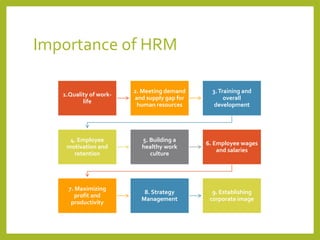
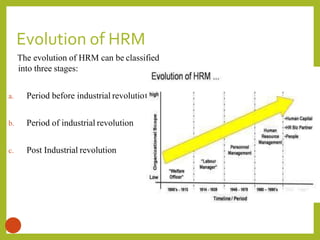
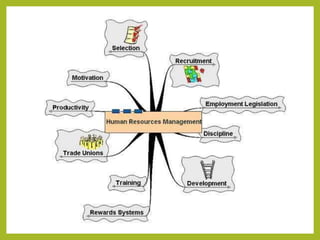
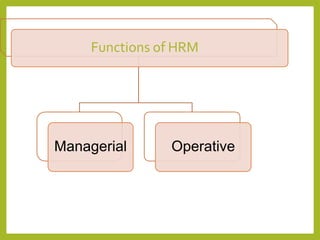
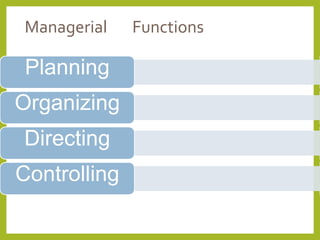
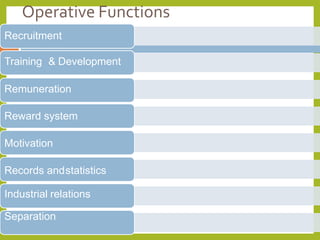
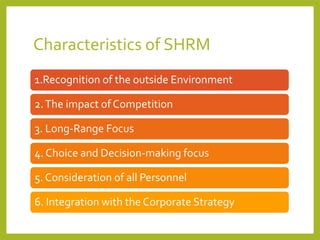
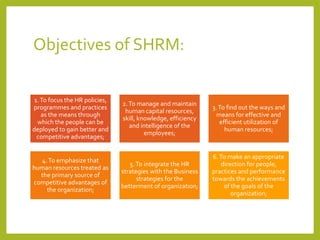
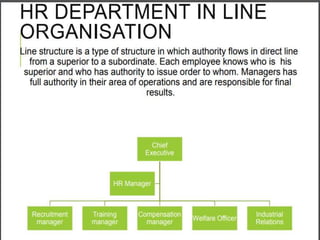
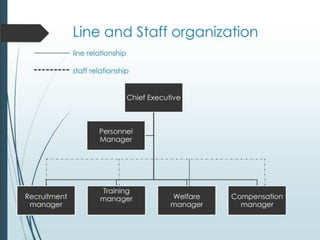
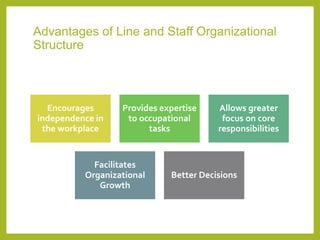
The document outlines a course on Human Resource Management (HRM) aimed at familiarizing students with HR concepts, its significance in organizations, and methods to achieve organizational objectives. It discusses the evolution of HRM, its importance, and how it can be strategically aligned with organizational goals for competitive advantage. Key topics include HR functions, management practices, and contemporary changes affecting HRM in a competitive environment.