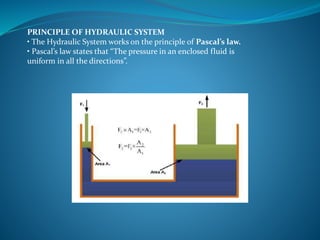
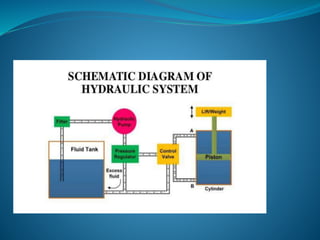
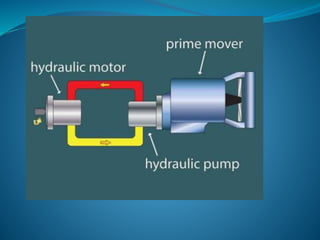
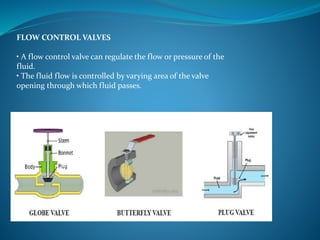
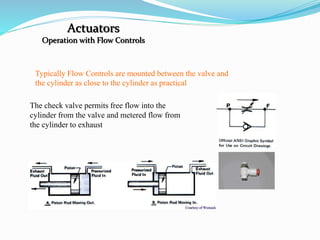
This document discusses hydraulics and pneumatics systems. It describes the key components of hydraulic systems, including prime movers, pumps, control valves, actuators, fluid, filters, and accumulators. Common applications are also listed. For pneumatic systems, it defines pneumatics as using compressed air and pressure differentials to create movement similar to hydraulics. The major parts of a pneumatic system are identified as the compressor, storage tanks, regulators, gauges, valves/solenoids, actuators, fittings and tubing. Specific pneumatic components like compressors, tanks, regulators, valves, actuators and their functions are then described in more detail.