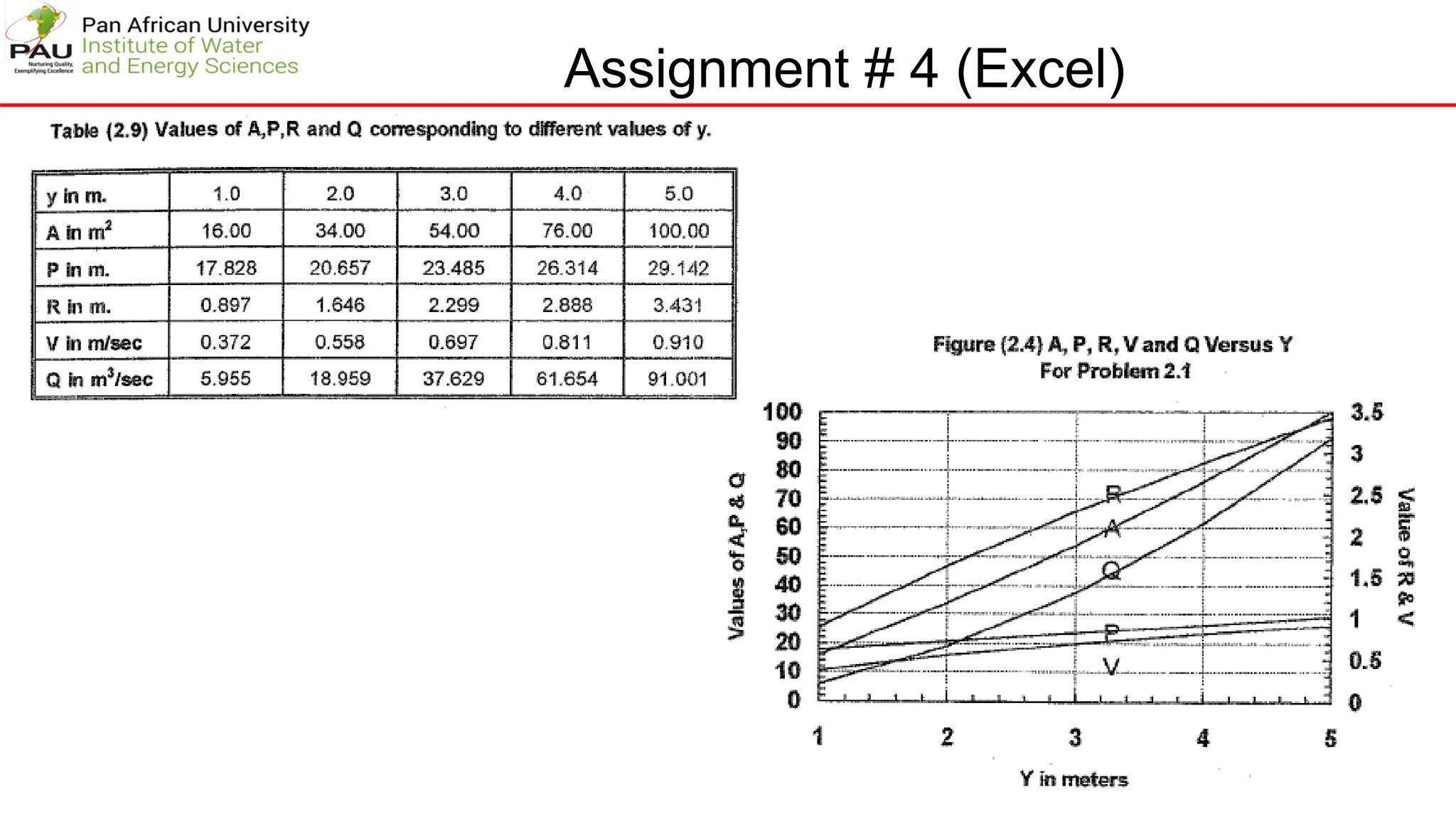
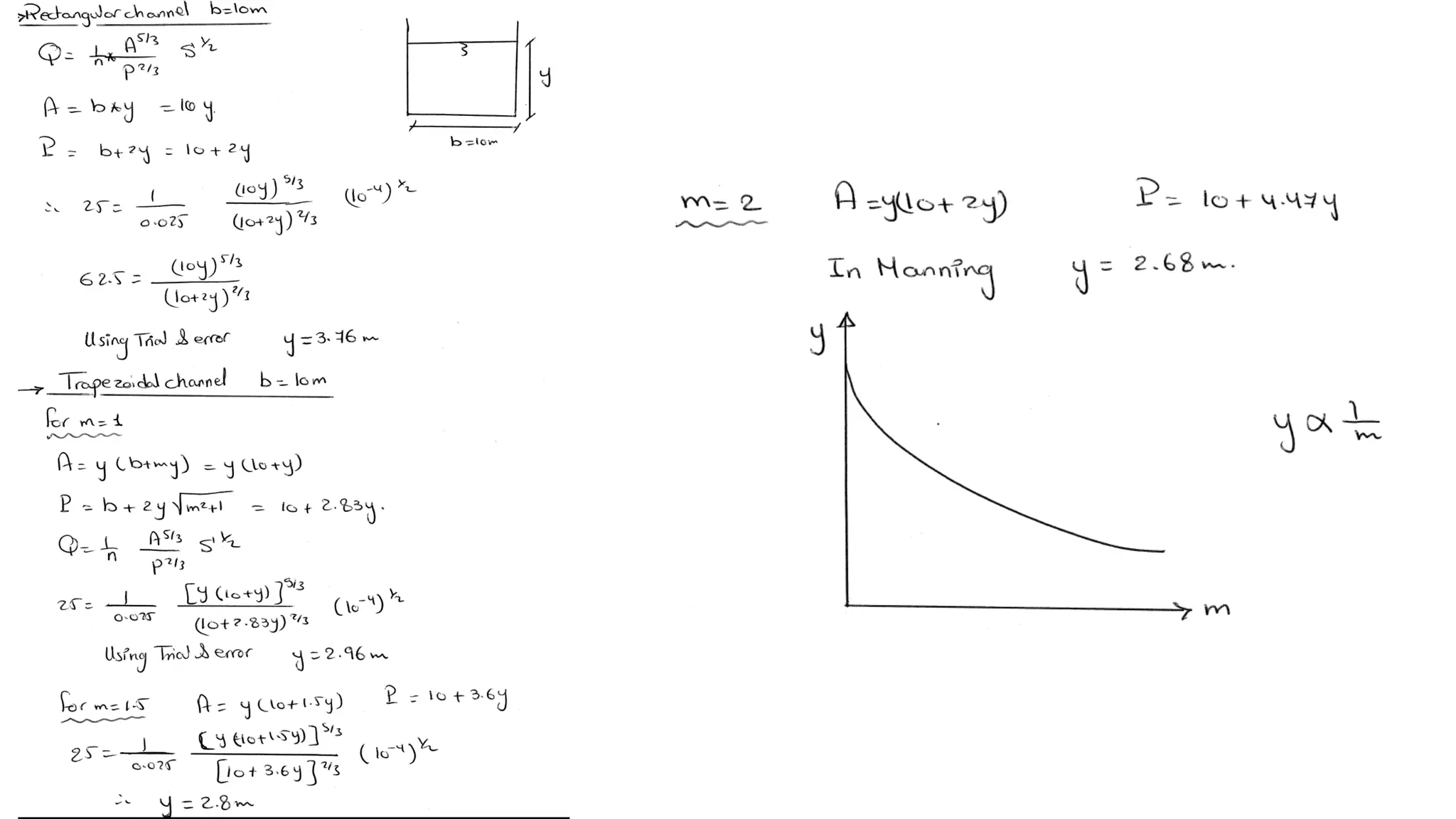
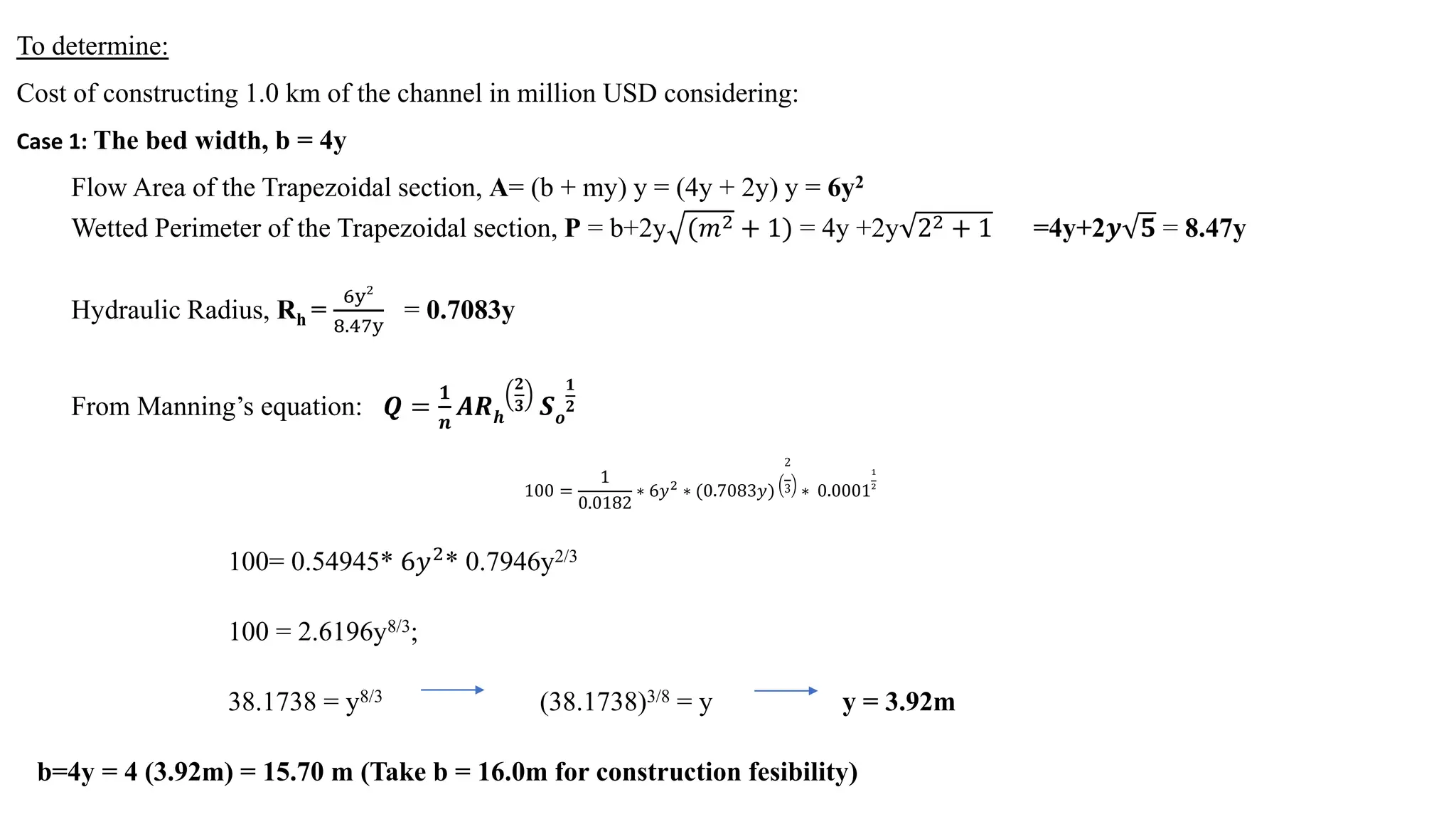
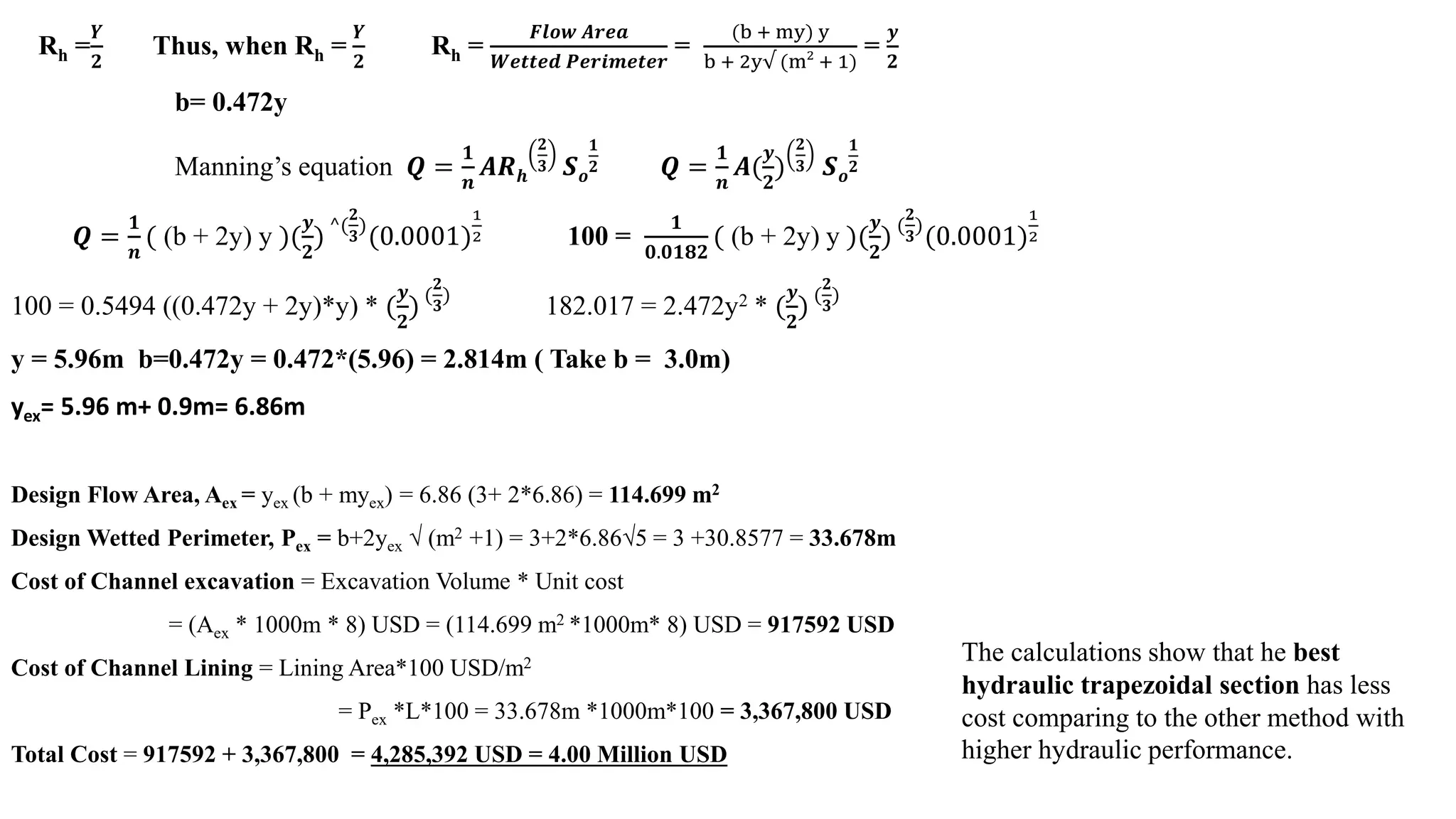
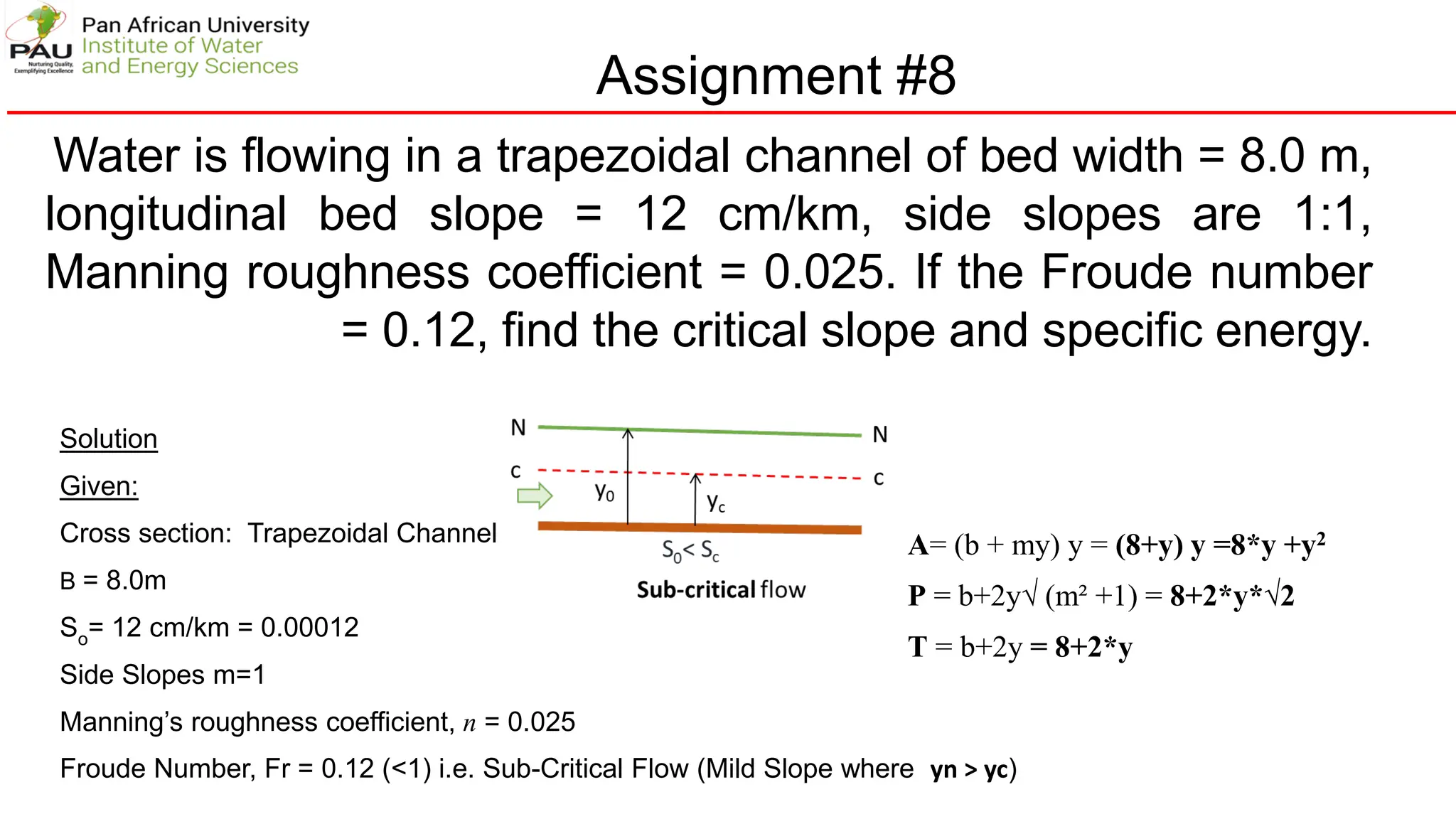
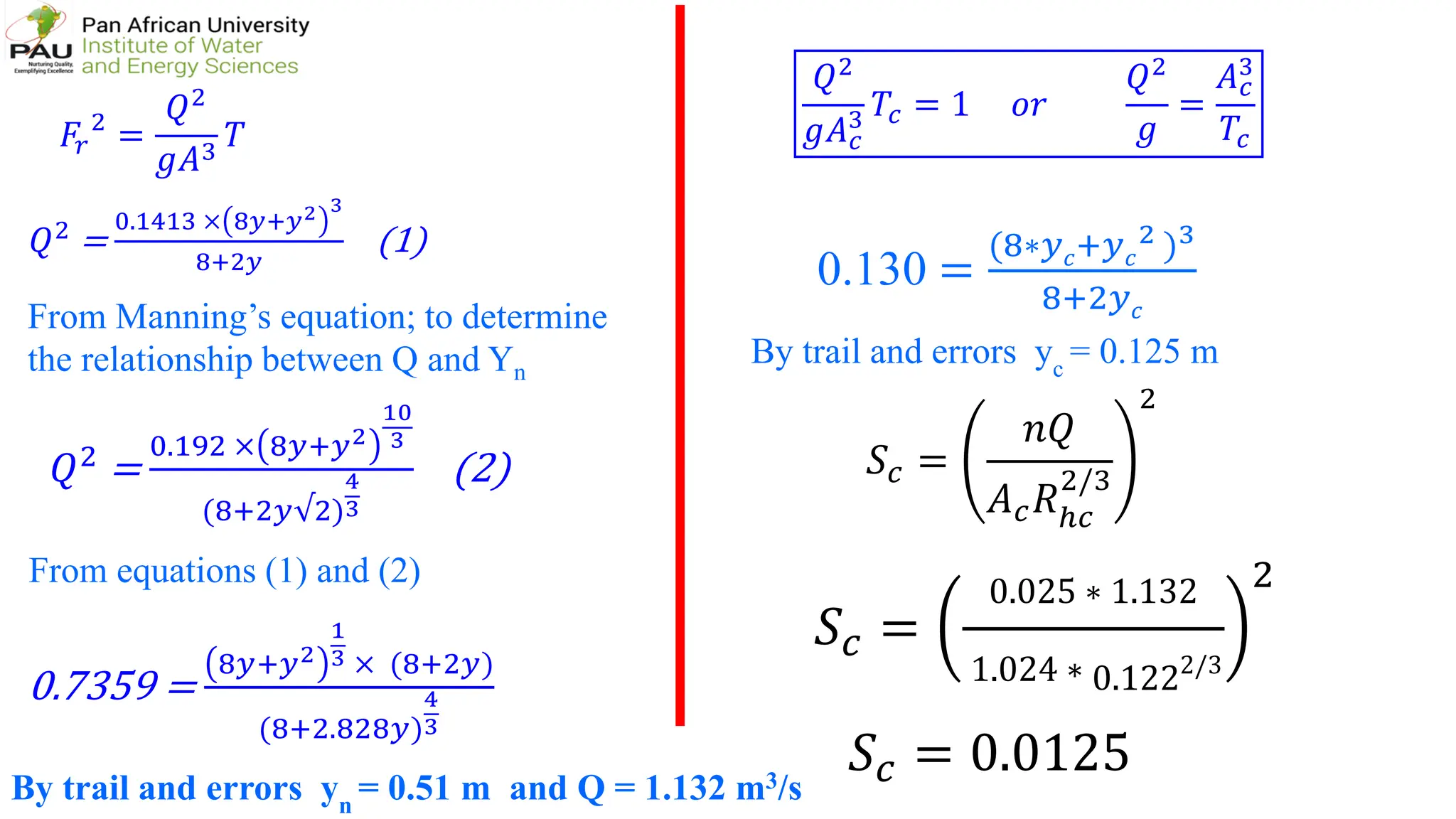
