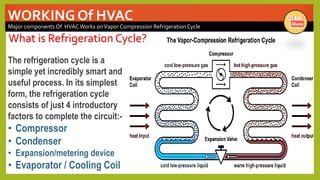
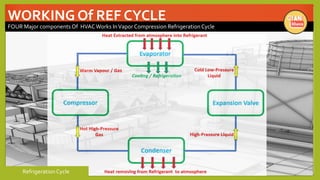
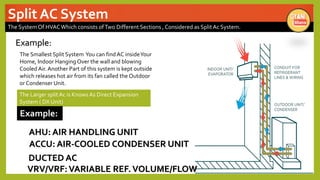
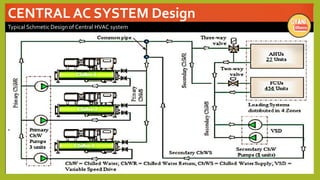
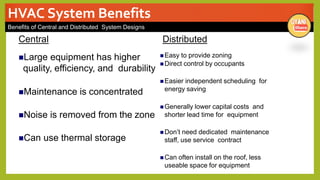
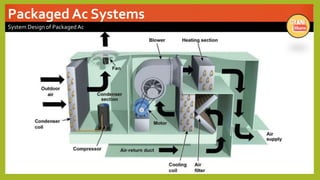
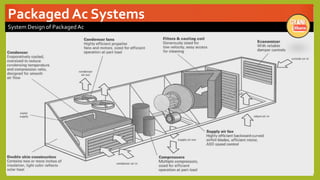
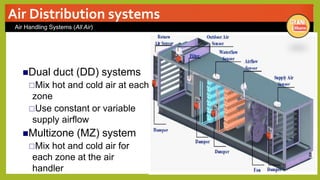
The document provides an overview of basic HVAC systems. It defines HVAC as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. It describes the major components of HVAC systems including compressors, condensers, expansion valves, and evaporators. It explains that HVAC systems work using a vapor compression refrigeration cycle consisting of these four components. The document also discusses different types of HVAC systems like split, central, and packaged AC systems. It provides diagrams of typical system designs and components.