The document provides solutions to several hydraulic engineering assignments. Assignment 8 asks to find the critical slope and specific energy for a trapezoidal channel given various parameters including a Froude number of 0.12. The solution shows:
1) Using Manning's equation and the given Froude number, relationships are developed between flow rate, depth, and other variables.
2) By iterative solution, the normal flow depth is found to be 0.51m and flow rate 1.132 m3/s.
3) Similarly, the critical depth is found to be 0.125m by setting the Froude number equal to 1.
4) The critical slope is then calculated using the critical flow parameters to

![Assignment 3
A piezometer and a Pitot tube are tapped into a horizontal water pipe, as shown in
Figure , to measure static and stagnation (static + dynamic) pressures. For the
indicated water column heights, determine the velocity at the center of the pipe.
datum
V2=0
z1=z2=0
Solution
Bernoulli equation for section 1 and 2; datum
as shown in the Figure
[ ]
2 2
1 1 2 2
1 2
2
1 1 2
1 2 3 1 2
2 1
1
p V p V
z z
2g 2g
p V p
2g
2g (h h h ) (h h )
2g(p p )
V
+ + = + +
γ γ
+ =
γ γ
γ + + − γ +
−
= =
γ γ
1 3
V 2gh 2 9.81 0.12 1.53(m / s)
= = × × =
p2
p1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weuef12hahmodelanswer-240220175538-2c27d3c3/75/hydraulics-and-advanced-hydraulics-solved-tutorials-4-2048.jpg)